
Landau distribution
Encyclopedia
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
, the Landau distribution is a probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
named after Lev Landau
Lev Landau
Lev Davidovich Landau was a prominent Soviet physicist who made fundamental contributions to many areas of theoretical physics...
.
Definition
The distribution is defined by the complexComplex number
A complex number is a number consisting of a real part and an imaginary part. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and adding a vertical axis to plot the imaginary part...
integral
Integral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
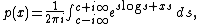
where
 is any positive real number, and log refers to the logarithm base e
is any positive real number, and log refers to the logarithm base eE (mathematical constant)
The mathematical constant ' is the unique real number such that the value of the derivative of the function at the point is equal to 1. The function so defined is called the exponential function, and its inverse is the natural logarithm, or logarithm to base...
, the natural logarithm
Natural logarithm
The natural logarithm is the logarithm to the base e, where e is an irrational and transcendental constant approximately equal to 2.718281828...
.
For numerical purposes it is more convenient to use the following equivalent form of the integral,
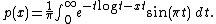
where log refers to the logarithm base e
E (mathematical constant)
The mathematical constant ' is the unique real number such that the value of the derivative of the function at the point is equal to 1. The function so defined is called the exponential function, and its inverse is the natural logarithm, or logarithm to base...
, the natural logarithm
Natural logarithm
The natural logarithm is the logarithm to the base e, where e is an irrational and transcendental constant approximately equal to 2.718281828...
.
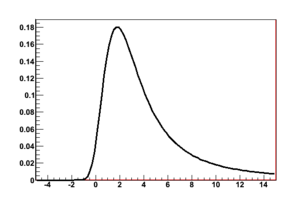
The Landau distribution is used in physics to describe the fluctuations in the energy loss of a charged particle passing through a thin layer of matter.
This distribution is a special case of the stable distribution with parameters α = 1, and β = 1.
The characteristic function
Characteristic function (probability theory)
In probability theory and statistics, the characteristic function of any random variable completely defines its probability distribution. Thus it provides the basis of an alternative route to analytical results compared with working directly with probability density functions or cumulative...
may be expressed as:
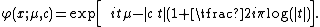
where μ and c are real, which yields a Landau distribution shifted by μ and scaled by c.
Related distributions
- If
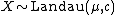 then
then 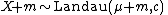
- Landau distribution is a Stable distribution
External links
- The Energy Loss Distribution of charged particles passing through matter (Use of the Landau Distribution in the high energy physics experiments")

