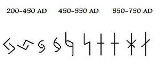
Jera
Encyclopedia
*Jēran or *Jēraz "harvest
, (good) year" is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic
name of the j-rune of the Elder Futhark
.
(oros) "year" (and (ora) "season", whence hour), Slavonic jarŭ "spring" and with the -or- in Latin hornus "of this year" (from *ho-jōrinus), all from a PIE
stem .
("C
(ᚲ) with stroke") while others consider it a Germanic innovation. The letter in any case appears from the very earliest runic inscriptions, figuring on the Vimose comb
inscription, harja.
The evolution of the rune was the most thorough transformation of all runes, and it was to have numerous versions.
is continued as Gēr and Ior, the latter a bind rune
of Gyfu
and Is
(compare also Ear
). Gēr is consistently written ᛡ eprigraphically and on artifacts, while the ᛄ form for [j] appears only rarely in later manuscripts (as does a separate symbol for Ior).
 ). As the form of the rune had changed considerably, an older 7th century form of the rune (
). As the form of the rune had changed considerably, an older 7th century form of the rune ( ) was assumed by the s-rune
) was assumed by the s-rune
. When the n-rune
had stabilized in its form during the 6th and 7th centuries, its vertical stroke slanted towards the right (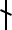 ), which made it possible to simplify the jēra-rune by having only one vertical stroke that slanted towards the left, giving the ᛅ ár-rune of the Younger Futhark. Since a simpler form of the rune was available for the /a/ phoneme, the older cross form of the rune came to be used for the /h/ phoneme.
), which made it possible to simplify the jēra-rune by having only one vertical stroke that slanted towards the left, giving the ᛅ ár-rune of the Younger Futhark. Since a simpler form of the rune was available for the /a/ phoneme, the older cross form of the rune came to be used for the /h/ phoneme.
is 𐌾 j, named jer, which is also based on the shape of the Elder Futhark rune. This is an exception, shared with urus
, due to the fact that neither the Latin
nor the Greek
alphabets at the time of the introduction of the Gothic one had graphemes corresponding to the distinction of j
and w
from i and u.
Harvest
Harvest is the process of gathering mature crops from the fields. Reaping is the cutting of grain or pulse for harvest, typically using a scythe, sickle, or reaper...
, (good) year" is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic language
Proto-Germanic , or Common Germanic, as it is sometimes known, is the unattested, reconstructed proto-language of all the Germanic languages, such as modern English, Frisian, Dutch, Afrikaans, German, Luxembourgish, Danish, Norwegian, Icelandic, Faroese, and Swedish.The Proto-Germanic language is...
name of the j-rune of the Elder Futhark
Elder Futhark
The Elder Futhark is the oldest form of the runic alphabet, used by Germanic tribes for Northwest Germanic and Migration period Germanic dialects of the 2nd to 8th centuries for inscriptions on artifacts such as jewellery, amulets, tools, weapons and runestones...
.
Etymology
Proto-Germanic *jē2ran is cognate with Avestan yāre "year", GreekAncient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
(oros) "year" (and (ora) "season", whence hour), Slavonic jarŭ "spring" and with the -or- in Latin hornus "of this year" (from *ho-jōrinus), all from a PIE
Pie
A pie is a baked dish which is usually made of a pastry dough casing that covers or completely contains a filling of various sweet or savoury ingredients....
stem .
Elder Futhark
The derivation of the rune is uncertain; some scholars see it as a modification of Latin GG
G is the seventh letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter 'G' was introduced in the Old Latin period as a variant of ⟨c⟩ to distinguish voiced, from voiceless, . The recorded originator of ⟨g⟩ is freedman Spurius Carvilius Ruga, the first Roman to open a fee-paying school,...
("C
C
Ĉ or ĉ is a consonant in Esperanto orthography, representing the sound .Esperanto orthography uses a diacritic for all four of its postalveolar consonants, as do the Latin-based Slavic alphabets...
(ᚲ) with stroke") while others consider it a Germanic innovation. The letter in any case appears from the very earliest runic inscriptions, figuring on the Vimose comb
Vimose inscriptions
Finds from Vimose, Funen, Denmark, include some of the very oldest datable Elder Futhark runic inscriptions in late Proto-Germanic or early Proto-Norse from the 2nd to 3rd centuries AD....
inscription, harja.
The evolution of the rune was the most thorough transformation of all runes, and it was to have numerous versions.
Anglo-Saxon runes
The rune in the Anglo-Saxon futhorcAnglo-Saxon Futhorc
Futhorc , a runic alphabet used by the Anglo-Saxons, was descended from the Elder Futhark of 24 runes and contained between 26 and 33 characters. It was used probably from the fifth century onward, for recording Old English and Old Frisian....
is continued as Gēr and Ior, the latter a bind rune
Bind rune
A bind rune is a ligature of two or more runes. They are extremely rare in Viking Age inscriptions, but are common in pre-Viking Age and in post-Viking Age inscriptions....
of Gyfu
Gyfu
Gyfu is the name for the g-rune in the Anglo-Saxon rune poem, meaning "gift" or "generosity":The corresponding letter of the Gothic alphabet is g, called giba. The same rune also appears in the Elder Futhark, with a suggested Proto-Germanic name *gebô "gift". J. H...
and Is
Isaz
*Isaz is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the i-rune , meaning "ice". In the Younger Futhark it is called Iss in Icelandic and isa in Old Norse. As rune of the Anglo-Saxon futhorc, it is called is....
(compare also Ear
Ear (rune)
The Ear rune of the Anglo-Saxon futhorc is a late addition to the alphabet. It is, however, still attested from epigraphical evidence, notably the Thames scramasax, and its introduction thus cannot postdate the 9th century...
). Gēr is consistently written ᛡ eprigraphically and on artifacts, while the ᛄ form for [j] appears only rarely in later manuscripts (as does a separate symbol for Ior).
From Elder to Younger Futhark
During the 7th and 8th centuries, the initial j in *jara was lost in Proto-Norse, which also changed the sound value of the rune from /j/ to an /a/ phoneme. The rune was then written as a vertical staff with a horizontal stroke in the centre, and scholars transliterate this form of the rune as A, with majuscule, to distinguish it from the ansuz rune, a. During the last phase of the Elder Futhark, the jēra-rune came to be written as a vertical staff with two slanting strokes in the form of an X in its centre ( ). As the form of the rune had changed considerably, an older 7th century form of the rune (
). As the form of the rune had changed considerably, an older 7th century form of the rune ( ) was assumed by the s-rune
) was assumed by the s-runeSowilo rune
*Sowilō or *sæwelō is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the s-rune, meaning "sun". The name is attested for the same rune in all three rune poems...
. When the n-rune
Naudiz
Abdul Rahman Pazhwak was an Afghan poet and diplomat. He was educated in Afghanistan and started out his career as a journalist, but eventually joined the foreign ministry. During the 1950s he became ambassador to the United Nations, and served as president of the UN General Assembly from 1966 to...
had stabilized in its form during the 6th and 7th centuries, its vertical stroke slanted towards the right (
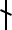 ), which made it possible to simplify the jēra-rune by having only one vertical stroke that slanted towards the left, giving the ᛅ ár-rune of the Younger Futhark. Since a simpler form of the rune was available for the /a/ phoneme, the older cross form of the rune came to be used for the /h/ phoneme.
), which made it possible to simplify the jēra-rune by having only one vertical stroke that slanted towards the left, giving the ᛅ ár-rune of the Younger Futhark. Since a simpler form of the rune was available for the /a/ phoneme, the older cross form of the rune came to be used for the /h/ phoneme.Gothic alphabet
The corresponding Gothic letterGothic alphabet
The Gothic alphabet is an alphabet for writing the Gothic language, created in the 4th century by Ulfilas for the purpose of translating the Christian Bible....
is 𐌾 j, named jer, which is also based on the shape of the Elder Futhark rune. This is an exception, shared with urus
Urus
Aberdeen is a town on the south shore of Hong Kong Island in Hong Kong. Administratively, it is part of the Southern District. Aberdeen Harbour is a harbour between Aberdeen and Ap Lei Chau. The name 'Aberdeen' usually covers the areas of Aberdeen, Wong Chuk Hang and Ap Lei Chau, but it is more...
, due to the fact that neither the Latin
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
nor the Greek
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
alphabets at the time of the introduction of the Gothic one had graphemes corresponding to the distinction of j
J
Ĵ or ĵ is a letter in Esperanto orthography representing the sound .While Esperanto orthography uses a diacritic for its four postalveolar consonants, as do the Latin-based Slavic alphabets, the base letters are Romano-Germanic...
and w
W
W is the 23rd letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.In other Germanic languages, including German, its pronunciation is similar or identical to that of English V...
from i and u.

