
Lepton number
Encyclopedia
In particle physics
, the lepton number is the number of lepton
s minus the number of antileptons.
In equation form,
so all leptons have assigned a value of +1, antileptons −1, and non-leptonic particles 0. Lepton number (sometimes also called lepton charge) is an additive quantum number
, which means that its sum is preserved in interactions (as opposed to multiplicative quantum number
s such as parity, where the product is preserved instead).
Beside the leptonic number, leptonic family numbers are also defined:
with the same assigning scheme as the leptonic number: +1 for particles of the corresponding family, −1 for the antiparticles, and 0 for leptons of other families or non-leptonic particles.
of particle physics, rely on the conservation of lepton number, in which the lepton number stays the same through an interaction. For example, in beta decay
:
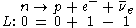
The lepton number before the reaction is 0 (the neutron, n, is a baryon and therefore there were no leptons before), whereas the total lepton number after the reaction is 0, with the proton having 0, the electron (a lepton) +1, and for the antineutrino (an antilepton) −1. Thus the lepton number is 0 after the decay, and so this quantity is conserved.
The lepton family numbers arise from the fact that lepton number is usually conserved in each leptonic family. For example, the muon almost always decays as:
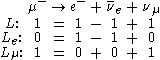
thus preserving the electronic and muonic numbers. This means that a lepton family number conservation law exist for each one of Le, Lμ, and Lτ.
, leptonic family numbers (LF numbers) would be preserved if neutrinos were massless. Since neutrino oscillations have been observed, neutrinos do have a tiny nonzero mass and conservation laws for LF numbers are therefore only approximate. This means the conservation laws are violated, although because of the smallness of the neutrino mass they still hold to a very large degree for interactions containing charged leptons. However, the (total) lepton number conservation law must still hold (under the Standard Model). Thus, it is possible to see rare muon decays such as:

Because the lepton number conservation law in fact is violated by chiral anomalies
, there are problems applying this symmetry universally over all energy scales. However, the quantum number B − L is much more likely to work and is seen in different models such as the Pati–Salam model.
Particle physics
Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the existence and interactions of particles that are the constituents of what is usually referred to as matter or radiation. In current understanding, particles are excitations of quantum fields and interact following their dynamics...
, the lepton number is the number of lepton
Lepton
A lepton is an elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. The best known of all leptons is the electron which governs nearly all of chemistry as it is found in atoms and is directly tied to all chemical properties. Two main classes of leptons exist: charged leptons , and neutral...
s minus the number of antileptons.
In equation form,
so all leptons have assigned a value of +1, antileptons −1, and non-leptonic particles 0. Lepton number (sometimes also called lepton charge) is an additive quantum number
Quantum number
Quantum numbers describe values of conserved quantities in the dynamics of the quantum system. Perhaps the most peculiar aspect of quantum mechanics is the quantization of observable quantities. This is distinguished from classical mechanics where the values can range continuously...
, which means that its sum is preserved in interactions (as opposed to multiplicative quantum number
Quantum number
Quantum numbers describe values of conserved quantities in the dynamics of the quantum system. Perhaps the most peculiar aspect of quantum mechanics is the quantization of observable quantities. This is distinguished from classical mechanics where the values can range continuously...
s such as parity, where the product is preserved instead).
Beside the leptonic number, leptonic family numbers are also defined:
- Le, the electronic number for the electronElectronThe electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
and the electron neutrinoElectron neutrinoThe electron neutrino is a subatomic lepton elementary particle which has no net electric charge. Together with the electron it forms the first generation of leptons, hence its name electron neutrino...
; - Lμ, the muonic number for the muonMuonThe muon |mu]] used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with a unitary negative electric charge and a spin of ½. Together with the electron, the tau, and the three neutrinos, it is classified as a lepton...
and the muon neutrinoMuon neutrinoThe muon neutrino is a subatomic lepton elementary particle which has the symbol and no net electric charge. Together with the muon it forms the second generation of leptons, hence its name muon neutrino. It was first hypothesized in the early 1940s by several people, and was discovered in 1962 by...
; - Lτ, the tauonic number for the tau and the tau neutrino;
with the same assigning scheme as the leptonic number: +1 for particles of the corresponding family, −1 for the antiparticles, and 0 for leptons of other families or non-leptonic particles.
Conservation laws for leptonic numbers
Many physical models, including the Standard ModelStandard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, which mediate the dynamics of the known subatomic particles. Developed throughout the mid to late 20th century, the current formulation was finalized in the mid 1970s upon...
of particle physics, rely on the conservation of lepton number, in which the lepton number stays the same through an interaction. For example, in beta decay
Beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle is emitted from an atom. There are two types of beta decay: beta minus and beta plus. In the case of beta decay that produces an electron emission, it is referred to as beta minus , while in the case of a...
:
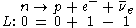
The lepton number before the reaction is 0 (the neutron, n, is a baryon and therefore there were no leptons before), whereas the total lepton number after the reaction is 0, with the proton having 0, the electron (a lepton) +1, and for the antineutrino (an antilepton) −1. Thus the lepton number is 0 after the decay, and so this quantity is conserved.
The lepton family numbers arise from the fact that lepton number is usually conserved in each leptonic family. For example, the muon almost always decays as:
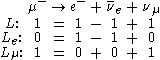
thus preserving the electronic and muonic numbers. This means that a lepton family number conservation law exist for each one of Le, Lμ, and Lτ.
Violations of the lepton number conservation laws
In the Standard ModelStandard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, which mediate the dynamics of the known subatomic particles. Developed throughout the mid to late 20th century, the current formulation was finalized in the mid 1970s upon...
, leptonic family numbers (LF numbers) would be preserved if neutrinos were massless. Since neutrino oscillations have been observed, neutrinos do have a tiny nonzero mass and conservation laws for LF numbers are therefore only approximate. This means the conservation laws are violated, although because of the smallness of the neutrino mass they still hold to a very large degree for interactions containing charged leptons. However, the (total) lepton number conservation law must still hold (under the Standard Model). Thus, it is possible to see rare muon decays such as:

Because the lepton number conservation law in fact is violated by chiral anomalies
Chiral anomaly
A chiral anomaly is the anomalous nonconservation of a chiral current. In some theories of fermions with chiral symmetry, the quantization may lead to the breaking of this chiral symmetry. In that case, the charge associated with the chiral symmetry is not conserved.The non-conservation happens...
, there are problems applying this symmetry universally over all energy scales. However, the quantum number B − L is much more likely to work and is seen in different models such as the Pati–Salam model.


