Loop gain
Encyclopedia
Loop gain is an engineering term used to quantify the gain of a system controlled by feedback loops. As such, the concept of loop gain is useful in a variety of disciplines. Traditionally, most of those have been in the field of electronics, telecommunications, or (electronic or non-electronic) control systems. It is also useful in biology.
In amplifier
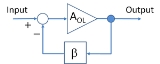
s with feedback, loop gain refers to the product of the gain
in the feedback loop and the feedback factor in that loop. In Figure 1, the loop gain is the product βAOL.
In telecommunication
s, the term loop gain has the following meanings:
1. The total usable power
gain
of a carrier
terminal
or two-wire repeater
.
Note: The maximum usable gain is determined by, and may not exceed, the losses in the closed path.
2. The sum of the gains, expressed in dB
, acting on a signal passing around a closed path, i.e., a loop.
In amplifier
Amplifier
Generally, an amplifier or simply amp, is a device for increasing the power of a signal.In popular use, the term usually describes an electronic amplifier, in which the input "signal" is usually a voltage or a current. In audio applications, amplifiers drive the loudspeakers used in PA systems to...
s with feedback, loop gain refers to the product of the gain
Gain
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal output of a system to the signal input of the same system. It may also be defined on a logarithmic scale,...
in the feedback loop and the feedback factor in that loop. In Figure 1, the loop gain is the product βAOL.
In telecommunication
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
s, the term loop gain has the following meanings:
1. The total usable power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
gain
Gain
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal output of a system to the signal input of the same system. It may also be defined on a logarithmic scale,...
of a carrier
Carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave or carrier is a waveform that is modulated with an input signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave is usually a much higher frequency than the input signal...
terminal
Terminal (telecommunication)
In the context of telecommunications, a terminal is a device which is capable of communicating over a line. Examples of terminals are telephones, fax machines, and network devices - printers and workstations....
or two-wire repeater
Repeater
A repeater is an electronic device that receives asignal and retransmits it at a higher level and/or higher power, or onto the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances.-Description:...
.
Note: The maximum usable gain is determined by, and may not exceed, the losses in the closed path.
2. The sum of the gains, expressed in dB
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
, acting on a signal passing around a closed path, i.e., a loop.

