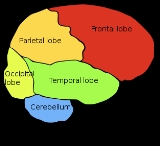
Lobes of the brain
Encyclopedia

Telencephalon
The cerebrum or telencephalon, together with the diencephalon, constitutes the forebrain. The cerebrum is the most anterior region of the vertebrate central nervous system. Telencephalon refers to the embryonic structure, from which the mature cerebrum develops...
(cerebrum), the largest portion of the human brain, is divided into lobes, but so is the cerebellum
Cerebellum
The cerebellum is a region of the brain that plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language, and in regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established...
. If not specified, the expression "lobes of the brain" refers to the telencephalon.
There are four uncontested lobes of the telencephalon (see individual articles for more information):
- Frontal lobeFrontal lobeThe frontal lobe is an area in the brain of humans and other mammals, located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere and positioned anterior to the parietal lobe and superior and anterior to the temporal lobes...
—conscious thought; damage can result in mood changes, social differences, etc. The frontal lobes are the most uniquely human of all the brain structures. - Parietal lobeParietal lobeThe parietal lobe is a part of the Brain positioned above the occipital lobe and behind the frontal lobe.The parietal lobe integrates sensory information from different modalities, particularly determining spatial sense and navigation. For example, it comprises somatosensory cortex and the...
—plays important roles in integrating sensory information from various senses, and in the manipulation of objects; portions of the parietal lobe are involved with visuospatial processingVisual perceptionVisual perception is the ability to interpret information and surroundings from the effects of visible light reaching the eye. The resulting perception is also known as eyesight, sight, or vision... - Occipital lobeOccipital lobeThe occipital lobe is the visual processing center of the mammalian brain containing most of the anatomical region of the visual cortex. The primary visual cortex is Brodmann area 17, commonly called V1...
—sense of sight; lesions can produce hallucinations - Temporal lobeTemporal lobeThe temporal lobe is a region of the cerebral cortex that is located beneath the Sylvian fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain....
—senses of smell and sound, as well as processing of complex stimuli like faces and scenes.
See also
- Poles of cerebral hemispheresPoles of cerebral hemispheresThe anterior end of the hemisphere is named the frontal pole. The posterior end is named the occipital pole. The anterior end of the temporal lobe, the temporal pole....
- GyrusGyrusA gyrus is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci .-Notable gyri:* Superior frontal gyrus, lat. gyrus frontalis superior* Middle frontal gyrus, lat. gyrus frontalis medius...
- List of regions in the human brain
- NeuroanatomyNeuroanatomyNeuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can begin to speak of...

