
Marangoni number
Encyclopedia
The Marangoni number is a dimensionless number named after Italian scientist Carlo Marangoni
.
The Marangoni number may be regarded as proportional to (thermal-) surface tension forces divided by viscous forces. It is – for example – applicable to bubble and foam research or calculations of cryogenic spacecraft propellant behaviour.

Carlo Marangoni
Carlo Giuseppe Matteo Marangoni was an Italian physicist.Marangoni graduated in 1865 from the University of Pavia, under the supervision of Giovanni Cantoni, with a dissertation entitled ""....
.
The Marangoni number may be regarded as proportional to (thermal-) surface tension forces divided by viscous forces. It is – for example – applicable to bubble and foam research or calculations of cryogenic spacecraft propellant behaviour.

 : surface tensionSurface tensionSurface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
: surface tensionSurface tensionSurface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
, (SISiSi, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
units: N/m)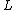 : characteristic length, (SI units: m)
: characteristic length, (SI units: m) : thermal diffusivityThermal diffusivityIn heat transfer analysis, thermal diffusivity is the thermal conductivity divided by density and specific heat capacity at constant pressure. It has the SI unit of m²/s...
: thermal diffusivityThermal diffusivityIn heat transfer analysis, thermal diffusivity is the thermal conductivity divided by density and specific heat capacity at constant pressure. It has the SI unit of m²/s...
, (SI units: m²/s)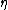 : dynamic viscosityViscosityViscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
: dynamic viscosityViscosityViscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
, (SI units: kg/(s·m)),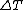 : temperatureTemperatureTemperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
: temperatureTemperatureTemperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
difference, (SI units: °C)),

