
Lymphangion
Encyclopedia
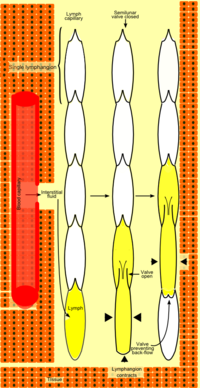
Lymph vessel
In anatomy, lymph vessels are thin walled, valved structures that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelial cells, and deep to that have a thin layer of smooth muscles, and adventitia that bind...
that lies between two semilunar (half moon-shaped) valve
Valve
A valve is a device that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically pipe fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category...
s.
Lymph vessels are channels larger than the lymph capillaries that have thicker walls, valves in their lumen and smooth muscles in their walls, thus lymph vessel lymphangion would be muscular, and capable of contracting on its own. Additionally the lymph in it is propelled forward only because of force exerted on its walls from the exterior. Such forces include skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle is a form of striated muscle tissue existing under control of the somatic nervous system- i.e. it is voluntarily controlled. It is one of three major muscle types, the others being cardiac and smooth muscle...
contractions and arterial
Artery
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. This blood is normally oxygenated, exceptions made for the pulmonary and umbilical arteries....
pulsations
Pulse
In medicine, one's pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the heartbeat by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed against a bone, such as at the neck , at the wrist , behind the knee , on the inside of the elbow , and near the...
. Also, the inspiration during respiration
Respiration (physiology)
'In physiology, respiration is defined as the transport of oxygen from the outside air to the cells within tissues, and the transport of carbon dioxide in the opposite direction...
provides a suction pressure within the lumen
Lumen (anatomy)
A lumen in biology is the inside space of a tubular structure, such as an artery or intestine...
.
The semilunar valves are directed towards the flow of the lymph and open when the pressure in the first lymphangion is greater than the pressure in the next lymphangion. Pressure in the first lymphangion may increase because of smooth muscle contraction (in lymph vessel) or because of pressure on the walls from outside (in a capillary) result because of. Alternatively, pressure within the next lymphangion may decrease because of negative pressure as a result of inspiration. Once, the lymph flows into the next lymphangion, it cannot return to the previous lymphangion, as the semilunar valves close tightly.
In conditions when the pressure in a lymphatic is sufficiently great, the valves may fail, and there can indeed be backward flow of lymph resulting in edema
Edema
Edema or oedema ; both words from the Greek , oídēma "swelling"), formerly known as dropsy or hydropsy, is an abnormal accumulation of fluid beneath the skin or in one or more cavities of the body that produces swelling...
of the drained region. This may happen with blockade of lymph flow because of pathology in the draining lymph node
Lymph node
A lymph node is a small ball or an oval-shaped organ of the immune system, distributed widely throughout the body including the armpit and stomach/gut and linked by lymphatic vessels. Lymph nodes are garrisons of B, T, and other immune cells. Lymph nodes are found all through the body, and act as...
or at some point in the vessel.

