
Laplace number
Encyclopedia
The Laplace number also known as the Suratman number (Su), is a dimensionless number used in the characterization of free surface fluid dynamics
. It represents a ratio of surface tension
to the momentum
-transport (especially dissipation
) inside a fluid.
It is defined as follows:
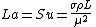
where:
Laplace number is related to Reynolds number (Re) and Weber number
(We) in the following way:
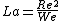
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
. It represents a ratio of surface tension
Surface tension
Surface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
to the momentum
Momentum
In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...
-transport (especially dissipation
Dissipation
In physics, dissipation embodies the concept of a dynamical system where important mechanical models, such as waves or oscillations, lose energy over time, typically from friction or turbulence. The lost energy converts into heat, which raises the temperature of the system. Such systems are called...
) inside a fluid.
It is defined as follows:
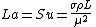
where:
- σ = surface tensionSurface tensionSurface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
- ρ = densityDensityThe mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
- L = length
- μ = liquid viscosityViscosityViscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
Laplace number is related to Reynolds number (Re) and Weber number
Weber number
The Weber number is a dimensionless number in fluid mechanics that is often useful in analysing fluid flows where there is an interface between two different fluids, especially for multiphase flows with strongly curved surfaces. It can be thought of as a measure of the relative importance of the...
(We) in the following way:
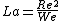
See also
- Ohnesorge number - There is an inverse relationship,
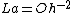 , between the Laplace number and the Ohnesorge number.
, between the Laplace number and the Ohnesorge number.

