
June 2012 lunar eclipse
Encyclopedia
| Partial Lunar Eclipse June 4, 2012 |
|
|---|---|
 The moon will pass partially into the northern umbral shadow of the earth. |
|
| Series (and member) Saros cycle The saros is a period of 223 synodic months , that can be used to predict eclipses of the Sun and Moon. One saros after an eclipse, the Sun, Earth, and Moon return to approximately the same relative geometry, and a nearly identical eclipse will occur, in what is referred to as an eclipse cycle... |
140 (25 of 80) |
| Duration (hr:mn:sc) | |
| Partial | 02:06:35 |
| Penumbral | 4:30:02 |
| Contacts | |
| P1 | 8:48:11 UTC |
| U1 | 09:59:53 UTC |
| Greatest | 11:03:12 UTC |
| U4 | 12:06:28 UTC |
| P4 | 13:18:13 UTC |
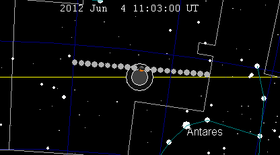 The moon's hourly motion across the Earth's shadow in the constellation of Ophiuchus (north of Scorpius) |
|
A partial lunar eclipse
Lunar eclipse
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes behind the Earth so that the Earth blocks the Sun's rays from striking the Moon. This can occur only when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are aligned exactly, or very closely so, with the Earth in the middle. Hence, a lunar eclipse can only occur the night of a...
will take place on June 4, 2012. The Moon will be about one third covered by the Earth's umbral shadow at maximum eclipse. The portion of the moon within the penumbral shadow will be significantly dimmed. The portion of the moon inside the umbral shadow will only be illuminated by sunlight refracted through the Earth's atmosphere, thus much dimmer, and having a reddish hue.
Visibility
It will be completely visible over Australia, rising over eastern Asia, and setting over western North America. This simulation shows the view of the earth from the moon from the center of the earth at greatest eclipse. The sun is seen here as a partial solar eclipse over the Earth's north pole. |

