
Long bone
Encyclopedia
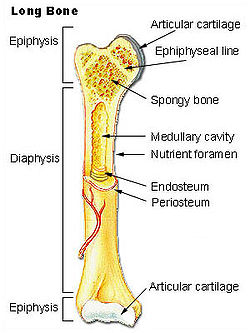
Long bone
The long bones are those that are longer than they are wide. They are one of five types of bones: long, short, flat, irregular and sesamoid. Long bones, especially the femur and tibia, are subjected to most of the load during daily activities and they are crucial for skeletal mobility. They grow...
, short
Short bone
The patella, together with the other sesamoid bones, are by some regarded as short bones. Many short bones break more easily than large bones due to lack of support and extensive bone marrow-References:*...
, flat
Flat bone
Flat bones are those bones which are found where the principal requirement is either extensive protection or the provision of broad surfaces for muscular attachment...
, irregular
Irregular bone
The irregular bones are bones which, from their peculiar form, cannot be grouped as long bone, short bone, flat bone or sesamoid bone. Irregular bones serve various purposes in the body, such as protection of nervous tissue , affording multiple anchor points for skeletal muscle attachment , and...
and sesamoid
Sesamoid bone
In anatomy, a sesamoid bone is a bone embedded within a tendon.Sesamoids are found in locations where a tendon passes over a joint, such as the hand, knee, and foot. Functionally, they act to protect the tendon and to increase its mechanical effect. The presence of the sesamoid bone holds the...
. Long bones, especially the femur
Femur
The femur , or thigh bone, is the most proximal bone of the leg in tetrapod vertebrates capable of walking or jumping, such as most land mammals, birds, many reptiles such as lizards, and amphibians such as frogs. In vertebrates with four legs such as dogs and horses, the femur is found only in...
and tibia
Tibia
The tibia , shinbone, or shankbone is the larger and stronger of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates , and connects the knee with the ankle bones....
, are subjected to most of the load during daily activities and they are crucial for skeletal mobility. They grow primarily by elongation of the diaphysis
Diaphysis
The diaphysis is the main or mid section of a long bone. It is made up of cortical bone and usually contains bone marrow and adipose tissue ....
, with an epiphysis
Epiphysis
The epiphysis is the rounded end of a long bone, at its joint with adjacent bone. Between the epiphysis and diaphysis lies the metaphysis, including the epiphyseal plate...
at the ends of the growing bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
. The ends of epiphyses are covered with a hyaline cartilage
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline cartilage consists of a slimy mass, pearly bluish in colour with firm consistency and considerable collagen. It contains no nerves or blood vessels, and its structure is relatively simple....
("articular cartilage"). The longitudinal growth of long bones is a result of endochondral ossification
Endochondral ossification
Endochondral ossification is one of the two essential processes during fetal development of the mammalian skeletal system by which bone tissue is created. Unlike intramembranous ossification, which is the other process by which bone tissue is created, cartilage is present during endochondral...
at the epiphyseal plate
Epiphyseal plate
The epiphyseal plate is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone...
. Bone growth in length is stimulated by the production of growth hormone
Growth hormone
Growth hormone is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction and regeneration in humans and other animals. Growth hormone is a 191-amino acid, single-chain polypeptide that is synthesized, stored, and secreted by the somatotroph cells within the lateral wings of the anterior...
(GH), a secretion of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland
Pituitary gland
In vertebrate anatomy the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland about the size of a pea and weighing 0.5 g , in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain, and rests in a small, bony cavity covered by a dural fold...
.
The long bones include the femur
Femur
The femur , or thigh bone, is the most proximal bone of the leg in tetrapod vertebrates capable of walking or jumping, such as most land mammals, birds, many reptiles such as lizards, and amphibians such as frogs. In vertebrates with four legs such as dogs and horses, the femur is found only in...
s, tibia
Tibia
The tibia , shinbone, or shankbone is the larger and stronger of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates , and connects the knee with the ankle bones....
s, and fibulas of the legs, the humeri
Humerus
The humerus is a long bone in the arm or forelimb that runs from the shoulder to the elbow....
, radii
Radius (bone)
The radius is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna, which exceeds it in length and size. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally...
, and ulna
Ulna
The ulna is one of the two long bones in the forearm, the other being the radius. It is prismatic in form and runs parallel to the radius, which is shorter and smaller. In anatomical position The ulna is one of the two long bones in the forearm, the other being the radius. It is prismatic in form...
s of the arms, metacarpals and metatarsals of the hands and feet, and the phalanges
Phalanx bones
In anatomy, phalanx bones are those that form the fingers and toes. In primates such as humans and monkeys, the thumb and big toe have two phalanges, while the other fingers and toes consist of three. Phalanges are classified as long bones.The phalanges do not have individual names...
of the fingers and toes. The long bones of the human leg comprise nearly half of adult height. The other primary skeletal component of height is the spine and skull
Human skull
The human skull is a bony structure, skeleton, that is in the human head and which supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.In humans, the adult skull is normally made up of 22 bones...
.
The outside of the bone consists of a layer of connective tissue called the periosteum
Periosteum
Periosteum is a membrane that lines the outer surface of all bones, except at the joints of long bones. Endosteum lines the inner surface of all bones....
. Additionally, the outer shell of the long bone is compact bone, then a deeper layer of cancellous bone (spongy bone) which contains red bone marrow
Bone marrow
Bone marrow is the flexible tissue found in the interior of bones. In humans, bone marrow in large bones produces new blood cells. On average, bone marrow constitutes 4% of the total body mass of humans; in adults weighing 65 kg , bone marrow accounts for approximately 2.6 kg...
. The interior part of the long bone is the medullary cavity
Medullary cavity
The medullary cavity is the central cavity of bone shafts where red bone marrow and/or yellow bone marrow is stored; hence, the medullary cavity is also known as the marrow cavity...
with the inner core of the bone cavity being composed of (in adults) of yellow marrow.

