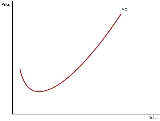
Marginal cost
Overview
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
and finance
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
, marginal cost is the change in total cost
Total cost
In economics, and cost accounting, total cost describes the total economic cost of production and is made up of variable costs, which vary according to the quantity of a good produced and include inputs such as labor and raw materials, plus fixed costs, which are independent of the quantity of a...
that arises when the quantity produced changes by one unit. That is, it is the cost of producing one more unit of a good. If the good being produced is infinitely divisible, so the size of a marginal cost will change with volume, as a non-linear and non-proportional cost function includes the following:
- variable terms dependent to volume,
- constant terms independent to volume and occurring with the respective lot size,
- jump fix cost increase or decrease dependent to steps of volume increase.
In practice the above definition of marginal cost as the change in total cost as a result of an increase in output of one unit is inconsistent with the calculation of marginal cost as MC=dTC/dQ for virtually all non-linear functions.

