
Ligand K-edge
Encyclopedia
Ligand
K-edge XAS is a spectroscopic technique that allows the direct study of metal-ligand bonding. In a XAS experiment, electrons in ligand 1s orbitals are excited to unfilled p (principal quantum number
n <= 4) and continuum states. This results in a large spectral feature known as a rising edge. Transitions at energies lower than the edge can occur, provided they are to orbitals with some ligand p character, and are called pre-edges. Such transitions are often observed in the data of complexs with metal-ligand bonding.
Pre-edge intensities (D0) are related to the amount of ligand (L) character in the unfilled orbital:

where is the wavefunction of the unfilled orbital, r is the transition dipole operator, and
is the wavefunction of the unfilled orbital, r is the transition dipole operator, and 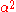 is the "covalency" or ligand character in the orbital. Since
is the "covalency" or ligand character in the orbital. Since  , the above expression relating intensity and quantum transition operators can be simplified to use experimental values:
, the above expression relating intensity and quantum transition operators can be simplified to use experimental values:
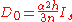
where n is the number of absorbing ligand atoms, h is the number of holes, and Is is the transition dipole integral which can be determined experimentally. Therefore, by measuring the intensity of pre-edges, it is possible to experimentally the determine the amount of ligand character in a molecular orbital.
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
K-edge XAS is a spectroscopic technique that allows the direct study of metal-ligand bonding. In a XAS experiment, electrons in ligand 1s orbitals are excited to unfilled p (principal quantum number
Principal quantum number
In atomic physics, the principal quantum symbolized as n is the firstof a set of quantum numbers of an atomic orbital. The principal quantum number can only have positive integer values...
n <= 4) and continuum states. This results in a large spectral feature known as a rising edge. Transitions at energies lower than the edge can occur, provided they are to orbitals with some ligand p character, and are called pre-edges. Such transitions are often observed in the data of complexs with metal-ligand bonding.
Pre-edge intensities (D0) are related to the amount of ligand (L) character in the unfilled orbital:

where
 is the wavefunction of the unfilled orbital, r is the transition dipole operator, and
is the wavefunction of the unfilled orbital, r is the transition dipole operator, and 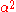 is the "covalency" or ligand character in the orbital. Since
is the "covalency" or ligand character in the orbital. Since  , the above expression relating intensity and quantum transition operators can be simplified to use experimental values:
, the above expression relating intensity and quantum transition operators can be simplified to use experimental values: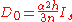
where n is the number of absorbing ligand atoms, h is the number of holes, and Is is the transition dipole integral which can be determined experimentally. Therefore, by measuring the intensity of pre-edges, it is possible to experimentally the determine the amount of ligand character in a molecular orbital.

