
Jewel bearing
Encyclopedia

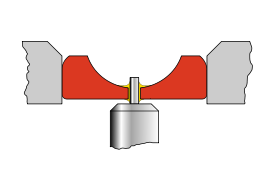
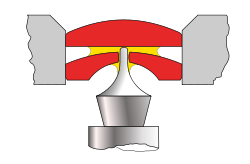
Plain bearing
A plain bearing, also known as a plane bearing or a friction bearing is the simplest type of bearing, comprising just a bearing surface and no rolling elements. Therefore the journal slides over the bearing surface. The simplest example of a plain bearing is a shaft rotating in a hole...
in which a metal spindle
Spindle (tool)
In machine tools, a spindle is a rotating axis of the machine, which often has a shaft at its heart. The shaft itself is called a spindle, but also, in shop-floor practice, the word often is used metonymically to refer to the entire rotary unit, including not only the shaft itself, but its bearings...
turns in a jewel
Gemstone
A gemstone or gem is a piece of mineral, which, in cut and polished form, is used to make jewelry or other adornments...
-lined pivot hole. The hole is typically shaped like a torus
Torus
In geometry, a torus is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three dimensional space about an axis coplanar with the circle...
and is slightly larger than the shaft diameter. The jewel material is usually synthetic sapphire
Sapphire
Sapphire is a gemstone variety of the mineral corundum, an aluminium oxide , when it is a color other than red or dark pink; in which case the gem would instead be called a ruby, considered to be a different gemstone. Trace amounts of other elements such as iron, titanium, or chromium can give...
. Jewel bearings are used in precision instruments, but their largest use is in mechanical watch
Mechanical watch
A mechanical watch is a watch that uses a mechanical mechanism to measure the passage of time, as opposed to modern quartz watches which function electronically. It is driven by a spring which must be wound periodically...
es.
History
Jewel bearings were invented in 1704 for use in watches by Nicolas Fatio de DuillierNicolas Fatio de Duillier
Nicolas Fatio de Duillier was a Swiss mathematician known for his work on the zodiacal light problem, for his very close relationship with Isaac Newton, for his role in the Newton v. Leibniz calculus controversy, and for originating the "push" or "shadow" theory of gravitation...
, Peter Debaufre, and Jacob Debaufre, who received an English patent for the idea. Originally natural jewels were used, such as diamond
Diamond
In mineralogy, diamond is an allotrope of carbon, where the carbon atoms are arranged in a variation of the face-centered cubic crystal structure called a diamond lattice. Diamond is less stable than graphite, but the conversion rate from diamond to graphite is negligible at ambient conditions...
, sapphire
Sapphire
Sapphire is a gemstone variety of the mineral corundum, an aluminium oxide , when it is a color other than red or dark pink; in which case the gem would instead be called a ruby, considered to be a different gemstone. Trace amounts of other elements such as iron, titanium, or chromium can give...
, ruby
Ruby
A ruby is a pink to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum . The red color is caused mainly by the presence of the element chromium. Its name comes from ruber, Latin for red. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires...
, and garnet
Garnet
The garnet group includes a group of minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives. The name "garnet" may come from either the Middle English word gernet meaning 'dark red', or the Latin granatus , possibly a reference to the Punica granatum , a plant with red seeds...
. In 1902, a process to make synthetic sapphire and ruby (crystalline aluminium oxide
Aluminium oxide
Aluminium oxide is an amphoteric oxide with the chemical formula 23. It is commonly referred to as alumina, or corundum in its crystalline form, as well as many other names, reflecting its widespread occurrence in nature and industry...
, also known as corundum
Corundum
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide with traces of iron, titanium and chromium. It is a rock-forming mineral. It is one of the naturally clear transparent materials, but can have different colors when impurities are present. Transparent specimens are used as gems, called ruby if red...
) was invented by Auguste Verneuil, making jewelled bearings much less expensive. Today most jewelled bearings are synthetic ruby or sapphire.
Historically, jewel pivots were made by grinding using diamond abrasive. Modern jewel pivots are often made using high-powered lasers, chemical etching, and ultrasonic milling
Milling machine
A milling machine is a machine tool used to machine solid materials. Milling machines are often classed in two basic forms, horizontal and vertical, which refers to the orientation of the main spindle. Both types range in size from small, bench-mounted devices to room-sized machines...
.
Characteristics
The advantages of jewel bearings include high accuracy, very small size and weight, low and predictable friction, including good temperature stability, and the ability to operate without lubrication and in corrosive environments. They are known for their low static friction and highly consistent dynamic friction. The static coefficient of frictionStiction
Stiction is the static friction that needs to be overcome to enable relative motion of stationary objects in contact. The term is a portmanteau of the term "static friction", perhaps also influenced by the verb "stick"....
of brass-on-steel is 0.35, while that of sapphire-on-steel is 0.10–0.15. Sapphire surfaces are very hard and durable, with Mohs hardness of 9 and Knoop hardness of 2000, and can maintain smoothness over decades of use, thus reducing friction variability. Disadvantages include brittleness and fragility, limited availability/applicability in medium and large bearing sizes and capacities, and friction variations if the load is not axial.
Uses
The largest use for jewel bearings is in mechanical watchMechanical watch
A mechanical watch is a watch that uses a mechanical mechanism to measure the passage of time, as opposed to modern quartz watches which function electronically. It is driven by a spring which must be wound periodically...
es, where their low and predictable friction improves watch accuracy. A typical mark of watch quality was a note such as 17 jewels. More jewel bearings often meant better precision. Some makers added non-functional or unnecessary jewels to give the impression of accuracy. Some watches had as many as 100 jewels, most of them of no use. A typical fully jeweled time-only watch has 17 jewels: two cap jewels, two pivot jewels, an impulse jewel for the balance wheel
Balance wheel
The balance wheel is the timekeeping device used in mechanical watches and some clocks, analogous to the pendulum in a pendulum clock. It is a weighted wheel that rotates back and forth, being returned toward its center position by a spiral spring, the balance spring or hairspring...
, two pivot jewels, two pallet jewels for the pallet fork
Pallet fork
The pallet fork or pallet lever is an integral component of the lever escapement of a typical mechanical watch. Its purpose is to release the escape wheel one tooth at a time, at each swing of the balance wheel, and also give the balance wheel small pushes to keep it going.The lever is shaped like...
, and two pivot jewels each for the escape, fourth, third, and center wheels. Modern electronic watches achieve accuracy entirely separate from the friction of the mechanism, but early quartz watches used jewels to increase battery
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
life, and high-grade quartz
Quartz
Quartz is the second-most-abundant mineral in the Earth's continental crust, after feldspar. It is made up of a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall formula SiO2. There are many different varieties of quartz,...
watches use jewels to reduce friction
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and/or material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:...
and wear.
Today, jewel bearings are also used widely in sensitive measuring equipment. They are typically used for very small applications, such as high-precision instruments; galvanometer
Galvanometer
A galvanometer is a type of ammeter: an instrument for detecting and measuring electric current. It is an analog electromechanical transducer that produces a rotary deflection of some type of pointer in response to electric current flowing through its coil in a magnetic field. .Galvanometers were...
s, compass
Compass
A compass is a navigational instrument that shows directions in a frame of reference that is stationary relative to the surface of the earth. The frame of reference defines the four cardinal directions – north, south, east, and west. Intermediate directions are also defined...
es, gimbal
Gimbal
A gimbal is a pivoted support that allows the rotation of an object about a single axis. A set of two gimbals, one mounted on the other with pivot axes orthogonal, may be used to allow an object mounted on the innermost gimbal to remain immobile regardless of the motion of its support...
s, and turbine flow meters. Bearing bores are typically less than 1 mm and typically support loads of under the weight of 1 gram
Gram
The gram is a metric system unit of mass....
, although they are made as large as 10 mm and support loads up to about the weight of 500 g.
External links
- Paul Baillio, "Jewel Bearings Solve Light Load Problems" (PDFPortable Document FormatPortable Document Format is an open standard for document exchange. This file format, created by Adobe Systems in 1993, is used for representing documents in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems....
) - A. C. Lawson, "Design Factors for Jewel Bearing Systems" (PDF)
- R. H. Warring, "Calculating Frictional Losses in Jewel Bearing Movements" (PDF)
- American Watchmakers-Clockmakers Institute
- TimeZone.com discussion of watch jeweling

