
Marcinkiewicz–Zygmund inequality
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, the Marcinkiewicz–Zygmund inequality, named after Józef Marcinkiewicz
and Antoni Zygmund
, gives relations between moment
s of a collection of independent random variables. It is a generalization of the rule for the sum of variance
s of independent random variables to moments of arbitrary order.
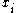 ,
, 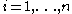 , are independent random variables such that
, are independent random variables such that 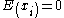 and
and 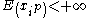 ,
, 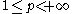 ,
,
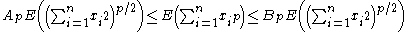
where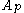 and
and 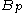 are positive constants, which depend only on
are positive constants, which depend only on 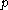 .
.
and Rosenthal inequalities, and there are also extensions to more general symmetric statistic
s of independent random variables.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, the Marcinkiewicz–Zygmund inequality, named after Józef Marcinkiewicz
Józef Marcinkiewicz
Józef Marcinkiewicz – died in 1940 in Kharkiv, Ukraine) was a Polish mathematician.He was a student of Antoni Zygmund; and later worked with Juliusz Schauder, and Stefan Kaczmarz. He was a professor of the Stefan Batory University in Wilno....
and Antoni Zygmund
Antoni Zygmund
Antoni Zygmund was a Polish-born American mathematician.-Life:Born in Warsaw, Zygmund obtained his PhD from Warsaw University and became a professor at Stefan Batory University at Wilno...
, gives relations between moment
Moment
- Science, engineering, and mathematics :* Moment , used in probability theory and statistics* Moment , several related concepts, including:** Angular momentum or moment of momentum, the rotational analog of momentum...
s of a collection of independent random variables. It is a generalization of the rule for the sum of variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
s of independent random variables to moments of arbitrary order.
Statement of the inequality
Theorem If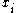 ,
, 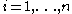 , are independent random variables such that
, are independent random variables such that 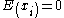 and
and 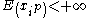 ,
, 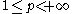 ,
,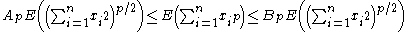
where
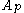 and
and 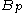 are positive constants, which depend only on
are positive constants, which depend only on 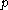 .
.See also
Several similar moment inequalities are known as Khintchine inequalityKhintchine inequality
In mathematics, the Khintchine inequality, named after Aleksandr Khinchin and spelled in multiple ways in the Roman alphabet, is a theorem from probability, and is also frequently used in analysis...
and Rosenthal inequalities, and there are also extensions to more general symmetric statistic
Statistic
A statistic is a single measure of some attribute of a sample . It is calculated by applying a function to the values of the items comprising the sample which are known together as a set of data.More formally, statistical theory defines a statistic as a function of a sample where the function...
s of independent random variables.

