.gif)
Isotope table (divided)
Encyclopedia
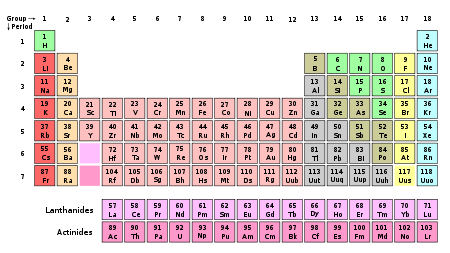
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
s of the chemical element
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
s, arranged with increasing atomic number
Atomic number
In chemistry and physics, the atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element...
from left to right and increasing neutron number
Neutron number
The neutron number, symbol N, is the number of neutrons in a nuclide.Atomic number plus neutron number equals mass number: Z+N=A....
from top to bottom.
Half lives
Half-life
Half-life, abbreviated t½, is the period of time it takes for the amount of a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half. The name was originally used to describe a characteristic of unstable atoms , but it may apply to any quantity which follows a set-rate decay.The original term, dating to...
are indicated by the color of each isotope's cell (see color chart in each section). Colored borders indicate half lives of the most stable nuclear isomer
Nuclear isomer
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus caused by the excitation of one or more of its nucleons . "Metastable" refers to the fact that these excited states have half-lives more than 100 to 1000 times the half-lives of the other possible excited nuclear states...
states.
The data for these tables came from Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory , is a United States national laboratory located in Upton, New York on Long Island, and was formally established in 1947 at the site of Camp Upton, a former U.S. Army base...
which has an interactive Table of Nuclides with data on ~3000 nuclides.
Isotopes for elements 0-14
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 15-29
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 30-44
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 45-59
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 60-74
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 75-89
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 90-104
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 105-118
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic table
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
s of the chemical element
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
s, arranged with increasing atomic number
Atomic number
In chemistry and physics, the atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element...
from left to right and increasing neutron number
Neutron number
The neutron number, symbol N, is the number of neutrons in a nuclide.Atomic number plus neutron number equals mass number: Z+N=A....
from top to bottom.
Half lives
Half-life
Half-life, abbreviated t½, is the period of time it takes for the amount of a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half. The name was originally used to describe a characteristic of unstable atoms , but it may apply to any quantity which follows a set-rate decay.The original term, dating to...
are indicated by the color of each isotope's cell (see color chart in each section). Colored borders indicate half lives of the most stable nuclear isomer
Nuclear isomer
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus caused by the excitation of one or more of its nucleons . "Metastable" refers to the fact that these excited states have half-lives more than 100 to 1000 times the half-lives of the other possible excited nuclear states...
states.
The data for these tables came from Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory , is a United States national laboratory located in Upton, New York on Long Island, and was formally established in 1947 at the site of Camp Upton, a former U.S. Army base...
which has an interactive Table of Nuclides with data on ~3000 nuclides.
Isotopes for elements 0-14
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 15-29
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 30-44
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 45-59
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 60-74
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 75-89
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 90-104
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 105-118
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic table
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
s of the chemical element
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
s, arranged with increasing atomic number
Atomic number
In chemistry and physics, the atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element...
from left to right and increasing neutron number
Neutron number
The neutron number, symbol N, is the number of neutrons in a nuclide.Atomic number plus neutron number equals mass number: Z+N=A....
from top to bottom.
Half lives
Half-life
Half-life, abbreviated t½, is the period of time it takes for the amount of a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half. The name was originally used to describe a characteristic of unstable atoms , but it may apply to any quantity which follows a set-rate decay.The original term, dating to...
are indicated by the color of each isotope's cell (see color chart in each section). Colored borders indicate half lives of the most stable nuclear isomer
Nuclear isomer
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus caused by the excitation of one or more of its nucleons . "Metastable" refers to the fact that these excited states have half-lives more than 100 to 1000 times the half-lives of the other possible excited nuclear states...
states.
The data for these tables came from Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory , is a United States national laboratory located in Upton, New York on Long Island, and was formally established in 1947 at the site of Camp Upton, a former U.S. Army base...
which has an interactive Table of Nuclides with data on ~3000 nuclides.
Isotopes for elements 0-14
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 15-29
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 30-44
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 45-59
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 60-74
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 75-89
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 90-104
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic tableIsotopes for elements 105-118
← Previous | Next →Go to Periodic table
