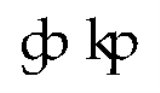
Labial-velar consonant
Encyclopedia
Labial–velar consonants are doubly articulated
at the velum
and the lip
s. They are sometimes called "labiovelar consonants", a term that can also refer to labialized velars, such as [kʷ] and the approximant [w].
Truly doubly articulated labial–velars occur as plosive
s and nasal stop
s in the majority of languages in West and Central Africa (for example in the name of Laurent Gbagbo
, former president of Ivory Coast; they are found in many Niger–Congo languages
as well as in the Ubangian
, Chadic
and Central Sudanic families), and are relatively common in the eastern end of New Guinea
. They include [k͡p, ɡ͡b, ŋ͡m]. To pronounce these, try saying [k, ɡ, ŋ], but close your lips as you would for [p, b, m]. Then release your lips as you produce the [k, ɡ, ŋ]. Note that, while 90% of the occlusion overlaps, the onset of the velar occurs slightly before that of the labial, and the release of the labial occurs slightly after that of the velar, so that the preceding vowel sounds as if followed by a velar, while the following vowel sounds as if followed by a labial. Thus the order of the symbols in k͡p and ɡ͡b is not arbitrary, but is motivated by the phonetic details of these sounds.
The Yélî Dnye language
of Rossel Island, Papua New Guinea
, has both labial–velars and labial–alveolar consonants. Labial–velar plosives and nasals also occur in Vietnamese
, albeit only at the ends of words.
These sounds are clearly single consonants rather than consonant cluster
s. The Eggon language
, for example, contrasts these possibilities, with /bɡ/ and /ɡb/ both distinct from /ɡ͡b/. Ignoring tone, we have:
Note that, although such symbols are readily understood, they are not sanctioned by the IPA, and have no Unicode
values. They can, however, be specified as the way an OpenType
font displays gb and kp digraphs
.
Labial–velar plosives also occur as ejective
[k͡pʼ] and implosive
[ɠɓ] (the tie bar has been removed for legibility). There may be labial–velar approximants in languages like Japanese
. Bilabial click
s are sometimes considered to be labial–velar consonants as well, though the validity of this classification is debated.
For transcribing these sounds ligatures can occasionally be seen instead of digraphs with a tie bar:

Doubly articulated consonant
Doubly articulated consonants are consonants with two simultaneous primary places of articulation of the same manner . They are a subset of co-articulated consonants. They are to be distinguished from co-articulated consonants with secondary articulation, that is, a second articulation not of the...
at the velum
Soft palate
The soft palate is the soft tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is distinguished from the hard palate at the front of the mouth in that it does not contain bone....
and the lip
Lip
Lips are a visible body part at the mouth of humans and many animals. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech...
s. They are sometimes called "labiovelar consonants", a term that can also refer to labialized velars, such as [kʷ] and the approximant [w].
Truly doubly articulated labial–velars occur as plosive
Stop consonant
In phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or an oral stop, is a stop consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases. The occlusion may be done with the tongue , lips , and &...
s and nasal stop
Nasal consonant
A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :...
s in the majority of languages in West and Central Africa (for example in the name of Laurent Gbagbo
Laurent Gbagbo
Laurent Koudou Gbagbo served as the fourth President of Côte d'Ivoire from 2000 until his arrest in April 2011. A historian by profession, he is also an amateur chemist and physicist....
, former president of Ivory Coast; they are found in many Niger–Congo languages
Niger–Congo languages
The Niger–Congo languages constitute one of the world's major language families, and Africa's largest in terms of geographical area, number of speakers, and number of distinct languages. They may constitute the world's largest language family in terms of distinct languages, although this question...
as well as in the Ubangian
Ubangian languages
The Ubangian languages form a fairly close-knit language family of some seventy languages centered on the Central African Republic. They are the predominant languages of the CAR, spoken by 2–3 million people, and include the national language, Sango....
, Chadic
Chadic languages
The Chadic languages constitute a language family of perhaps 200 languages spoken across northern Nigeria, Niger, Chad, Central African Republic and Cameroon, belonging to the Afroasiatic phylum...
and Central Sudanic families), and are relatively common in the eastern end of New Guinea
New Guinea
New Guinea is the world's second largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 786,000 km2. Located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, it lies geographically to the east of the Malay Archipelago, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago...
. They include [k͡p, ɡ͡b, ŋ͡m]. To pronounce these, try saying [k, ɡ, ŋ], but close your lips as you would for [p, b, m]. Then release your lips as you produce the [k, ɡ, ŋ]. Note that, while 90% of the occlusion overlaps, the onset of the velar occurs slightly before that of the labial, and the release of the labial occurs slightly after that of the velar, so that the preceding vowel sounds as if followed by a velar, while the following vowel sounds as if followed by a labial. Thus the order of the symbols in k͡p and ɡ͡b is not arbitrary, but is motivated by the phonetic details of these sounds.
The Yélî Dnye language
Yélî Dnye language
The Yélî Dnye language, also known as Yele, is the language of Rossel island, the easternmost island in the Louisiade Archipelago off the eastern tip of Papua New Guinea. For now it is best considered a language isolate, but it may turn out to be related to the Anêm and Ata language isolates of New...
of Rossel Island, Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea , officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania, occupying the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and numerous offshore islands...
, has both labial–velars and labial–alveolar consonants. Labial–velar plosives and nasals also occur in Vietnamese
Vietnamese language
Vietnamese is the national and official language of Vietnam. It is the mother tongue of 86% of Vietnam's population, and of about three million overseas Vietnamese. It is also spoken as a second language by many ethnic minorities of Vietnam...
, albeit only at the ends of words.
| IPA | Description | Example | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | Orthography | IPA | Meaning | ||
| k͡p | voiceless labial–velar plosive | Logba Logba language Logba is a Kwa language spoken in the south-eastern Ghana by approximately 7 500 people. The Logba people call themselves and their language Ikpana, which means ‘defenders of truth’... |
ò-kpàyɔ̀ | [ò-k͡pàjɔ̀] | 'God' |
| ɡ͡b | voiced labial–velar plosive | Ewe Ewe language Ewe is a Niger–Congo language spoken in Ghana, Togo and Benin by approximately six million people. Ewe is part of a cluster of related languages commonly called Gbe, spoken in southeastern Ghana, Togo, and parts of Benin. Other Gbe languages include Fon, Gen, Phla Phera, and Aja... |
Ewegbe | [ɛβɛɡ͡be] | 'the Ewe language' |
| ŋ͡m | labial–velar nasal | Vietnamese Vietnamese language Vietnamese is the national and official language of Vietnam. It is the mother tongue of 86% of Vietnam's population, and of about three million overseas Vietnamese. It is also spoken as a second language by many ethnic minorities of Vietnam... |
cung | [kuŋ͡m] | 'sector' |
These sounds are clearly single consonants rather than consonant cluster
Consonant cluster
In linguistics, a consonant cluster is a group of consonants which have no intervening vowel. In English, for example, the groups and are consonant clusters in the word splits....
s. The Eggon language
Eggon language
Eggon is one of the Benue–Congo languages spoken in Nigeria.EggonTaken from the introduction to "A dictionary of Eggon", edited by Roger Blench...
, for example, contrasts these possibilities, with /bɡ/ and /ɡb/ both distinct from /ɡ͡b/. Ignoring tone, we have:
| Single consonant | |Two-consonant sequence | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| pom | to pound | kba | to dig |
| abu | a dog | bɡa | to beat, to kill |
| aku | a room | ak͡pki | a stomach |
| ɡom | to break | ɡ͡bɡa | to grind |
| k͡pu | to die | kpu | to kneel |
| ɡ͡bu | to arrive | ɡba | to divide |
Note that, although such symbols are readily understood, they are not sanctioned by the IPA, and have no Unicode
Unicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
values. They can, however, be specified as the way an OpenType
OpenType
OpenType is a format for scalable computer fonts. It was built on its predecessor TrueType, retaining TrueType's basic structure and adding many intricate data structures for prescribing typographic behavior...
font displays gb and kp digraphs
Digraph (orthography)
A digraph or digram is a pair of characters used to write one phoneme or a sequence of phonemes that does not correspond to the normal values of the two characters combined...
.
Labial–velar plosives also occur as ejective
Ejective consonant
In phonetics, ejective consonants are voiceless consonants that are pronounced with simultaneous closure of the glottis. In the phonology of a particular language, ejectives may contrast with aspirated or tenuis consonants...
[k͡pʼ] and implosive
Implosive consonant
Implosive consonants are stops with a mixed glottalic ingressive and pulmonic egressive airstream mechanism. That is, the airstream is controlled by moving the glottis downward in addition to expelling air from the lungs. Therefore, unlike the purely glottalic ejective consonants, implosives can...
[ɠɓ] (the tie bar has been removed for legibility). There may be labial–velar approximants in languages like Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
. Bilabial click
Bilabial click
The bilabial clicks are a family of click consonants that sound something like a smack of the lips. They are found as phonemes only in the small Tuu language family, in the language of Botswana, and in the extinct Damin ritual jargon of Australia....
s are sometimes considered to be labial–velar consonants as well, though the validity of this classification is debated.
For transcribing these sounds ligatures can occasionally be seen instead of digraphs with a tie bar:


