
Jog (dislocations)
Encyclopedia
Jog is a term related to the concept of dislocation
. It is used to describe the turns of a dislocation
line inside a crystal structure
. A dislocation
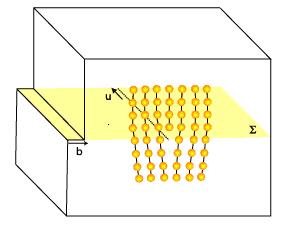
line is rarely uniformly straight as in the figure, often containing many curves and/or steps to facilitate movement through the crystal in incremental amounts, rather than shifting the entire line at once. One of these step types is a jog, the other is a kink. However, both are typically referred to as jogs, which can be a source of confusion.
Segments of dislocation
line that have a component of their sense vector normal to the glide plane are termed jogs. See image for the definitions of the sense vector and the glide plane.
Segments of dislocation line that do not leave the original glide plan are termed kinks.
Jogs are often very immobile compared to kinks, and require diffusion of crystallographic defects like vacancies or interstitial atoms to climb. They are not capable of glide (movement in the glide plane
) because the direction of motion is in the plane normal direction, not on the plane itself as with kinks.
Dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation is a crystallographic defect, or irregularity, within a crystal structure. The presence of dislocations strongly influences many of the properties of materials...
. It is used to describe the turns of a dislocation
Dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation is a crystallographic defect, or irregularity, within a crystal structure. The presence of dislocations strongly influences many of the properties of materials...
line inside a crystal structure
Crystal structure
In mineralogy and crystallography, crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. A crystal structure is composed of a pattern, a set of atoms arranged in a particular way, and a lattice exhibiting long-range order and symmetry...
. A dislocation
Dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation is a crystallographic defect, or irregularity, within a crystal structure. The presence of dislocations strongly influences many of the properties of materials...
line is rarely uniformly straight as in the figure, often containing many curves and/or steps to facilitate movement through the crystal in incremental amounts, rather than shifting the entire line at once. One of these step types is a jog, the other is a kink. However, both are typically referred to as jogs, which can be a source of confusion.
Segments of dislocation
Dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation is a crystallographic defect, or irregularity, within a crystal structure. The presence of dislocations strongly influences many of the properties of materials...
line that have a component of their sense vector normal to the glide plane are termed jogs. See image for the definitions of the sense vector and the glide plane.
Segments of dislocation line that do not leave the original glide plan are termed kinks.
Jogs are often very immobile compared to kinks, and require diffusion of crystallographic defects like vacancies or interstitial atoms to climb. They are not capable of glide (movement in the glide plane
Glide plane
In crystallography, a glide plane is symmetry operation describing how a reflection in a plane, followed by a translation parallel with that plane, may leave the crystal unchanged....
) because the direction of motion is in the plane normal direction, not on the plane itself as with kinks.


