
Isogeny
Encyclopedia
In mathematics, an isogeny is a morphism
of varieties between two abelian varieties (e.g. elliptic curves) that is surjective and has a finite kernel.
Every isogeny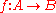 is automatically a group homomorphism
is automatically a group homomorphism
between the groups of k-valued points of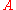 and
and 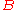 , for any field k over which
, for any field k over which  is defined.
is defined.
Let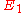 and
and 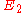 be elliptic curves over a field k. An isogeny between
be elliptic curves over a field k. An isogeny between 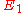 and
and 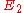 is a surjective morphism
is a surjective morphism 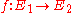 of varieties that preserves basepoints (i.e.
of varieties that preserves basepoints (i.e.  maps the infinite point on
maps the infinite point on 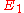 to that on
to that on 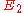 ).
).
Two elliptic curves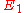 and
and 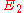 are called isogenous if there is an isogeny
are called isogenous if there is an isogeny 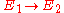 . This is an equivalence relation, symmetry being due to the existence of the dual isogeny. As above, every isogeny induces homomorphisms of the groups of the k-valued points of the elliptic curves.
. This is an equivalence relation, symmetry being due to the existence of the dual isogeny. As above, every isogeny induces homomorphisms of the groups of the k-valued points of the elliptic curves.
Morphism
In mathematics, a morphism is an abstraction derived from structure-preserving mappings between two mathematical structures. The notion of morphism recurs in much of contemporary mathematics...
of varieties between two abelian varieties (e.g. elliptic curves) that is surjective and has a finite kernel.
Every isogeny
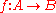 is automatically a group homomorphism
is automatically a group homomorphismGroup homomorphism
In mathematics, given two groups and , a group homomorphism from to is a function h : G → H such that for all u and v in G it holds that h = h \cdot h...
between the groups of k-valued points of
 and
and  , for any field k over which
, for any field k over which  is defined.
is defined.Etymology
From the Greek (iso-) and Latin (genus), the term isogeny means "equal origins", a reference to the geometrical fact that an isogeny sends the point at infinity (the origin) of the source elliptic curve to the point at infinity of the target elliptic curve.Case of elliptic curves
For elliptic curves, this notion can also be formulated as follows:Let
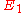 and
and 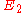 be elliptic curves over a field k. An isogeny between
be elliptic curves over a field k. An isogeny between 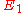 and
and 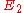 is a surjective morphism
is a surjective morphism 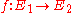 of varieties that preserves basepoints (i.e.
of varieties that preserves basepoints (i.e.  maps the infinite point on
maps the infinite point on 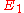 to that on
to that on 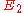 ).
).Two elliptic curves
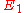 and
and 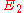 are called isogenous if there is an isogeny
are called isogenous if there is an isogeny  . This is an equivalence relation, symmetry being due to the existence of the dual isogeny. As above, every isogeny induces homomorphisms of the groups of the k-valued points of the elliptic curves.
. This is an equivalence relation, symmetry being due to the existence of the dual isogeny. As above, every isogeny induces homomorphisms of the groups of the k-valued points of the elliptic curves.

