
Love wave
Encyclopedia
Seismology
Seismology is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. The field also includes studies of earthquake effects, such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, oceanic,...
, Love waves (also known as Q waves (Quer: German for lateral)) are surface seismic wave
Seismic wave
Seismic waves are waves of energy that travel through the earth, and are a result of an earthquake, explosion, or a volcano that imparts low-frequency acoustic energy. Many other natural and anthropogenic sources create low amplitude waves commonly referred to as ambient vibrations. Seismic waves...
s that cause horizontal shifting of the earth during an earthquake
Earthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
. A.E.H. Love
Augustus Edward Hough Love
Augustus Edward Hough Love FRS , often known as A. E. H. Love, was a mathematician famous for his work on the mathematical theory of elasticity...
predicted the existence of Love waves mathematically in 1911; the name comes from him (Chapter 11 from Love's book "Some problems of geodynamics", first published in 1911). They form a distinct class, different from other types of seismic wave
Seismic wave
Seismic waves are waves of energy that travel through the earth, and are a result of an earthquake, explosion, or a volcano that imparts low-frequency acoustic energy. Many other natural and anthropogenic sources create low amplitude waves commonly referred to as ambient vibrations. Seismic waves...
s, such as P-wave
P-wave
P-waves are a type of elastic wave, also called seismic waves, that can travel through gases , solids and liquids, including the Earth. P-waves are produced by earthquakes and recorded by seismographs...
s and S-wave
S-wave
A type of seismic wave, the S-wave, secondary wave, or shear wave is one of the two main types of elastic body waves, so named because they move through the body of an object, unlike surface waves....
s (both body waves), or Rayleigh waves (another type of surface wave). Love waves travel with a slower velocity than P- or S- waves, but faster than Rayleigh waves.These waves are observed only when there is a low velocity layer overlying a high velocity layer/ sub stratum.
Description
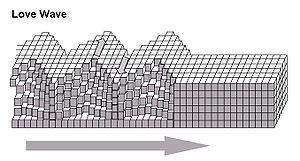
The particle motion of a Love wave forms a horizontal line perpendicular to the direction of propagationWave propagation
Wave propagation is any of the ways in which waves travel.With respect to the direction of the oscillation relative to the propagation direction, we can distinguish between longitudinal wave and transverse waves....
(i.e. are transverse waves). Moving deeper into the material, motion can decrease to a "node" and then alternately increase and decrease as one examines deeper layers of particles. The amplitude
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
, or maximum particle motion, often decreases rapidly with depth.
Since Love waves travel on the Earth's surface, the strength (or amplitude
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
) of the waves decrease exponentially with the depth of an earthquake. However, given their confinement to the surface, their amplitude decays only as
 , where
, where  represents the distance the wave has traveled from the earthquake. Surface waves therefore decay more slowly with distance than do body waves, which travel in three dimensions. Large earthquakes may generate Love waves that travel around the Earth several times before dissipating.
represents the distance the wave has traveled from the earthquake. Surface waves therefore decay more slowly with distance than do body waves, which travel in three dimensions. Large earthquakes may generate Love waves that travel around the Earth several times before dissipating.Since they decay so slowly, Love waves are the most destructive outside the immediate area of the focus or epicentre of an earthquake. They are what most people feel directly during an earthquake.
In the past, it was often thought that animals like cats and dogs could predict an earthquake before it happened. However, they are simply more sensitive to ground vibrations
Ground vibrations
Ground vibrations is a technical term that is being used to describe mostly man-made vibrations of the ground, in contrast to natural vibrations of the Earth studied by seismology. For example, vibrations caused by explosions, construction works, railway and road transport, etc - all belong to...
than humans and able to detect the subtler body waves that precede Love waves, like the P-waves and the S-waves.

