
Magnetic-coded lock
Encyclopedia
A magnetic-coded lock is a lock
device that uses pins in combination with magnets to prevent entry by either non-matching keys
by teething or magnetic polarity. Magnetic-coded locks encompass knob locks, cylinder lock
s, lever locks, and deadbolt
locks as well as applications in other security devices.
The magnetic pins are made with permanent magnets which means the magnets stay magnetized. The intensity of the magnet will not decay over time or be affected by other magnetic fields.
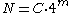
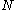 - Magnetic-coded lock key combinations
- Magnetic-coded lock key combinations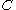 - Conventional pin-tumbler lock combinations
- Conventional pin-tumbler lock combinations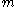 - Pairs of embedded magnets. (multiple pairs can be embedded)
- Pairs of embedded magnets. (multiple pairs can be embedded)
Lock (device)
A lock is a mechanical or electronic fastening device that is released by a physical object or secret information , or combination of more than one of these....
device that uses pins in combination with magnets to prevent entry by either non-matching keys
Key (lock)
A key is an instrument that is used to operate a lock. A typical key consists of two parts: the blade, which slides into the keyway of the lock and distinguishes between different keys, and the bow, which is left protruding so that torque can be applied by the user. The blade is usually intended to...
by teething or magnetic polarity. Magnetic-coded locks encompass knob locks, cylinder lock
Cylinder lock
A cylinder lock is a lock constructed with a cylinder that a locksmith can easily unscrew to facilitate rekeying. The cylinder may contain any of a variety of locking mechanisms, including the pin tumbler lock, the wafer tumbler lock and the disc tumbler lock....
s, lever locks, and deadbolt
Deadbolt
A dead bolt or dead lock , is a locking mechanism distinct from a spring bolt lock because a deadbolt cannot be moved to the open position except by rotating the lock cylinder. The more common spring bolt lock uses a spring to hold the bolt in place, allowing retraction by applying force to the...
locks as well as applications in other security devices.
History
The magnetic-coded lock was invented by an engineer in Nanchang, China. There have been several Chinese patents taken out on this technology. The improved version of this technology is currently on patent pending status granted by US Patent and Trademark Office.Design
Magnetic-coded technology utilizes multiple pairs of magnetic pins with opposing poles that are embedded inside keys and plugs. When a correctly matched key is inserted into the lock, not only are all the mechanical pins pushed into the correct positions, the magnetic pins are also driven to the appropriate level by the magnetic force inside the key.The magnetic pins are made with permanent magnets which means the magnets stay magnetized. The intensity of the magnet will not decay over time or be affected by other magnetic fields.
Operation
In order to open a magnetic-coded lock, three criteria must be met: correct teething of the key, magnetic pin locations and poles of the magnetic pins. If any of these three criteria are not satisfied, the lock stays inoperable and cannot be turned.Equations
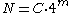
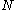 - Magnetic-coded lock key combinations
- Magnetic-coded lock key combinations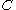 - Conventional pin-tumbler lock combinations
- Conventional pin-tumbler lock combinations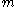 - Pairs of embedded magnets. (multiple pairs can be embedded)
- Pairs of embedded magnets. (multiple pairs can be embedded)Advantages
- Anti-picking:
- The embedded magnetic pins are not exposed to the key way, therefore, no lifting force can be applied to move the magnetic pins. Most standard forms of lock pickingLock pickingLock picking is the art of unlocking a lock by analyzing and manipulating the components of the lock device, without the original key. Although lock picking can be associated with criminal intent, it is an essential skill for a locksmith...
are therefore preventable.- Anti-bumping :
- Lock bumpingLock bumpingLock bumping is a lock picking technique for opening a pin tumbler lock using a specially crafted bump key. One bump key will work for all locks of the same type.-History:A US patent first appears in 1928 by H.R. Simpson called a "rapping" or bump-key...
transmits kinetic energy from the key to the drive pins, to split the bottom and top pins. The embedded magnetic technology has no physical contact points between key and magnetic pins, therefore no kinetic energy is transmitted.- Key control:
- Due to the magnetic cylinder elements embedded in the keys, there is a high degree of key control. Unlawful key duplications are minimized by limited access to key blankKey blankA key blank is a key that has not been cut to a specific bitting. The blank has a specific cross-sectional profile to match the keyway in a corresponding lock cylinder. Key blanks can be stamped with a manufacturer name, end-user logo or with a phrase, the most commonly seen being 'Do not duplicate'...
s (locksmiths) and unique magnetic coding in the key that cannot easily be determined by inspecting the target lock.- Cost Effectiveness :
- Because the manufacturing process is based on the pin and tumbler platform, the cost of manufacturing is significantly reduced when compared to high security locks with comparable security features. These high security locks often utilize new locking mechanisms which increase the cost of manufacturing.
Disadvantages
- Manufacturing Complexities:
- A special tool set and procedures have to be developed to accomplish the task of embedding the magnets inside both the keys and the locks.
Installation
- The same as conventional lock installation. Drilling with hole sawHole sawA hole saw , also known as a hole cutter, is a circular saw designed to cut through relatively thin workpieces. It is used in a drill.-Construction:...
may be required in doors lacking a hole for assembly.

