
London penetration depth
Encyclopedia
In superconductors, the London penetration depth (usually denoted as  or
or 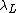 ) characterizes the distance to which a magnetic field
) characterizes the distance to which a magnetic field
penetrates into a superconductor and becomes equal to 1/e times that of the magnetic field at the surface of the superconductor. Typical values of λL range from 50 to 500 nm.
The London penetration depth results from considering the London equation
and Ampère's circuital law. If one considers a superconducting medium occupying x0, and weak external magnetic field B0> applied along zx0, then inside the superconductor the magnetic field is given by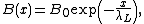
 can be seen as the distance across in which the magnetic field becomes
can be seen as the distance across in which the magnetic field becomes  times weaker. The form of
times weaker. The form of 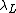 is found by this method to be
is found by this method to be ,
,
for charge carriers of mass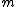 , number density
, number density  and charge
and charge 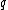 .
.
The penetration depth is determined by the superfluid density, which is an important quantity that determines Tc in high-temperature superconductors. If some superconductors have some node in their energy gap, the penetration depth at 0 K depends on magnetic field because superfluid density is changed by magnetic field and vice versa. So, accurate and precise measurements of the absolute value of penetration depth at 0 K are very important to understand the mechanism of high-temperature superconductivity.
London penetration depth can be measured by muon spin spectroscopy
when the superconductor doesn't have an intrinsic magnetic constitution. The penetration depth is directly converted from the depolarization rate of muon spin in relation which
σ(T) is proportional to λ2(T). The shape of σ(T) is different with the kind of superconducting energy gap in temperature, so that this immediately indicates the shape of energy gap and gives some clues about the origin of superconductivity to us.
 or
or 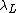 ) characterizes the distance to which a magnetic field
) characterizes the distance to which a magnetic fieldMagnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
penetrates into a superconductor and becomes equal to 1/e times that of the magnetic field at the surface of the superconductor. Typical values of λL range from 50 to 500 nm.
The London penetration depth results from considering the London equation
London equations
The London equations, developed by brothers Fritz and Heinz London in 1935,relate current to electromagnetic fields in and around a superconductor...
and Ampère's circuital law. If one considers a superconducting medium occupying x0, and weak external magnetic field B0> applied along z
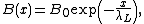
 can be seen as the distance across in which the magnetic field becomes
can be seen as the distance across in which the magnetic field becomes  times weaker. The form of
times weaker. The form of 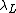 is found by this method to be
is found by this method to be ,
,for charge carriers of mass
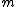 , number density
, number density  and charge
and charge 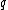 .
.The penetration depth is determined by the superfluid density, which is an important quantity that determines Tc in high-temperature superconductors. If some superconductors have some node in their energy gap, the penetration depth at 0 K depends on magnetic field because superfluid density is changed by magnetic field and vice versa. So, accurate and precise measurements of the absolute value of penetration depth at 0 K are very important to understand the mechanism of high-temperature superconductivity.
London penetration depth can be measured by muon spin spectroscopy
Muon spin spectroscopy
Muon spin spectroscopy is an experimental technique based on the implantation of spin-polarized muons in matter and on the detection of the influence of the atomic, molecular or crystalline surroundings on their spin motion...
when the superconductor doesn't have an intrinsic magnetic constitution. The penetration depth is directly converted from the depolarization rate of muon spin in relation which
σ(T) is proportional to λ2(T). The shape of σ(T) is different with the kind of superconducting energy gap in temperature, so that this immediately indicates the shape of energy gap and gives some clues about the origin of superconductivity to us.
Further reading
- http://scitation.aip.org/getabs/servlet/GetabsServlet?prog=normal&id=PRLTAO000094000012127001000001&idtype=cvips&gifs=yes

