List of images in Gray's Anatomy: XI. Splanchnology
Encyclopedia
the respiratory apparatus

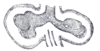
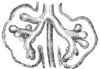
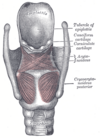
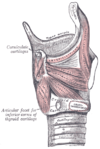
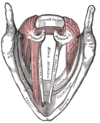
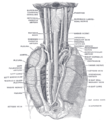
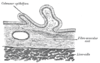
the larynxLarynxThe larynx , commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the neck of amphibians, reptiles and mammals involved in breathing, sound production, and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. It manipulates pitch and volume...
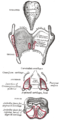
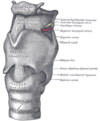
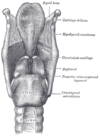

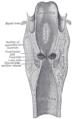
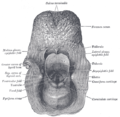
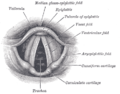
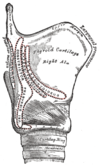
the tracheaVertebrate tracheaIn tetrapod anatomy the trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that connects the pharynx or larynx to the lungs, allowing the passage of air. It is lined with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium cells with goblet cells that produce mucus...
and bronchi
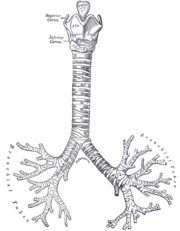
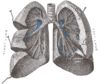
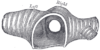

the mediastinumMediastinumThe mediastinum is a non-delineated group of structures in the thorax, surrounded by loose connective tissue. It is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity...
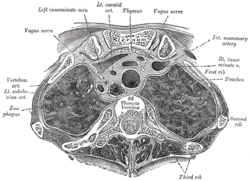
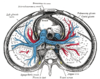
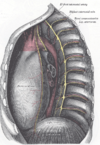
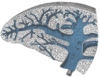
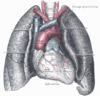
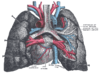
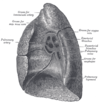
the lungs



the digestive apparatus
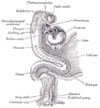

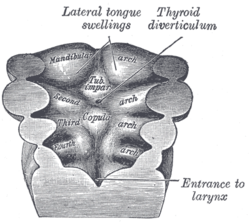
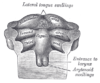
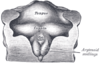
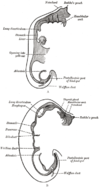

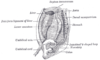

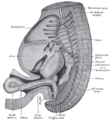
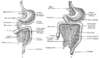
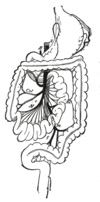



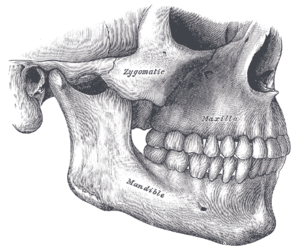
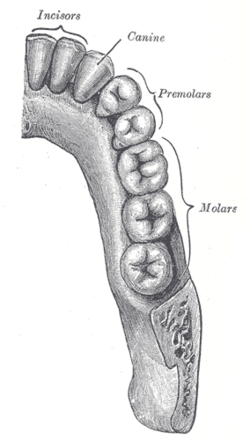
the mouthMouthThe mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food andsaliva. The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane epithelium lining the inside of the mouth....
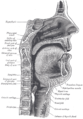

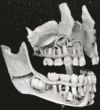
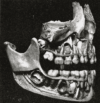


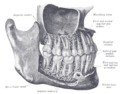

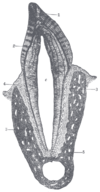
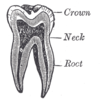
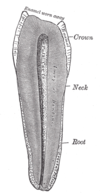
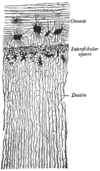



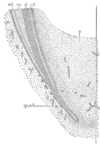
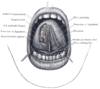
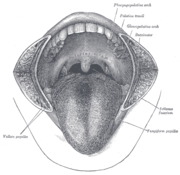


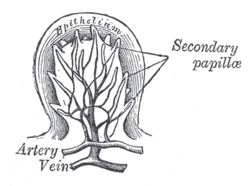





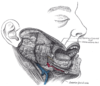

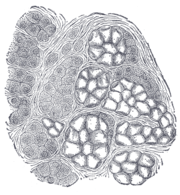
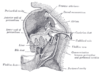
the pharynxPharynxThe human pharynx is the part of the throat situated immediately posterior to the mouth and nasal cavity, and anterior to the esophagus and larynx. The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx , the oropharynx , and the laryngopharynx...
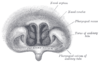

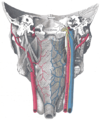
the esophagusEsophagusThe esophagus is an organ in vertebrates which consists of a muscular tube through which food passes from the pharynx to the stomach. During swallowing, food passes from the mouth through the pharynx into the esophagus and travels via peristalsis to the stomach...
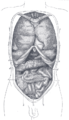
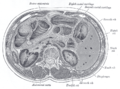
the abdomenAbdomenIn vertebrates such as mammals the abdomen constitutes the part of the body between the thorax and pelvis. The region enclosed by the abdomen is termed the abdominal cavity...


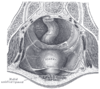
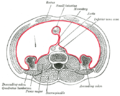
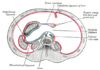
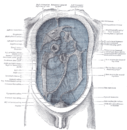


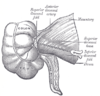

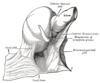
the stomachStomachThe stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated part of the alimentary canal which functions as an important organ of the digestive tract in some animals, including vertebrates, echinoderms, insects , and molluscs. It is involved in the second phase of digestion, following mastication .The stomach is...
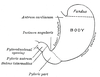

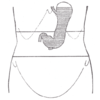
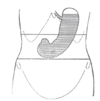
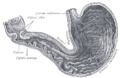

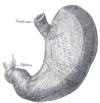



the small intestineSmall intestineThe small intestine is the part of the gastrointestinal tract following the stomach and followed by the large intestine, and is where much of the digestion and absorption of food takes place. In invertebrates such as worms, the terms "gastrointestinal tract" and "large intestine" are often used to...

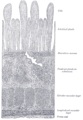
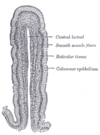

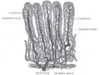
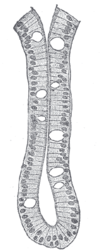

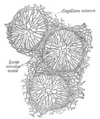
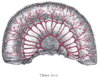
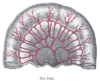
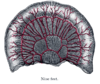
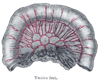
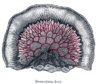
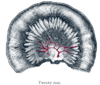
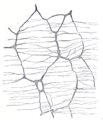

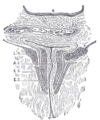
the large intestineLarge intestineThe large intestine is the third-to-last part of the digestive system — — in vertebrate animals. Its function is to absorb water from the remaining indigestible food matter, and then to pass useless waste material from the body...



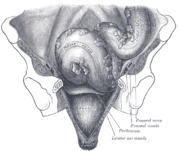



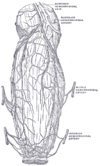
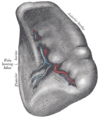
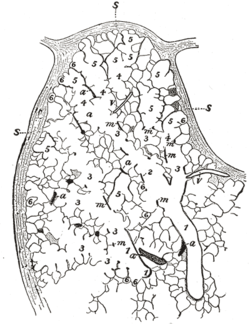
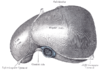
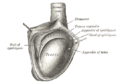
the liverLiverThe liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
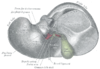


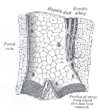
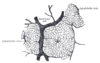
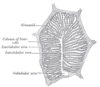


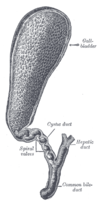
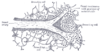
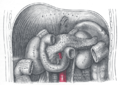
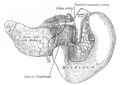
the pancreasPancreasThe pancreas is a gland organ in the digestive and endocrine system of vertebrates. It is both an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin, as well as a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist...
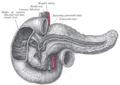



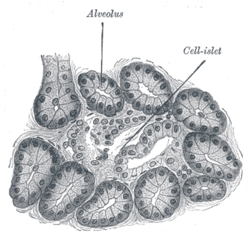
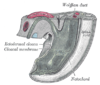
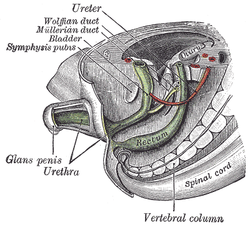
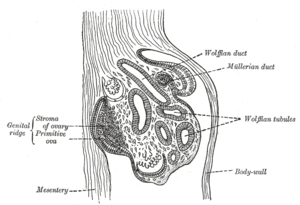
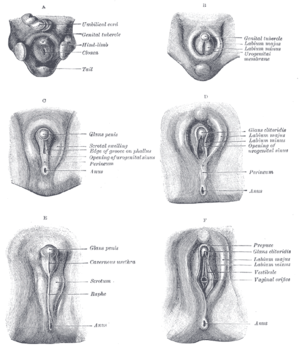
development of the urinary and generative organs


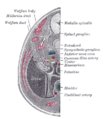
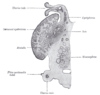

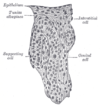
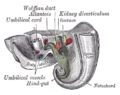
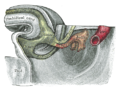
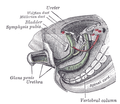

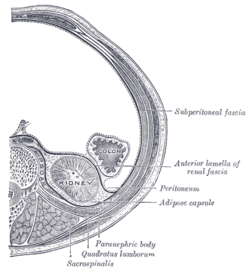
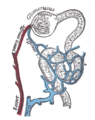
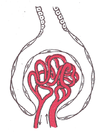
the kidneys
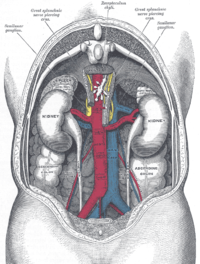
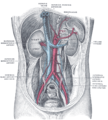
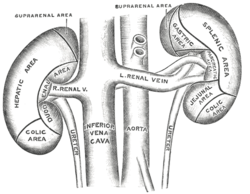





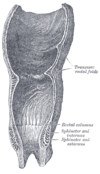
the urinary bladderUrinary bladderThe urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. A hollow muscular, and distensible organ, the bladder sits on the pelvic floor...
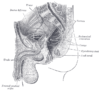
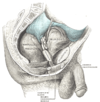




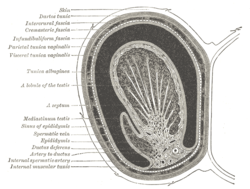
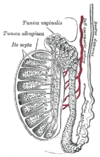
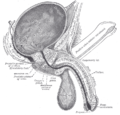
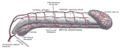
the testes and their coverings
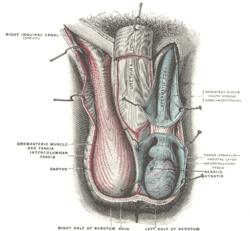
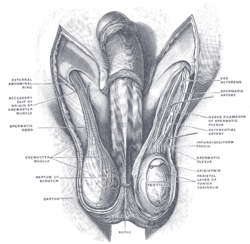
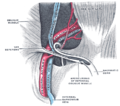
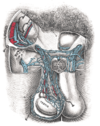
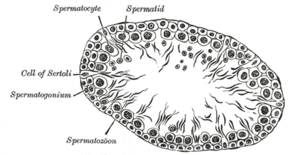
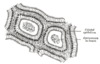
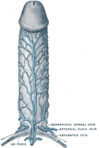
the penisPenisThe penis is a biological feature of male animals including both vertebrates and invertebrates...



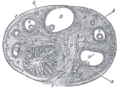
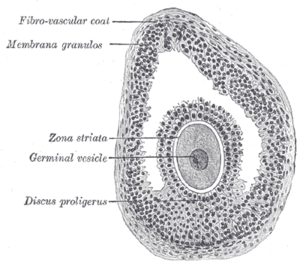
the ovaries

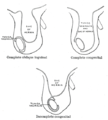
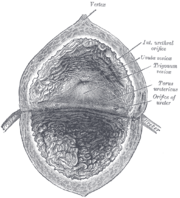
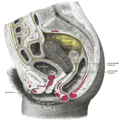
the uterusUterusThe uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species...
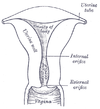
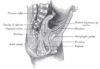

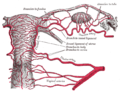
the mammæ

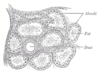
the thyroid gland
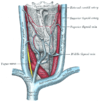
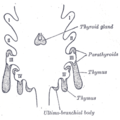
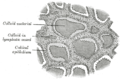
the hypophysis cerebri
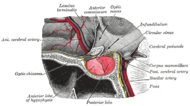


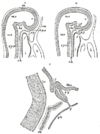
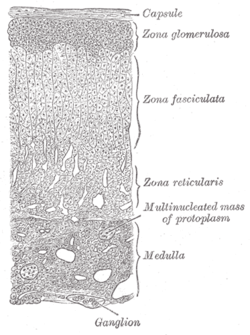
the chromaphil and cortical systems

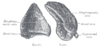


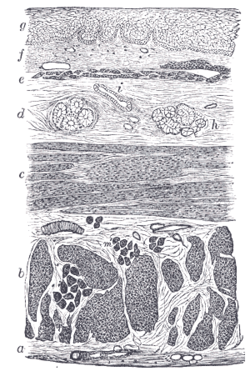
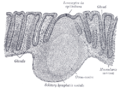
the spleenSpleenThe spleen is an organ found in virtually all vertebrate animals with important roles in regard to red blood cells and the immune system. In humans, it is located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. It removes old red blood cells and holds a reserve of blood in case of hemorrhagic shock...