
Launch control center (ICBM)
Encyclopedia

United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, is the main control facility for intercontinental ballistic missile
Intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile is a ballistic missile with a long range typically designed for nuclear weapons delivery...
s (ICBMs). A launch control center monitors and controls missile launch facilities. From a launch control center, the missile combat crew can monitor the complex, launch the missile
Missile
Though a missile may be any thrown or launched object, it colloquially almost always refers to a self-propelled guided weapon system.-Etymology:The word missile comes from the Latin verb mittere, meaning "to send"...
, or relax in the living quarters (depending on the ICBM system). The LCC is designed to provide maximum protection for the missile combat crew and equipment vital to missile launch.
General information
All LCCs were dependent on a missile support base (MSB) for logistics support. For example, Minot AFB is the MSB for the 91st Missile Wing. This is important to note, for some wayward maintenance crews have strayed from their MSB/missile complex, into another base's complex unwittingly.Three types of Minuteman
LGM-30 Minuteman
The LGM-30 Minuteman is a U.S. nuclear missile, a land-based intercontinental ballistic missile . As of 2010, the version LGM-30G Minuteman-III is the only land-based ICBM in service in the United States...
LCCs exist:
- Alternate Command Post (ACP) - performed backup functions to missile support base; control missile wing communications
- Squadron Command Post (SCP) - perform backup functions to ACP; control squadron execution and communications
- Primary LCC (PLCC) - perform execution and rapid message processing
There are four configurations of the LCC, differing primarily in the amount and location of communications equipment. Functionally, there are three LCC designations. One Alternate Comniand Post (ACP) LCC is located within each Minuteman wing and serves as backup for the wing command post. Three Squadron Command Posts (SCPS) serve as command units for the remaining squadrons within the wing, and report directly to the wing command post. The ACP doubles as SCP for the squadron it is located within. The remainder of the LCCS (16) are classified as primary LCCS. Four primary LCCS are located within each squadron and report to their respective command post.
Titan II LCC
The Titan LCCs held four crew members: the Missile Combat Crew Commander (MCCC), the Deputy Missile Combat Crew Commander (DMCCC), Ballistic Missile Analyst Technician (BMAT), and the Missile Facilities Technician (MFT).Titan II had a three story LCC dome. The first level was the crews living area and contained a kitchen, bathroom, bedroom, and a small equipment area that housed an exhaust fan and a water heater. The second level was the launch control area and held the LCCFC (Launch Control Complex Facility Console, the main launch console), the ALOC (Alternate Launch Officer Console), the Control Monitor Group (monitored the missile), and several other pieces of equipment. The lowest level, level 3, held communications equipment, the two battery backup supplies, the sewage lift station, the motor-generator, and several other pieces of equipment.
There were two types of Titan II sites: standard, and ACP (alternate command post) sites. ACPs had all of the equipment that one would find on a standard site plus additional communication equipment.
Launch Control Center
The LCC is an underground structure of reinforced concrete and steel of sufficient strength to withstand weapon effects. It contains equipment and personnel capable of controlling, monitoring, and launching 50 missiles in the unmanned launch facilities within the squadron.The LCC outer structure is cylindrical with hemispherical ends. Walls are approximately 4.5 feet thick. A blast door permits entry into the LCC from the tunnel junction. An escape hatch 3-ft in diameter is located at the far end of the LCC. The escape hatch and associate tunnel are constructed to withstand weapon effects and allow personnel egress in the event of damage to the vertical access shaft. Essential LCC launch equipment along with the missile combat crew are located in a shock isolated room suspended within the blast−proof outer structure. The room is steel and suspended as a pendulum by four shock isolators (see picture below).
REACT-B LCCs
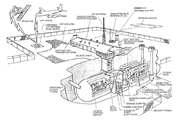

CDB LCCs
Command-data Buffer (CDB) was a configuration for early Minuteman missilesLGM-30 Minuteman
The LGM-30 Minuteman is a U.S. nuclear missile, a land-based intercontinental ballistic missile . As of 2010, the version LGM-30G Minuteman-III is the only land-based ICBM in service in the United States...
. The overall layout of the LCC did not change through the upgrade to REACT, however there are some major equipment changes.
Missile Alert Facility
The Missile Alert Facility (MAF), previously known as the Launch Control Facility (LCF), consists ofNetlink
As of 2006, all Minuteman LCCs were modified to handle the LCC Netlink upgrade. The Netlink system brought internet access underground for missile combat crews.Communications equipment
- Primary Alerting SystemPrimary Alerting SystemThe Primary Alerting System , was a network of land-line connections used by the Strategic Air Command for command and control of its nuclear forces.-See also:*Post Attack Command and Control System *Airborne Launch Control System...
(PASPrimary Alerting SystemThe Primary Alerting System , was a network of land-line connections used by the Strategic Air Command for command and control of its nuclear forces.-See also:*Post Attack Command and Control System *Airborne Launch Control System...
) - Strategic Automated Command and Control System (SACCS) - formerly known as Strategic Air Command Digital Information NetworkStrategic Air Command Digital Information NetworkThe Strategic Air Command DIgital Network was a United States military computer network that provided computerized record communications, replacing the Data Transmission Subsystem and part of the Data Display Subsystem of the SAC Automated Command and Control System.SACDIN enabled a rapid flow of...
(SACDIN) - Minimum Essential Emergency Communications NetworkMinimum Essential Emergency Communications NetworkThe Minimum Essential Emergency Communications Network is a network of systems providing uninterrupted communications throughout the pre-, trans-, and post-nuclear warfare environment...
(MEECN) - AFSATCOM, using both MILSTAR and DSCS satellites
- Survivable Low Frequency Communications SystemSurvivable Low Frequency Communications SystemThe AN/FRC-117 Survivable Low Frequency Communications System was a communications system designed to be able to operate, albeit at low data transfer rates, during and after a nuclear attack....
(SLFCSSurvivable Low Frequency Communications SystemThe AN/FRC-117 Survivable Low Frequency Communications System was a communications system designed to be able to operate, albeit at low data transfer rates, during and after a nuclear attack....
) - Hardened Intersite Cable System lines (HICS)
- Voice Dial Lines 1 & 2
The Minuteman LCC differs from previous missile systems in that it only held room for two personnel, the Missile Combat Crew Commander (MCCC) and the Deputy Missile Combat Crew Commander (DMCCC).
Previously, each MAF was equipped with the ICBM SHF Satellite Terminal (ISST) communications system. This system has since been deactivated, with Francis E. Warren Air Force Base
Francis E. Warren Air Force Base
Francis E. Warren Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located approximately west of Cheyenne, Wyoming. It is one of three strategic missile bases in the United States. It is named in honor of Francis E. Warren....
being the first to completely remove the system components.
Peacekeeper LCC
The PeacekeeperLGM-118A Peacekeeper
The LGM-118A Peacekeeper, also known as the MX missile , was a land-based ICBM deployed by the United States starting in 1986. A total of 50 missiles were deployed. They have since been deactivated....
LCCs were just non-REACT modified CDB LCCs. Instead of replacing the command and control equipment, the 'old' Minuteman CDB C2 system was modified for the 50 Peacekeeper ICBMs.
Photo gallery
File: LCC Blast Door 1.png|LCC Blast Door
File: LCEB Blast Door.png|Launch Control Equipment Building Blast Door
File: SAS Container.png|Sealed Authenticator System safe w/two crew locks
File: Foxtrot LCC Artwork.png|Art work at Foxtrot-01 LCC
File: Hotel LCC Artwork.png|Art work at Hotel-01 LCC
File: Blast Door Pins.png|Blast Door Pins
File: REACT-B Deployment1.PNG|REACT-B Deployment at Grand Forks AFB, ND
File: Command Data Buffer configuration.png|Command Data Buffer configuration
See also
- Post Attack Command and Control SystemPost Attack Command and Control SystemThe Post Attack Command and Control System was a network of communication sites for use before, during and after a nuclear attack on the United States. PACCS was designed to ensure that National Command Authority would retain sole, exclusive, and complete control over US nuclear weapons...
(PACCS) - Airborne Launch Control SystemAirborne Launch Control SystemThe United States' Airborne Launch Control System is a method of assured command and control of nuclear weapons, specifically ICBMs and SLBMs...
(ALCS) - Airborne Launch Control CenterAirborne Launch Control CenterThe United States' Airborne Launch Control Center is a component of the Airborne Launch Control System, the emergency back-up means of launching the United States' ICBM force...
(ALCC) - Survivable Low Frequency Communications SystemSurvivable Low Frequency Communications SystemThe AN/FRC-117 Survivable Low Frequency Communications System was a communications system designed to be able to operate, albeit at low data transfer rates, during and after a nuclear attack....
(SLFCSSurvivable Low Frequency Communications SystemThe AN/FRC-117 Survivable Low Frequency Communications System was a communications system designed to be able to operate, albeit at low data transfer rates, during and after a nuclear attack....
) - Ground Wave Emergency NetworkGround Wave Emergency NetworkThe Ground Wave Emergency Network was a command and control communications system intended for use by the United States government to facilitate military communications before, during and after a nuclear war...
(GWENGround Wave Emergency NetworkThe Ground Wave Emergency Network was a command and control communications system intended for use by the United States government to facilitate military communications before, during and after a nuclear war...
) - Minimum Essential Emergency Communications NetworkMinimum Essential Emergency Communications NetworkThe Minimum Essential Emergency Communications Network is a network of systems providing uninterrupted communications throughout the pre-, trans-, and post-nuclear warfare environment...
(MEECNMinimum Essential Emergency Communications NetworkThe Minimum Essential Emergency Communications Network is a network of systems providing uninterrupted communications throughout the pre-, trans-, and post-nuclear warfare environment...
) - Emergency Rocket Communications SystemEmergency Rocket Communications SystemThe Emergency Rocket Communications System was a back-up communications method for the United States National Command Authority, using a UHF repeater placed atop a Blue Scout rocket or Minuteman II intercontinental ballistic missile. ERCS was deactivated as a communication means when President...
(ERCSEmergency Rocket Communications SystemThe Emergency Rocket Communications System was a back-up communications method for the United States National Command Authority, using a UHF repeater placed atop a Blue Scout rocket or Minuteman II intercontinental ballistic missile. ERCS was deactivated as a communication means when President...
) - The Cold War
- Game theoryGame theoryGame theory is a mathematical method for analyzing calculated circumstances, such as in games, where a person’s success is based upon the choices of others...
- Continuity of governmentContinuity of governmentContinuity of government is the principle of establishing defined procedures that allow a government to continue its essential operations in case of nuclear war or other catastrophic event....
External links
- U.S. National Park Service article with detailed information on Minuteman missile launch control centers.
- Titan Missile Museum: Pima Air & Space Museum
- 20th Century Castles: LCC real estate sales

