
KDE4
Encyclopedia
KDE Software Compilation 4 (KDE SC 4) is the current series of releases of KDE Software Compilation
. The first major version (4.0) of this series was released on 11 January 2008, and the latest major version (4.7) was released on 27 July 2011. Major releases (4.x) are scheduled for every six months, while minor bugfix releases (4.x.y) are released monthly.
The new series includes updates to several of the KDE Platform’s
core components, notably a port to Qt 4. It contains a new multimedia API, called Phonon
, a device integration framework called Solid
and a new style guide and default icon set called Oxygen
. It also includes a new, unified desktop and panel user interface called Plasma, which supports desktop widgets, replacing K Desktop Environment 3’s separate components.
One of the overall goals of KDE Platform 4 is to make it easy for KDE applications to be portable to different operating systems. This was made possible by the port to Qt 4, which facilitated support for non-X11-based platforms, including Microsoft Windows
and Mac OS X
. Versions 4.0 to 4.3 of the KDE Software Compilation were known simply as KDE 4 – the name change was a component of the KDE project’s re-branding to reflect KDE’s increased scope.
2.29, Xfce
4.6, and LXDE
0.5. Qt 4 is available under the LGPL for Mac OS X
and Windows
, which allows KDE 4 to run on those platforms. The ports to both platforms are in an early state. , KDE Software compilation 4 on Mac OS X is currently considered beta , while on Windows it is not in the final state, so applications can be unsuitable for day to day use yet. Both ports are trying to use as little divergent code as possible to make the applications function almost identically on all platforms. During Summer of Code 2007
an icon cache was created to decrease application start-up times for use in KDE 4. Improvements were varied – Kfind, an application which used several hundred icons, started up in almost a quarter of the time it took previously. Other applications and a full KDE session started up a little over a second faster.
Many applications in the Extragear
and KOffice
modules have received numerous improvements with the new features of KDE 4 and Qt 4. But since they follow their own release schedule, they were not all available at the time of the first KDE 4 release – these include Amarok, K3b
, digiKam
, KWord
, and Krita
.
. These represent a break from previous KDE icons and graphics, which had a cartoonish look. Instead Oxygen icons opt for a more photorealistic style. The Oxygen Project builds on the freedesktop.org
Icon Naming Specification and Icon Theme Specification, allowing consistency across applications. The Oxygen team uses community help for better visuals in KDE 4, with both alternate icon sets and the winners of a wallpaper contest held by the Oxygen project being included in KDE 4. There is also a new set of human interface guidelines
for a more standardized layout.
Plasma provides the main desktop user interface and is a rewrite of several core KDE applications, like the desktop drawing and most notably the widget engine. Plasma allows for a more customizable desktop and more versatile widgets.
KWin
, the KDE Window Manager, now provides its own compositing effects, similar to Compiz
.
is the name of the multimedia API in KDE 4. Phonon is a different approach to multimedia backends than in previous versions of KDE. This is because Phonon only functions as a wrapper, abstracting the various multimedia frameworks available for Unix-like operating systems into runtime switchable backends that can be accessed through a single API. This was done to provide a stable API for KDE 4 and to prevent it from depending on a single multimedia framework. Applications that use the Phonon API can be switched between multimedia frameworks seamlessly by simply changing the backend used in System Settings
. Nokia
adopted Phonon for multimedia use in Qt 4.4 and are developing backends for Gstreamer, Windows and OS X in the KDE SVN repository under the LGPL.
Solid
is the hardware API in KDE 4. It functions similarly to Phonon as it doesn’t manage hardware on its own but makes existing solutions accessible through a single API. The current solution uses HAL
, NetworkManager
and BlueZ (the official Linux bluetooth stack), but any and all parts can be replaced without breaking the application, making applications using Solid extremely flexible and portable.
ThreadWeaver
is a programming library to help applications take advantage of multicore processors and is included with kdelibs.
Kross
is the new scripting framework for KDE 4. Kross itself is not a scripting language, but makes it easier for developers to add support for other scripting languages. Once an application adds support for Kross, any language Kross supports can be used by developers. New scripting languages can be added by creating a plugin for Kross, which benefits all applications using it.
Decibel
is a Telepathy-based communication framework, which was expected to be fully used by Kopete by KDE 4.2, but which is reported to be postponed indefinitely.
Strigi
is the default search tool for KDE 4, chosen for its speed and few dependencies. In concert with other software like Soprano
, an RDF
storage framework, and the NEPOMUK
specification, Strigi will provide the beginnings of a semantic desktop
in KDE 4. Users can tag files with additional information through Dolphin
, which Strigi can index for more accurate searches.
KDE 4 uses CMake
for its build system. Since previous versions of KDE were only on Unix systems, autotools
were used, but a new build system was needed for builds on operating systems like Windows. CMake also dramatically simplified the build process. The autotools build system had become so complicated by KDE 3 that few developers understood it, requiring hours of work for simple changes. In early 2007 CMake was shown to compile the KDE 4 version of KDElibs 40 % faster than the autotools compiled KDE 3 version.
DXS, previously known as GHNS (Get Hot New Stuff) and now adopted by freedesktop.org
, is a web service that lets applications download and install data from the Internet with one click. It was used in the KDE 3 series but has been extended for use throughout KDE 4. One example was Kstars, that can use Astronomical data that is free for personal use but cannot be redistributed. DXS allows that data to be easily downloaded and installed from within the application instead of manually downloading it.
Akonadi
is a new PIM
framework for KDE 4. Akonadi is a unification of previously separate KDE PIM components. In the past each application would have its own method for storing information and handling data. Akonadi itself functions as a server that provides data and search functions to PIM applications. It is also able to update the status of contacts. So if one application changes information about a contact, all other applications are immediately informed of the change.
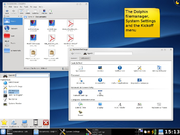 The majority of development went into implementing most of the new technologies and frameworks of KDE 4. Plasma and the Oxygen style were two of the biggest user-facing changes.
The majority of development went into implementing most of the new technologies and frameworks of KDE 4. Plasma and the Oxygen style were two of the biggest user-facing changes.
Dolphin
replaces Konqueror as the default file manager in KDE 4.0. This was done to address complaints of Konqueror being too complicated for a simple file manager. However Dolphin and Konqueror will share as much code as possible, and Dolphin can be embedded in Konqueror to allow Konqueror to still be used as a file manager.
Okular
replaces several document viewers used in KDE 3, like KPDF, KGhostView and KDVI. Okular makes use of software libraries and can be extended to view almost any kind of document. Like Konqueror and KPDF in KDE 3, Okular can be embedded in other applications.
and Phonon
. Dolphin
and Okular
were integrated and a new visual appearance was provided through Oxygen icons
.
On 4 July 2007, Alpha 2 was released. The release focused on integrating the Plasma desktop, improving functionality and stabilizing KDE.
On 2 August 2007, Beta 1 was released. Major features included a pixmap cache – speeding up icon loading, KDE PIM improvements, improved KWin
effects and configuration, better interaction between Konqueror and Dolphin and Metalink
support added to KGet
for improved downloads.
On 6 September 2007, Beta 2 was released with improved BSD and Solaris support. The release included the addition of the Blitz graphic library – allowing for developers to use high performance graphical tricks like icon animation – and an overhaul of KRDC
(K Remote Desktop Client) for Google’s Summer of Code
. Plasma
was also integrated with Amarok to provide Amarok’s central context view.
On 16 October 2007, Beta 3 was released. The beta 3 release was focused on stabilizing and finishing the design of libraries for the release of the KDE Development Platform. Plasma received many new features including an applet browser. The Educational software received many improvements in Marble and Parley (formerly known as KVoctrain) with bugfixes in other applications. A program called Step, an interactive physics simulator, was produced as part of the Google Summer of Code
.
On 30 October 2007, Beta 4 was released. A list of release blockers was compiled, listing issues that need to be resolved before KDE will start with the release candidate cycle for the desktop. The goals were to focus on stabilization and fixing the release blockers.
At the same time, the first release candidate of the KDE 4.0 Development Platform was released. The development platform contains all the base libraries to develop KDE applications, including "high-level widget libraries, a network abstraction layer and various libraries for multimedia integration, hardware integration and transparent access to resources on the network."
On 20 November 2007, Release Candidate (RC) 1 was released. This release was called a "Release Candidate" despite Plasma requiring further work and not being ready for release. On 11 December 2007, RC2 was released. The codebase was declared feature-complete. Some work was still required to fix bugs, finish off artwork and smooth out the user experience.
which fix bugs and add some minor features such as resizable desktop panels.
KDE 4.0 was met with a mixed reaction. Despite being labelled as a stable release, it was intended for early adopters.
Continuing to use KDE 3.5 was suggested for users wanting a more stable, "feature complete" desktop.
The intent was for 4.0 to be a developers release. It was included in a number of distributions in order to promote the migration from KDE 3.5 among the Linux developers.
The message got lost among the release excitement, and as a result the release disappointed some end users. This resulted in a backlash over the introduction of 4.0.
switched from GNOME to KDE on December 2005, he switched back to GNOME after Fedora – as only major Linux distribution – replaced KDE 3.5 with 4.0. In an interview with ComputerWorld, Linus described KDE 4.0 as a “break everything” model and “half-baked” release, claiming that he expected it to be an upgrade of KDE 3.5, when the reality was that there were significant cases of features being regressed due to its extensive changes (Linus did point out, however, that he understood why the developers in charge of the KDE project had chosen to make such drastic changes to the desktop environment in KDE 4.0 and the reason for its pre-mature release, and that his criticism was more on the way KDE 4.0 was pushed out to the public)/ The criticism has emerged in spite of the environment being labeled as “less mature” or “cutting edge” in distributions such as openSUSE
and Kubuntu
. Despite the criticism, reviewers such as ArsTechnica’s Ryan Paul noted that the visual style “is very attractive and easy on the eyes” and “exhibits a relatively high level of polish” and that “the underlying technologies still have a lot of very serious potential”.
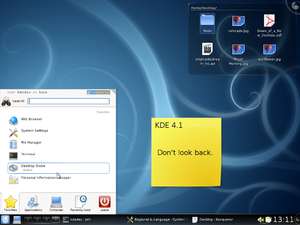 KDE 4.1 was released on 29 July 2008. KDE 4.1 includes a shared emoticon theming system which is used in PIM and Kopete, and DXS, a service that lets applications download and install data from the Internet with one click. Also introduced are GStreamer
KDE 4.1 was released on 29 July 2008. KDE 4.1 includes a shared emoticon theming system which is used in PIM and Kopete, and DXS, a service that lets applications download and install data from the Internet with one click. Also introduced are GStreamer
, QuickTime
7, and DirectShow
9 Phonon
backends. Plasma improvements include support for Qt 4 widgets and WebKit
integration – allowing many Apple Dashboard widgets to be displayed. There will also be ports of some applications to Windows and Mac OS X
.
New applications include:
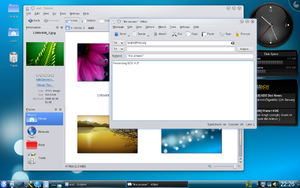 KDE 4.2 was released on 27 January 2009. The release is considered a significant improvement beyond KDE 4.1 in nearly all aspects, and a suitable replacement for KDE 3.5 for most users.
KDE 4.2 was released on 27 January 2009. The release is considered a significant improvement beyond KDE 4.1 in nearly all aspects, and a suitable replacement for KDE 3.5 for most users.
These include grouping and multiple row layout in the task bar, icon hiding in the system tray, panel autohiding, window previews and tooltips are back in the panel and task bar, notifications and job tracking by Plasma, and the ability to have icons on the desktop again by using a Folder View as the desktop background where icons now remain where they are placed.
New Plasma applets include applets for leaving messages on a locked screen, previewing files, switching desktop Activity, monitoring news feeds, and utilities like the pastebin applet, the calendar, timer, special character selector, a QuickLaunch widget, and a system monitor, among many others. The Plasma workspace can now load Google Gadgets. Plasma widgets can be written in Ruby and Python. Support for applets written in JavaScript and Mac OS X dashboard widgets has been further improved. Theming improvements in the Task Bar, Application Launcher, System Tray and most other Plasma components streamline the look and feel and increase consistency. A new System Settings module, Desktop Theme Details, gives the user control over each element of various Plasma themes. Wallpapers are now provided plugins, so developers can easily write custom wallpaper systems in KDE 4.2. Available wallpaper plugins in KDE 4.2 will be slideshows, Mandelbrot fractals, and regular static images.
New desktop effects have been added such as the Magic Lamp, Minimize effect and the Cube and Sphere desktop switchers. Others, such as the desktop grid, have been improved. The user interface for choosing effects has been reworked for easy selection of the most commonly used effects. Compositing desktop effects have been enabled by default where hardware and drivers support them. Automatic checks confirm that compositing works before enabling it on the workspace.
KRunner – the "Run command…" dialog – has extended functionality through several new plugins, including spellchecking, Konqueror browser history, power management control through PowerDevil, KDE Places, Recent Documents, and the ability to start specific sessions of the Kate editor, Konqueror and Konsole. The converter plugin now also supports quickly converting between units of speed, mass and distances.
Multi-screen support has been improved through the Kephal library, fixing many bugs when running KDE on more than one monitor.
All applications have seen bugfixes, feature additions and user interface improvements. Dolphin now supports previews of files in toolbars and has gained a slider to zoom in and out on file item views. It can now also show the full path in the breadcrumb bar. Konqueror offers increased loading speed by prefetching domain name data in KHTML. A find-as-you-type bar improves navigation in webpages. KMail has a new message header list, and reworked attachment view. The KWrite and Kate text editors can now operate in Vi input mode, accommodating those used to the traditional UNIX editor. Ark, the archiving tool has gained support for password-protected archives and is accessible via a context menu from the file managers now. KRDC, the remote desktop client improves support for Microsoft’s Active Directory through LDAP. Kontact has gained a new planner summary and support for drag and drop in the free/busy view. KSnapshot now uses the window title when saving screenshots, making it easier to index them using search engines.
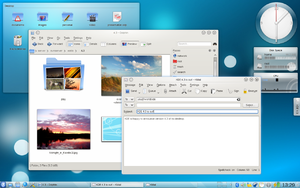 KDE 4.3 was released on 4 August 2009. Polishing KDE 4 was a focus of 4.3, with this release being described as incremental and lacking in major new features.KDE 4.3 fixed over 10,000 bugs and implemented almost 2,000 feature requests. Integration with other technologies, such as PolicyKit
KDE 4.3 was released on 4 August 2009. Polishing KDE 4 was a focus of 4.3, with this release being described as incremental and lacking in major new features.KDE 4.3 fixed over 10,000 bugs and implemented almost 2,000 feature requests. Integration with other technologies, such as PolicyKit
, NetworkManager
& Geolocation
services, was another focus of this release. KRunner’s interface has been overhauled. A much more flexible system tray has been developed. Many new Plasmoids have been added, including the openDesktop.org
Plasmoid – an initial take on the Social Desktop
. Plasma also receives more keyboard shortcuts.
toolkit. As such, KDE SC 4.4 carries Qt’s performance improvements as well as Qt 4.6's new features, such as the new animation framework Kinetic.
KAddressBook Is replaced by a completely new application with the same name – previously tentatively called KContactManager. Key features of the new KAddressBook are Akonadi
integration and a streamlined user interface.
Another major new feature is an additional new Plasma interface, targeted towards netbook
s.
Kopete
is released as version 1.0.
KAuth, a cross-platform authentication API, made its début in KDE SC 4.4. Initially only PolicyKit
is supported as back-end.
library, an open-source web browser engine, which is used in major browsers such as Apple Safari and Google Chrome
. KDE's own KHTML
engine will continue to be developed.
KPackage
has been deprecated. KPackageKit
was suggested to replace it but it didn't make it to replace it.
Aside from the desktop environment, version 4.7 updates many applications within the Software Compilation. Dolphin file manager has been updated to include a cleaner user interface. Marble, the virtual globe software, now supports voice navigation, a map creation wizard, as well as many new plugins. Gwenview image viewer now allows users to compare two or more photos side by side. The Kontact database has also been ported to Akonadi which allows the database to be easily accessible from other applications. Furthermore, the KMail database has also been ported to Akonadi. DigiKam has been updated to support face detection, image versioning, and image tagging. Other applications such as Kate, Kalzium, KAlgebra, KStars, and KDevelop have also been updated in this release. Moreover, version 4.7 fixed over 12,000 bugs.
Release 4.8 – scheduled for late January – won’t feature an upgrade to the KDE Platform
libraries (kdelibs,…). Instead it will be based on Platform 4.7 in order to concentrate development efforts on KDE Frameworks 5.0 which will be based on Qt 5.
rendering performance will be increased by optimizing effect rendering. Window resizing will also be improved.
Other Kwin features are: QML based Window switcher (Tabbox), AnimationEffect class and initial Wayland support.
It is planned that by default the system tray entry for most applications will be merged with the task bar entry.
Cantor
will ship with an additional back-end based on Qalculate.
Dragon Player 3 may ship with Applications 4.8, although a release with 4.9 is considered more likely.
KDE Software Compilation
The KDE Software Compilation is a desktop environment and an associated range of KDE Applications produced by KDE. Prior to version 4.4, released in February 2010, the Software Compilation was known as KDE, which used to stand for K Desktop Environment until November 2009...
. The first major version (4.0) of this series was released on 11 January 2008, and the latest major version (4.7) was released on 27 July 2011. Major releases (4.x) are scheduled for every six months, while minor bugfix releases (4.x.y) are released monthly.
The new series includes updates to several of the KDE Platform’s
KDE Platform
KDE Platform is a set of frameworks by KDE that serve as technological foundation for all KDE applications. Ever since KDE’s brand repositioning the Platform is released as separate product in sync with KDE’s Plasma Workspaces as part of the KDE Software Compilation 4...
core components, notably a port to Qt 4. It contains a new multimedia API, called Phonon
Phonon (KDE)
Phonon is the multimedia API provided by Qt and is the standard abstraction for handling multimedia streams within the KDE Software Compilation 4....
, a device integration framework called Solid
Solid (KDE)
KDE Platform is a set of frameworks by KDE that serve as technological foundation for all KDE applications. Ever since KDE’s brand repositioning the Platform is released as separate product in sync with KDE’s Plasma Workspaces as part of the KDE Software Compilation 4...
and a new style guide and default icon set called Oxygen
Oxygen Project
The Oxygen Project is a project created to give a visual refresh to KDE Plasma Workspaces.It consists of a set of computer icons, a window decoration for KWin, widget toolkit themes for GTK and Qt, and two themes for KDE Plasma Workspaces....
. It also includes a new, unified desktop and panel user interface called Plasma, which supports desktop widgets, replacing K Desktop Environment 3’s separate components.
One of the overall goals of KDE Platform 4 is to make it easy for KDE applications to be portable to different operating systems. This was made possible by the port to Qt 4, which facilitated support for non-X11-based platforms, including Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
and Mac OS X
Mac OS X
Mac OS X is a series of Unix-based operating systems and graphical user interfaces developed, marketed, and sold by Apple Inc. Since 2002, has been included with all new Macintosh computer systems...
. Versions 4.0 to 4.3 of the KDE Software Compilation were known simply as KDE 4 – the name change was a component of the KDE project’s re-branding to reflect KDE’s increased scope.
General
The port to the Qt 4 series was expected to enable KDE 4 to use less memory and be noticeably faster than KDE 3. The KDE libraries themselves have also been made more efficient. However, tests reveal that KDE 4.4 has the highest memory utilization on default Ubuntu installations when compared to GNOMEGNOME
GNOME is a desktop environment and graphical user interface that runs on top of a computer operating system. It is composed entirely of free and open source software...
2.29, Xfce
Xfce
Xfce is a free software desktop environment for Unix and other Unix-like platforms, such as Linux, Solaris, and BSD – though recent compatibility issues have arisen with regard to BSD Unix platforms...
4.6, and LXDE
LXDE
LXDE is a free and open source desktop environment for Unix and other POSIX compliant platforms, such as Linux or BSD. The goal of the project is to provide a desktop environment that is fast and energy efficient...
0.5. Qt 4 is available under the LGPL for Mac OS X
Mac OS X
Mac OS X is a series of Unix-based operating systems and graphical user interfaces developed, marketed, and sold by Apple Inc. Since 2002, has been included with all new Macintosh computer systems...
and Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
, which allows KDE 4 to run on those platforms. The ports to both platforms are in an early state. , KDE Software compilation 4 on Mac OS X is currently considered beta , while on Windows it is not in the final state, so applications can be unsuitable for day to day use yet. Both ports are trying to use as little divergent code as possible to make the applications function almost identically on all platforms. During Summer of Code 2007
Google Summer of Code
The Google Summer of Code is an annual program, first held from May to August 2005, in which Google awards stipends to hundreds of students who successfully complete a requested free or open-source software coding project during the summer...
an icon cache was created to decrease application start-up times for use in KDE 4. Improvements were varied – Kfind, an application which used several hundred icons, started up in almost a quarter of the time it took previously. Other applications and a full KDE session started up a little over a second faster.
Many applications in the Extragear
Extragear
The Extragear is a collection of KDE applications that are associated with the KDE project. Those applications are not part of the main KDE software compilation, which is released regularly, but they are still part of the project...
and KOffice
KOffice
Calligra Suite is a graphic art and office suite by KDE created from KOffice in 2010. It is available for desktop PCs, tablet computers, and smartphones...
modules have received numerous improvements with the new features of KDE 4 and Qt 4. But since they follow their own release schedule, they were not all available at the time of the first KDE 4 release – these include Amarok, K3b
K3b
K3b is a CD and DVD authoring application by KDE for Unix-like computer operating systems. It provides a graphical user interface to perform most CD/DVD burning tasks like creating an Audio CD from a set of audio files or copying a CD/DVD, as well as more advanced tasks such as burning eMoviX...
, digiKam
DigiKam
digiKam is an image organizer and editor using KDE Platform. It runs on most known desktop environments and window managers if the required libraries are installed. It supports all major image file formats, and can organize collections of photographs in directory-based albums, or dynamic albums by...
, KWord
KWord
Calligra Words is a free word processor, part of Calligra Suite and developed by KDE.The text-layout scheme in Words is based on frames, making it similar to FrameMaker by Adobe. These can be placed anywhere on the page, and can incorporate text, graphics and embedded objects...
, and Krita
Krita
Krita is the digital painting and illustration software included based on the KDE Platform and Calligra Suite libraries. Designed as a digital painting and illustration suite, Krita is free software and distributed under GNU General Public License...
.
Visual
The most noticeable changes for users are the new icons, theme and sounds provided by the Oxygen ProjectOxygen Project
The Oxygen Project is a project created to give a visual refresh to KDE Plasma Workspaces.It consists of a set of computer icons, a window decoration for KWin, widget toolkit themes for GTK and Qt, and two themes for KDE Plasma Workspaces....
. These represent a break from previous KDE icons and graphics, which had a cartoonish look. Instead Oxygen icons opt for a more photorealistic style. The Oxygen Project builds on the freedesktop.org
Freedesktop.org
freedesktop.org is a project to work on interoperability and shared base technology for free software desktop environments for the X Window System on Linux and other Unix-like operating systems. It was founded by Havoc Pennington from Red Hat in March 2000.The organisation focuses on the user....
Icon Naming Specification and Icon Theme Specification, allowing consistency across applications. The Oxygen team uses community help for better visuals in KDE 4, with both alternate icon sets and the winners of a wallpaper contest held by the Oxygen project being included in KDE 4. There is also a new set of human interface guidelines
Human Interface Guidelines
Human interface guidelines are software development documents which offer application developers a set of recommendations. Their aim is to improve the experience for the users by making application interfaces more intuitive, learnable, and consistent. Most guides limit themselves to defining a...
for a more standardized layout.
Plasma provides the main desktop user interface and is a rewrite of several core KDE applications, like the desktop drawing and most notably the widget engine. Plasma allows for a more customizable desktop and more versatile widgets.
KWin
KWin
KWin is a window manager for the X Window System. It is an integral part of the KDE Software Compilation, although it can be used on its own or with other desktop environments.- History :- Look and feel :...
, the KDE Window Manager, now provides its own compositing effects, similar to Compiz
Compiz
Compiz is one of the first compositing window managers for the X Window System that uses 3D graphics hardware to create fast compositing desktop effects for window management. The effects, such as a minimization effect and a cube workspace are implemented as loadable plugins...
.
Development
PhononPhonon (KDE)
Phonon is the multimedia API provided by Qt and is the standard abstraction for handling multimedia streams within the KDE Software Compilation 4....
is the name of the multimedia API in KDE 4. Phonon is a different approach to multimedia backends than in previous versions of KDE. This is because Phonon only functions as a wrapper, abstracting the various multimedia frameworks available for Unix-like operating systems into runtime switchable backends that can be accessed through a single API. This was done to provide a stable API for KDE 4 and to prevent it from depending on a single multimedia framework. Applications that use the Phonon API can be switched between multimedia frameworks seamlessly by simply changing the backend used in System Settings
System Settings
System Settings is a KDE application which is used configure the system under KDE Plasma Workspaces. It replaces K Desktop Environment 3’s KControl.- Features :* Control Center for global KDE platform settings...
. Nokia
Nokia
Nokia Corporation is a Finnish multinational communications corporation that is headquartered in Keilaniemi, Espoo, a city neighbouring Finland's capital Helsinki...
adopted Phonon for multimedia use in Qt 4.4 and are developing backends for Gstreamer, Windows and OS X in the KDE SVN repository under the LGPL.
Solid
Solid (KDE)
KDE Platform is a set of frameworks by KDE that serve as technological foundation for all KDE applications. Ever since KDE’s brand repositioning the Platform is released as separate product in sync with KDE’s Plasma Workspaces as part of the KDE Software Compilation 4...
is the hardware API in KDE 4. It functions similarly to Phonon as it doesn’t manage hardware on its own but makes existing solutions accessible through a single API. The current solution uses HAL
HAL (software)
HAL was a software project providing a hardware abstraction layer for Unix-like computer systems.HAL is now deprecated on GNU/Linux systems, with functionality being merged into udev as of 2008–2010...
, NetworkManager
NetworkManager
Network Manager is a software utility aimed at simplifying the use of computer networks on Linux-based and other Unix-like operating systems.- Overview :...
and BlueZ (the official Linux bluetooth stack), but any and all parts can be replaced without breaking the application, making applications using Solid extremely flexible and portable.
ThreadWeaver
ThreadWeaver
ThreadWeaver is a programming library developed for KDE 4 by Mirko Boehm that allows developers to easily take advantage of multi-core processors. In ThreadWeaver the workload is divided into individual jobs, then relationship between jobs ; from that ThreadWeaver will work out the most efficient...
is a programming library to help applications take advantage of multicore processors and is included with kdelibs.
Kross
Kross (KDE)
Kross is the new scripting framework for KDE SC 4, the latest version of the KDE SC. Originally Kross was designed for use in Koffice but eventually became the official scripting framework in KDE SC 4...
is the new scripting framework for KDE 4. Kross itself is not a scripting language, but makes it easier for developers to add support for other scripting languages. Once an application adds support for Kross, any language Kross supports can be used by developers. New scripting languages can be added by creating a plugin for Kross, which benefits all applications using it.
Decibel
Decibel (KDE)
Decibel is a new communication framework for KDE Software Compilation 4, the current major release of the KDE desktop environment. Decibel aims to integrate all communication protocols into the desktop. As of now users have all their contacts in different applications: AOL, MSN, E-mail, Skype, etc...
is a Telepathy-based communication framework, which was expected to be fully used by Kopete by KDE 4.2, but which is reported to be postponed indefinitely.
Strigi
Strigi
Strigi is a desktop search daemon, which is operating system-independent and desktop-independent. Strigi was initiated by Jos van den Oever. Strigi's goals are to be fast, use a small amount of RAM, and use flexible backends and plug-ins. A benchmark as of January 2007 showed that Strigi is faster...
is the default search tool for KDE 4, chosen for its speed and few dependencies. In concert with other software like Soprano
Soprano (KDE)
Soprano is a software library that provides an object-oriented C++/Qt4 framework for RDF data. Soprano was created as a sub project under the NEPOMUK project and forms a part of the semantic desktop in KDE Software Compilation 4...
, an RDF
Resource Description Framework
The Resource Description Framework is a family of World Wide Web Consortium specifications originally designed as a metadata data model...
storage framework, and the NEPOMUK
NEPOMUK (framework)
NEPOMUK is an open-source software specification that is concerned with the development of a social semantic desktop that enriches and interconnects data from different desktop applications using semantic metadata stored as RDF...
specification, Strigi will provide the beginnings of a semantic desktop
Semantic desktop
In computer science, the Semantic Desktop is a collective term for ideas related to changing a computer's user interface and data handling capabilities so that data is more easily shared between different applications or tasks and so that data that once could not be automatically processed by a...
in KDE 4. Users can tag files with additional information through Dolphin
Dolphin (software)
Dolphin is a free and open source software file manager for and part of the KDE Software Compilation. It is the default file manager in the current version, KDE Software Compilation 4, and can be optionally installed on K Desktop Environment 3...
, which Strigi can index for more accurate searches.
KDE 4 uses CMake
CMake
CMake is a cross-platform, open-source system for managing the build process of software using a compiler-independent method. It is designed to support directory hierarchies and applications that depend on multiple libraries, and for use in conjunction with native build environments such as Make,...
for its build system. Since previous versions of KDE were only on Unix systems, autotools
GNU build system
The GNU build system, also known as the Autotools, is a suite of programming tools designed to assist in making source-code packages portable to many Unix-like systems....
were used, but a new build system was needed for builds on operating systems like Windows. CMake also dramatically simplified the build process. The autotools build system had become so complicated by KDE 3 that few developers understood it, requiring hours of work for simple changes. In early 2007 CMake was shown to compile the KDE 4 version of KDElibs 40 % faster than the autotools compiled KDE 3 version.
DXS, previously known as GHNS (Get Hot New Stuff) and now adopted by freedesktop.org
Freedesktop.org
freedesktop.org is a project to work on interoperability and shared base technology for free software desktop environments for the X Window System on Linux and other Unix-like operating systems. It was founded by Havoc Pennington from Red Hat in March 2000.The organisation focuses on the user....
, is a web service that lets applications download and install data from the Internet with one click. It was used in the KDE 3 series but has been extended for use throughout KDE 4. One example was Kstars, that can use Astronomical data that is free for personal use but cannot be redistributed. DXS allows that data to be easily downloaded and installed from within the application instead of manually downloading it.
Akonadi
Akonadi
Akonadi is a storage service for personal information management data and metadata named after the oracle goddess of justice in Ghana. It is one of the “pillars” behind the KDE SC 4 project, although it is designed to be used in any desktop environment...
is a new PIM
Personal information management
Personal information management refers to the practice and the study of the activities people perform in order to acquire, organize, maintain, retrieve and use information items such as documents , web pages and email messages for everyday use to complete tasks and fulfill a person’s various...
framework for KDE 4. Akonadi is a unification of previously separate KDE PIM components. In the past each application would have its own method for storing information and handling data. Akonadi itself functions as a server that provides data and search functions to PIM applications. It is also able to update the status of contacts. So if one application changes information about a contact, all other applications are immediately informed of the change.
KDE 4.0

Dolphin
Dolphin (software)
Dolphin is a free and open source software file manager for and part of the KDE Software Compilation. It is the default file manager in the current version, KDE Software Compilation 4, and can be optionally installed on K Desktop Environment 3...
replaces Konqueror as the default file manager in KDE 4.0. This was done to address complaints of Konqueror being too complicated for a simple file manager. However Dolphin and Konqueror will share as much code as possible, and Dolphin can be embedded in Konqueror to allow Konqueror to still be used as a file manager.
Okular
Okular
Okular is the document viewer for KDE SC 4 . It is based on KPDF and it replaced KPDF, KGhostView, KFax, KFaxview and KDVI in KDE 4.Its functionality can be easily embedded in other applications....
replaces several document viewers used in KDE 3, like KPDF, KGhostView and KDVI. Okular makes use of software libraries and can be extended to view almost any kind of document. Like Konqueror and KPDF in KDE 3, Okular can be embedded in other applications.
Pre-releases
On 11 May 2007, KDE 4.0 Alpha 1 was released marking the end of the addition of large features to the KDE base libraries and shifting the focus onto integrating the new technologies into applications and the basic desktop. Alpha 1 included new frameworks to build applications with, providing improved hardware and multimedia integration through SolidSolid (KDE)
KDE Platform is a set of frameworks by KDE that serve as technological foundation for all KDE applications. Ever since KDE’s brand repositioning the Platform is released as separate product in sync with KDE’s Plasma Workspaces as part of the KDE Software Compilation 4...
and Phonon
Phonon (KDE)
Phonon is the multimedia API provided by Qt and is the standard abstraction for handling multimedia streams within the KDE Software Compilation 4....
. Dolphin
Dolphin (software)
Dolphin is a free and open source software file manager for and part of the KDE Software Compilation. It is the default file manager in the current version, KDE Software Compilation 4, and can be optionally installed on K Desktop Environment 3...
and Okular
Okular
Okular is the document viewer for KDE SC 4 . It is based on KPDF and it replaced KPDF, KGhostView, KFax, KFaxview and KDVI in KDE 4.Its functionality can be easily embedded in other applications....
were integrated and a new visual appearance was provided through Oxygen icons
Oxygen Project
The Oxygen Project is a project created to give a visual refresh to KDE Plasma Workspaces.It consists of a set of computer icons, a window decoration for KWin, widget toolkit themes for GTK and Qt, and two themes for KDE Plasma Workspaces....
.
On 4 July 2007, Alpha 2 was released. The release focused on integrating the Plasma desktop, improving functionality and stabilizing KDE.
On 2 August 2007, Beta 1 was released. Major features included a pixmap cache – speeding up icon loading, KDE PIM improvements, improved KWin
KWin
KWin is a window manager for the X Window System. It is an integral part of the KDE Software Compilation, although it can be used on its own or with other desktop environments.- History :- Look and feel :...
effects and configuration, better interaction between Konqueror and Dolphin and Metalink
Metalink
Metalink is a cross-platform and cross-application Internet standard/framework/file format for programs that download, including download managers, BitTorrent clients, Web browsers, FTP clients, and P2P programs...
support added to KGet
KGet
KGet is a free download manager for KDE. By default it is the download manager used for Konqueror, but can also be used with Mozilla Firefox. KGet is part of the KDE Network package, and was featured by Tux Magazine and Free Software Magazine.-History:...
for improved downloads.
On 6 September 2007, Beta 2 was released with improved BSD and Solaris support. The release included the addition of the Blitz graphic library – allowing for developers to use high performance graphical tricks like icon animation – and an overhaul of KRDC
KRDC
KRDC is the KDE Remote Desktop Client. KRDC was overhauled as part of the Google Summer of Code 2007 by Urs Wolfer and other developers to be included in the KDE 4.0...
(K Remote Desktop Client) for Google’s Summer of Code
Google Summer of Code
The Google Summer of Code is an annual program, first held from May to August 2005, in which Google awards stipends to hundreds of students who successfully complete a requested free or open-source software coding project during the summer...
. Plasma
Plasma (KDE)
Plasma Workspaces is the umbrella term for all graphical environments provided by KDE.Three Plasma sub-projects are currently being developed: Plasma Desktop for traditional desktop PCs and notebooks, Plasma Netbook for netbooks, and Plasma Active for Tablet PCs, Nokia N900 style smartphones and...
was also integrated with Amarok to provide Amarok’s central context view.
On 16 October 2007, Beta 3 was released. The beta 3 release was focused on stabilizing and finishing the design of libraries for the release of the KDE Development Platform. Plasma received many new features including an applet browser. The Educational software received many improvements in Marble and Parley (formerly known as KVoctrain) with bugfixes in other applications. A program called Step, an interactive physics simulator, was produced as part of the Google Summer of Code
Google Summer of Code
The Google Summer of Code is an annual program, first held from May to August 2005, in which Google awards stipends to hundreds of students who successfully complete a requested free or open-source software coding project during the summer...
.
On 30 October 2007, Beta 4 was released. A list of release blockers was compiled, listing issues that need to be resolved before KDE will start with the release candidate cycle for the desktop. The goals were to focus on stabilization and fixing the release blockers.
At the same time, the first release candidate of the KDE 4.0 Development Platform was released. The development platform contains all the base libraries to develop KDE applications, including "high-level widget libraries, a network abstraction layer and various libraries for multimedia integration, hardware integration and transparent access to resources on the network."
On 20 November 2007, Release Candidate (RC) 1 was released. This release was called a "Release Candidate" despite Plasma requiring further work and not being ready for release. On 11 December 2007, RC2 was released. The codebase was declared feature-complete. Some work was still required to fix bugs, finish off artwork and smooth out the user experience.
Stable releases
KDE 4.0 was released on 11 January 2008. There were maintenance releases every month through to June,which fix bugs and add some minor features such as resizable desktop panels.
KDE 4.0 was met with a mixed reaction. Despite being labelled as a stable release, it was intended for early adopters.
Continuing to use KDE 3.5 was suggested for users wanting a more stable, "feature complete" desktop.
The intent was for 4.0 to be a developers release. It was included in a number of distributions in order to promote the migration from KDE 3.5 among the Linux developers.
The message got lost among the release excitement, and as a result the release disappointed some end users. This resulted in a backlash over the introduction of 4.0.
Reception
The release of KDE 4.0 was met with a mixed reception. While early adopters were tolerant of the lack of finish for some of its new features, the release was widely criticized because of a lack of stability and its “beta” quality. A Computer World reporter (Steven Vaughan-Nichols) criticised KDE 4.0 and KDE 4.1 and called for a fork of KDE 3.5 by rebuilding it on top of Qt4. The same reporter later praised KDE 4.3 and welcomed the KDE 3.5 continuation project Trinity. Although Linus TorvaldsLinus Torvalds
Linus Benedict Torvalds is a Finnish software engineer and hacker, best known for having initiated the development of the open source Linux kernel. He later became the chief architect of the Linux kernel, and now acts as the project's coordinator...
switched from GNOME to KDE on December 2005, he switched back to GNOME after Fedora – as only major Linux distribution – replaced KDE 3.5 with 4.0. In an interview with ComputerWorld, Linus described KDE 4.0 as a “break everything” model and “half-baked” release, claiming that he expected it to be an upgrade of KDE 3.5, when the reality was that there were significant cases of features being regressed due to its extensive changes (Linus did point out, however, that he understood why the developers in charge of the KDE project had chosen to make such drastic changes to the desktop environment in KDE 4.0 and the reason for its pre-mature release, and that his criticism was more on the way KDE 4.0 was pushed out to the public)/ The criticism has emerged in spite of the environment being labeled as “less mature” or “cutting edge” in distributions such as openSUSE
OpenSUSE
openSUSE is a general purpose operating system built on top of the Linux kernel, developed by the community-supported openSUSE Project and sponsored by SUSE...
and Kubuntu
Kubuntu
Kubuntu is an official derivative of the Ubuntu operating system using the KDE Plasma Desktop instead of the Unity graphical environment. It is part of the Ubuntu project and uses the same underlying system. It is possible to install both the KDE Plasma Desktop as well as the Unity desktop on...
. Despite the criticism, reviewers such as ArsTechnica’s Ryan Paul noted that the visual style “is very attractive and easy on the eyes” and “exhibits a relatively high level of polish” and that “the underlying technologies still have a lot of very serious potential”.
KDE 4.1

GStreamer
GStreamer is a pipeline-based multimedia framework written in the C programming language with the type system based on GObject.GStreamer allows a programmer to create a variety of media-handling components, including simple audio playback, audio and video playback, recording, streaming and editing...
, QuickTime
QuickTime
QuickTime is an extensible proprietary multimedia framework developed by Apple Inc., capable of handling various formats of digital video, picture, sound, panoramic images, and interactivity. The classic version of QuickTime is available for Windows XP and later, as well as Mac OS X Leopard and...
7, and DirectShow
DirectShow
DirectShow , codename Quartz, is a multimedia framework and API produced by Microsoft for software developers to perform various operations with media files or streams. It is the replacement for Microsoft's earlier Video for Windows technology...
9 Phonon
Phonon (KDE)
Phonon is the multimedia API provided by Qt and is the standard abstraction for handling multimedia streams within the KDE Software Compilation 4....
backends. Plasma improvements include support for Qt 4 widgets and WebKit
WebKit
WebKit is a layout engine designed to allow web browsers to render web pages. WebKit powers Google Chrome and Apple Safari and by October 2011 held over 33% of the browser market share between them. It is also used as the basis for the experimental browser included with the Amazon Kindle ebook...
integration – allowing many Apple Dashboard widgets to be displayed. There will also be ports of some applications to Windows and Mac OS X
Mac OS X
Mac OS X is a series of Unix-based operating systems and graphical user interfaces developed, marketed, and sold by Apple Inc. Since 2002, has been included with all new Macintosh computer systems...
.
New applications include:
- Dragon Player multimedia player (formerly Codeine)
- KDE-PIM module, with some AkonadiAkonadiAkonadi is a storage service for personal information management data and metadata named after the oracle goddess of justice in Ghana. It is one of the “pillars” behind the KDE SC 4 project, although it is designed to be used in any desktop environment...
functionality - Skanlite scanner application
- StepStep (software)Step is an open source two-dimensional physics simulation engine that is included in the KDE SC as a part of KDE Education Project. The software include the StepCore, a physical simulation library.- History :...
physics simulator - Games – Kdiamond (a BejeweledBejeweledBejeweled is a puzzle game by PopCap Games, first developed for browsers in 2001. Three follow-ups to this game have been released. More than 75 million copies of Bejeweled have been sold, and the game has been downloaded more than 500 million times....
clone), Kollision, Kubrick, KsirK, KBreakout
KDE 4.2

KDE Workspace improvements
The 4.2 release includes thousands of bugs fixes and has implemented many features that were present in KDE 3.5 but had been missing in KDE 4.0 and 4.1.These include grouping and multiple row layout in the task bar, icon hiding in the system tray, panel autohiding, window previews and tooltips are back in the panel and task bar, notifications and job tracking by Plasma, and the ability to have icons on the desktop again by using a Folder View as the desktop background where icons now remain where they are placed.
New Plasma applets include applets for leaving messages on a locked screen, previewing files, switching desktop Activity, monitoring news feeds, and utilities like the pastebin applet, the calendar, timer, special character selector, a QuickLaunch widget, and a system monitor, among many others. The Plasma workspace can now load Google Gadgets. Plasma widgets can be written in Ruby and Python. Support for applets written in JavaScript and Mac OS X dashboard widgets has been further improved. Theming improvements in the Task Bar, Application Launcher, System Tray and most other Plasma components streamline the look and feel and increase consistency. A new System Settings module, Desktop Theme Details, gives the user control over each element of various Plasma themes. Wallpapers are now provided plugins, so developers can easily write custom wallpaper systems in KDE 4.2. Available wallpaper plugins in KDE 4.2 will be slideshows, Mandelbrot fractals, and regular static images.
New desktop effects have been added such as the Magic Lamp, Minimize effect and the Cube and Sphere desktop switchers. Others, such as the desktop grid, have been improved. The user interface for choosing effects has been reworked for easy selection of the most commonly used effects. Compositing desktop effects have been enabled by default where hardware and drivers support them. Automatic checks confirm that compositing works before enabling it on the workspace.
KRunner – the "Run command…" dialog – has extended functionality through several new plugins, including spellchecking, Konqueror browser history, power management control through PowerDevil, KDE Places, Recent Documents, and the ability to start specific sessions of the Kate editor, Konqueror and Konsole. The converter plugin now also supports quickly converting between units of speed, mass and distances.
Multi-screen support has been improved through the Kephal library, fixing many bugs when running KDE on more than one monitor.
New and improved applications
New applications include PowerDevil, a power management system for controlling various aspects of mobile devices. A new printing configuration system brings back a number of features users have been missing in KDE 4.0 and 4.1. The components "printer-applet" and "system-config-printer-kde" are shipped with the kdeadmin and kdeutils module. Killbots is a new game shipped with the kdegames module.All applications have seen bugfixes, feature additions and user interface improvements. Dolphin now supports previews of files in toolbars and has gained a slider to zoom in and out on file item views. It can now also show the full path in the breadcrumb bar. Konqueror offers increased loading speed by prefetching domain name data in KHTML. A find-as-you-type bar improves navigation in webpages. KMail has a new message header list, and reworked attachment view. The KWrite and Kate text editors can now operate in Vi input mode, accommodating those used to the traditional UNIX editor. Ark, the archiving tool has gained support for password-protected archives and is accessible via a context menu from the file managers now. KRDC, the remote desktop client improves support for Microsoft’s Active Directory through LDAP. Kontact has gained a new planner summary and support for drag and drop in the free/busy view. KSnapshot now uses the window title when saving screenshots, making it easier to index them using search engines.
Reception
The KDE 4.2 release “marks the end of the testing phase by being the first release ready for everyone – instead of just developers and enthusiasts” according to Thom Holwerda, a member of OSNews.KDE 4.3

PolicyKit
PolicyKit is an operating system component for controlling system-wide privileges in Unix-like operating systems. It provides an organized way for non-privileged processes to communicate with privileged ones. In contrast to systems such as sudo, it does not grant root permission to an entire...
, NetworkManager
NetworkManager
Network Manager is a software utility aimed at simplifying the use of computer networks on Linux-based and other Unix-like operating systems.- Overview :...
& Geolocation
Geolocation
Geolocation is the identification of the real-world geographic location of an object, such as a radar, mobile phone or an Internet-connected computer terminal...
services, was another focus of this release. KRunner’s interface has been overhauled. A much more flexible system tray has been developed. Many new Plasmoids have been added, including the openDesktop.org
OpenDesktop.org
The website openDesktop.org is a social networking site with main focus on the open source community. It centers on sharing of user generated contents such as applications and artwork with social components. openDesktop.org is one of the biggest online communities, social networks and portals for...
Plasmoid – an initial take on the Social Desktop
Social Desktop
The Social Desktop idea describes how online communities and web collaborations can be integrated into desktop environments such as KDE and GNOME and how they could directly be accessed by desktop applications such as a Plasmoids....
. Plasma also receives more keyboard shortcuts.
KDE SC 4.4
KDE SC 4.4 was released on 9 February 2010 and is based on version 4.6 of the Qt 4Qt (toolkit)
Qt is a cross-platform application framework that is widely used for developing application software with a graphical user interface , and also used for developing non-GUI programs such as command-line tools and consoles for servers...
toolkit. As such, KDE SC 4.4 carries Qt’s performance improvements as well as Qt 4.6's new features, such as the new animation framework Kinetic.
KAddressBook Is replaced by a completely new application with the same name – previously tentatively called KContactManager. Key features of the new KAddressBook are Akonadi
Akonadi
Akonadi is a storage service for personal information management data and metadata named after the oracle goddess of justice in Ghana. It is one of the “pillars” behind the KDE SC 4 project, although it is designed to be used in any desktop environment...
integration and a streamlined user interface.
Another major new feature is an additional new Plasma interface, targeted towards netbook
Netbook
Netbooks are a category of small, lightweight, legacy-free, and inexpensive laptop computers.At their inception in late 2007 as smaller notebooks optimized for low weight and low cost — netbooks omitted certain features , featured smaller screens and keyboards, and offered reduced computing...
s.
Kopete
Kopete
Kopete is a multi-protocol, free software instant messaging client. Although it can run in numerous environments, it was designed for and integrates with the KDE desktop environment...
is released as version 1.0.
KAuth, a cross-platform authentication API, made its début in KDE SC 4.4. Initially only PolicyKit
PolicyKit
PolicyKit is an operating system component for controlling system-wide privileges in Unix-like operating systems. It provides an organized way for non-privileged processes to communicate with privileged ones. In contrast to systems such as sudo, it does not grant root permission to an entire...
is supported as back-end.
KDE SC 4.5
KDE SC 4.5 was released on 10 August 2010. New features include the integration of the WebKitWebKit
WebKit is a layout engine designed to allow web browsers to render web pages. WebKit powers Google Chrome and Apple Safari and by October 2011 held over 33% of the browser market share between them. It is also used as the basis for the experimental browser included with the Amazon Kindle ebook...
library, an open-source web browser engine, which is used in major browsers such as Apple Safari and Google Chrome
Google Chrome
Google Chrome is a web browser developed by Google that uses the WebKit layout engine. It was first released as a beta version for Microsoft Windows on September 2, 2008, and the public stable release was on December 11, 2008. The name is derived from the graphical user interface frame, or...
. KDE's own KHTML
KHTML
KHTML is the HTML layout engine developed by the KDE project. It is the engine used by the Konqueror web browser. A forked version of KHTML called WebKit is used by several web browsers, among them Safari and Google Chrome...
engine will continue to be developed.
KPackage
KPackage
KPackage was KDE's package manager frontend.It supported BSD, Debian, Gentoo, RPM and Slackware packages. It provided a GUI for the management and upgrade of existing packages and the installation and acquirement of new packages...
has been deprecated. KPackageKit
PackageKit
PackageKit is an open source and free suite of software applications designed to provide a consistent and high-level front end for a number of different package management systems...
was suggested to replace it but it didn't make it to replace it.
KDE SC 4.6
KDE SC 4.6 was released on 26 January 2011 and has better OpenGL compositing along with the usual myriad of fixes and features.KDE SC 4.7
KDE SC 4.7 was released on July 28 2011. This version updated KWin in order to be compatible with OpenGL ES 2.0, which will enhance its portability to mobile and tablet platforms. Other optimizations, such as the use of Qt Quick, were made in order to enhance this portability. This version also brought updates and enhancements to Plasma Desktop such as better network management and updates to certain widgets (like the Kickoff menu) as well as activities.Aside from the desktop environment, version 4.7 updates many applications within the Software Compilation. Dolphin file manager has been updated to include a cleaner user interface. Marble, the virtual globe software, now supports voice navigation, a map creation wizard, as well as many new plugins. Gwenview image viewer now allows users to compare two or more photos side by side. The Kontact database has also been ported to Akonadi which allows the database to be easily accessible from other applications. Furthermore, the KMail database has also been ported to Akonadi. DigiKam has been updated to support face detection, image versioning, and image tagging. Other applications such as Kate, Kalzium, KAlgebra, KStars, and KDevelop have also been updated in this release. Moreover, version 4.7 fixed over 12,000 bugs.
KDE Plasma Workspaces and Applications 4.8
Despite the early development stage, some new features are already in development.Release 4.8 – scheduled for late January – won’t feature an upgrade to the KDE Platform
KDE Platform
KDE Platform is a set of frameworks by KDE that serve as technological foundation for all KDE applications. Ever since KDE’s brand repositioning the Platform is released as separate product in sync with KDE’s Plasma Workspaces as part of the KDE Software Compilation 4...
libraries (kdelibs,…). Instead it will be based on Platform 4.7 in order to concentrate development efforts on KDE Frameworks 5.0 which will be based on Qt 5.
Plasma Workspaces
KWin’sKWin
KWin is a window manager for the X Window System. It is an integral part of the KDE Software Compilation, although it can be used on its own or with other desktop environments.- History :- Look and feel :...
rendering performance will be increased by optimizing effect rendering. Window resizing will also be improved.
Other Kwin features are: QML based Window switcher (Tabbox), AnimationEffect class and initial Wayland support.
It is planned that by default the system tray entry for most applications will be merged with the task bar entry.
Applications
A new major version of Dolphin is expected to ship with KDE Applications 4.8. It will have improved performance, better file name display, animated transitions, and many other new and improved features.Cantor
Cantor (software)
Cantor is a free software mathematics application for scientific statistics and analysis. It is part of the KDE Software Compilation 4, and was introduced with the 4.4 release as part of the KDE Education Project's kdeedu package.- Features :...
will ship with an additional back-end based on Qalculate.
Dragon Player 3 may ship with Applications 4.8, although a release with 4.9 is considered more likely.
Release schedule
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 4.0 | |
| 2 April 2007 | Subsystem Freeze From this date forward, no new KDE subsystem or major changes can be committed to kdelibs. |
| 1 May 2007 | kdelibs soft API Freeze The kdelibs API is "soft-frozen", meaning that changes can be made with the consent of the core developers. |
| 11 May 2007 | Alpha 1 |
| 1 June 2007 | trunk/KDE is module frozen Trunk is frozen for new or resurrected applications. |
| 4 July 2007 | Alpha 2 Initially due to be called Beta 1, it was decided to retain the alpha designation because this release wasn’t judged to be beta quality. |
| 24 July 2007 | Core Library API Freeze |
| 2 August 2007 | Beta 1 |
| 6 September 2007 | Beta 2 Trunk is frozen for feature commits. |
| 18 October 2007 | Beta 3 |
| 24 October 2007 | KDE 4 Release Freeze Source and binary compatibility until KDE 5, hard freeze Platform & soft freeze Desktop. |
| 30 October 2007 | Beta 4 |
| 20 November 2007 | Release candidate 1 |
| KDE Development Platform released | |
| 11 December 2007 | Release candidate 2 Only regressions or serious bugs can be fixed. |
| 11 January 2008 | KDE 4.0 released |
| 4 June 2008 | 4.0.5 Maintenance release. Predated by 4.0.1 to 4.0.4. |
| 4.1 | |
| 29 April 2008 | Alpha 1 |
| 19 May 2008 | Feature Freeze |
| 27 May 2008 | Beta 1 |
| 24 June 2008 | Beta 2 |
| 15 July 2008 | Release candidate 1 |
| 29 July 2008 | KDE 4.1 released |
| 13 January 2009 | 4.1.4 Maintenance release. Predated by 4.1.1 to 4.1.3. |
| 4.2 | |
| 17 November 2008 | Feature Freeze |
| 26 November 2008 | Beta 1 |
| 18 December 2008 | Beta 2 |
| 13 January 2009 | Release candidate 1 |
| 27 January 2009 | KDE 4.2 released |
| 2 June 2009 | 4.2.4 Maintenance release. Predated by 4.2.1 to 4.2.3. |
| 4.3 | |
| 4 May 2009 | Feature Freeze |
| 12 May 2009 | Beta 1 |
| 9 June 2009 | Beta 2 |
| 30 June 2009 | Release candidate 1 |
| 9 July 2009 | Release candidate 2 |
| 22 July 2009 | Release candidate 3 |
| 4 August 2009 | KDE 4.3 released |
| 26 January 2010 | 4.3.5 Maintenance release. Predated by 4.3.1 to 4.3.4. |
| 4.4 | |
| 25 November 2009 | Feature Freeze |
| 4 December 2009 | Beta 1 |
| 21 December 2009 | Beta 2 |
| 8 January 2010 | Release candidate 1 |
| 25 January 2010 | Release candidate 2 |
| 1 February 2010 | Release candidate 3 |
| 9 February 2010 | KDE SC 4.4 released |
| 30 June 2010 | 4.4.5 Maintenance release. Predated by 4.4.1 to 4.4.4. |
| 4.5 | |
| 11 May 2010 | Feature Freeze |
| 26 May 2010 | Beta 1 |
| 9 June 2010 | Beta 2 |
| 27 June 2010 | Release candidate 1 |
| 8 July 2010 | Release candidate 2 |
| 26 July 2010 | Release candidate 3 |
| 10 August 2010 | KDE SC 4.5 released |
| 7 January 2011 | 4.5.5 Maintenance release. Predated by 4.5.1 to 4.5.4. |
| 4.6 | |
| 11 November 2010 | Feature Freeze |
| 24 November 2010 | Beta 1 |
| 8 December 2010 | Beta 2 |
| 23 December 2010 | Release candidate 1 |
| 5 January 2011 | Release candidate 2 |
| 26 January 2011 | KDE SC 4.6 released |
| 5 July 2011 | 4.6.5 Maintenance release. Predated by 4.6.1 to 4.6.4. |
| 4.7 | |
| 12 May 2011 | Feature Freeze |
| 25 May 2011 | Beta 1 |
| 8 June 2011 | Beta 2 |
| 22 June 2011 | Release candidate 1 |
| 6 July 2011 | Release candidate 2 |
| 27 July 2011 | KDE SC 4.7 released |
| 29 September 2011 | 4.7.1 Maintenance Release |
| 5 October 2011 | 4.7.2 Maintenance Release |
| 2 November 2011 | 4.7.3 Maintenance Release |
| Feature Freeze - From herein, no new features are allowed. All future dates are provisional. |
|
External links
- The KDE website
- LifeStream, aggregate of tweets, etc.
- KDE Documentation
- KDE Localization
- KDE Bug Tracking System
- KDE-Apps, KDE and Qt software repository
- KDE-Look
- KDE on Windows Initiative
- KDE on Mac OS X

