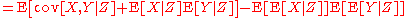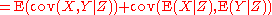Law of total covariance
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
, the law of total covariance or covariance decomposition formula states that if X, Y, and Z are random variable
s on the same probability space
, and the covariance
of X and Y is finite, then
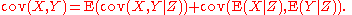
The nomenclature in this article's title parallels the phrase law of total variance
. Some writers on probability call this the "conditional covariance formula" or use other names.
(The conditional expected values E( X | Z ) and E( Y | Z ) are random variables in their own right, whose values depends on the value of Z. Notice that the conditional expected value of X given the event Z = z is a function of z (this is where adherence to the conventional rigidly case-sensitive notation of probability theory becomes important!). If we write E( X | Z = z) = g(z) then the random variable E( X | Z ) is just g(Z). Similar comments apply to the conditional covariance.)
: First,
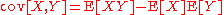
from the definition of covariance. Then we apply the law of total expectation by conditioning on the random variable Z:
Now we rewrite the term inside the first expectation using the definition of covariance:
Since expectation of a sum is the sum of expectations, we can regroup the terms:
Finally, we recognize the final two terms as the covariance of the conditional expectations E[X|Z] and E[Y|Z]:
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
, the law of total covariance or covariance decomposition formula states that if X, Y, and Z are random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
s on the same probability space
Probability space
In probability theory, a probability space or a probability triple is a mathematical construct that models a real-world process consisting of states that occur randomly. A probability space is constructed with a specific kind of situation or experiment in mind...
, and the covariance
Covariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of how much two variables change together. Variance is a special case of the covariance when the two variables are identical.- Definition :...
of X and Y is finite, then
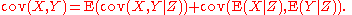
The nomenclature in this article's title parallels the phrase law of total variance
Law of total variance
In probability theory, the law of total variance or variance decomposition formula states that if X and Y are random variables on the same probability space, and the variance of Y is finite, then...
. Some writers on probability call this the "conditional covariance formula" or use other names.
(The conditional expected values E( X | Z ) and E( Y | Z ) are random variables in their own right, whose values depends on the value of Z. Notice that the conditional expected value of X given the event Z = z is a function of z (this is where adherence to the conventional rigidly case-sensitive notation of probability theory becomes important!). If we write E( X | Z = z) = g(z) then the random variable E( X | Z ) is just g(Z). Similar comments apply to the conditional covariance.)
Proof
The law of total covariance can be proved using the law of total expectationLaw of total expectation
The proposition in probability theory known as the law of total expectation, the law of iterated expectations, the tower rule, the smoothing theorem, among other names, states that if X is an integrable random variable The proposition in probability theory known as the law of total expectation, ...
: First,
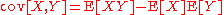
from the definition of covariance. Then we apply the law of total expectation by conditioning on the random variable Z:
Now we rewrite the term inside the first expectation using the definition of covariance:
Since expectation of a sum is the sum of expectations, we can regroup the terms:
Finally, we recognize the final two terms as the covariance of the conditional expectations E[X|Z] and E[Y|Z]:
See also
- Law of total varianceLaw of total varianceIn probability theory, the law of total variance or variance decomposition formula states that if X and Y are random variables on the same probability space, and the variance of Y is finite, then...
, a special case corresponding to X = Y.