
Iterative learning control
Encyclopedia
Iterative Learning Control (ILC) is a method of tracking control
for systems that work in a repetitive mode. Examples of systems that operate in a repetitive manner include robot
arm manipulators, chemical batch processes and reliability testing
rigs. In each of these tasks the system is required to perform the same action over and over again with high precision
. This action is represented by the objective of accurately tracking a chosen reference signal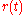 on a finite time interval.
on a finite time interval.
Repetition allows the system to improve tracking accuracy from repetition to repetition, in effect learning the required input needed to track the reference exactly. The learning process uses information from previous repetitions to improve the control signal ultimately enabling a suitable control action can be found iteratively
. The internal model
principle yields conditions under which perfect tracking can be achieved but the design of the control algorithm still leaves many decisions to be made to suit the application. A typical, simple control law is of the form:
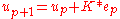
where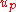 is the input to the system during the pth repetition,
is the input to the system during the pth repetition, 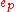 is the tracking error during the pth repetition and K is a design parameter representing operations on
is the tracking error during the pth repetition and K is a design parameter representing operations on 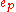 . Achieving perfect tracking through iteration is represented by the mathematical requirement of convergence of the input signals as
. Achieving perfect tracking through iteration is represented by the mathematical requirement of convergence of the input signals as 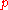 becomes large whilst the rate of this convergence represents the desirable practical need for the learning process to be rapid. There is also the need to ensure good algorithm performance even in the presence of uncertainty about the details of process dynamics. The operation
becomes large whilst the rate of this convergence represents the desirable practical need for the learning process to be rapid. There is also the need to ensure good algorithm performance even in the presence of uncertainty about the details of process dynamics. The operation 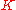 is crucial to achieving design objectives and ranges from simple scalar gains to sophisticated optimization computations.
is crucial to achieving design objectives and ranges from simple scalar gains to sophisticated optimization computations.
Process control
Process control is a statistics and engineering discipline that deals with architectures, mechanisms and algorithms for maintaining the output of a specific process within a desired range...
for systems that work in a repetitive mode. Examples of systems that operate in a repetitive manner include robot
Robot
A robot is a mechanical or virtual intelligent agent that can perform tasks automatically or with guidance, typically by remote control. In practice a robot is usually an electro-mechanical machine that is guided by computer and electronic programming. Robots can be autonomous, semi-autonomous or...
arm manipulators, chemical batch processes and reliability testing
Reliability engineering
Reliability engineering is an engineering field, that deals with the study, evaluation, and life-cycle management of reliability: the ability of a system or component to perform its required functions under stated conditions for a specified period of time. It is often measured as a probability of...
rigs. In each of these tasks the system is required to perform the same action over and over again with high precision
Accuracy and precision
In the fields of science, engineering, industry and statistics, the accuracy of a measurement system is the degree of closeness of measurements of a quantity to that quantity's actual value. The precision of a measurement system, also called reproducibility or repeatability, is the degree to which...
. This action is represented by the objective of accurately tracking a chosen reference signal
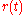 on a finite time interval.
on a finite time interval.Repetition allows the system to improve tracking accuracy from repetition to repetition, in effect learning the required input needed to track the reference exactly. The learning process uses information from previous repetitions to improve the control signal ultimately enabling a suitable control action can be found iteratively
Iteration
Iteration means the act of repeating a process usually with the aim of approaching a desired goal or target or result. Each repetition of the process is also called an "iteration," and the results of one iteration are used as the starting point for the next iteration.-Mathematics:Iteration in...
. The internal model
Internal model
An internal model is a postulated neural process that simulates the response of the motor system in order to estimate the outcome of a motor command....
principle yields conditions under which perfect tracking can be achieved but the design of the control algorithm still leaves many decisions to be made to suit the application. A typical, simple control law is of the form:
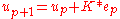
where
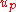 is the input to the system during the pth repetition,
is the input to the system during the pth repetition, 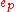 is the tracking error during the pth repetition and K is a design parameter representing operations on
is the tracking error during the pth repetition and K is a design parameter representing operations on 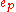 . Achieving perfect tracking through iteration is represented by the mathematical requirement of convergence of the input signals as
. Achieving perfect tracking through iteration is represented by the mathematical requirement of convergence of the input signals as 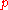 becomes large whilst the rate of this convergence represents the desirable practical need for the learning process to be rapid. There is also the need to ensure good algorithm performance even in the presence of uncertainty about the details of process dynamics. The operation
becomes large whilst the rate of this convergence represents the desirable practical need for the learning process to be rapid. There is also the need to ensure good algorithm performance even in the presence of uncertainty about the details of process dynamics. The operation  is crucial to achieving design objectives and ranges from simple scalar gains to sophisticated optimization computations.
is crucial to achieving design objectives and ranges from simple scalar gains to sophisticated optimization computations.
