
Irwin-Hall distribution
Encyclopedia
In probability
and statistics
, the Irwin–Hall distribution, named after Joseph Oscar Irwin
and Philip Hall
, is probability distribution
for a random variable
defined as sum of a number of independent random variables, each having a uniform distribution
. For this reason it is also known as the uniform sum distribution.
The generation of pseudo-random number
s having an approximately normal distribution is sometimes accomplished by computing the sum of a number of pseudo-random numbers having a uniform distribution; usually for the sake of simplicity of programming. Rescaling the Irwin–Hall distribution provides the exact distribution of the random varites being generated.
This distribution is sometimes confused with the Bates distribution
, which is the mean (not sum) of n independent random variables uniformly distributed from 0 to 1.
for the sum of n independent and identically distributed U(0, 1)
random variables:
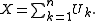
The probability density function
(pdf) is given by
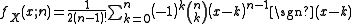
where sgn(x − k) denotes the sign function
:
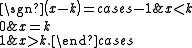
Thus the pdf is a spline
(piecewise polynomial function) of degree n − 1 over the knots 0, 1, ..., n. In fact, for x between the knots located at k and k + 1, the pdf is equal to
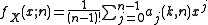
where the coefficients aj(k,n) may be found from a recurrence relation
over k
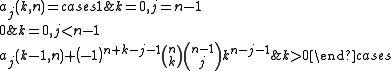
The coefficients are also A188816 in OEIS
. The coefficients for the cumulative distribution is A188668.
The mean
and variance
are n/2 and n/12, respectively.
Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
and statistics
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the Irwin–Hall distribution, named after Joseph Oscar Irwin
Joseph Oscar Irwin
Joseph Oscar Irwin British statistician who advanced the use of statistical methods in biological assay and other fields of laboratory medicine. Irwin’s grasp of modern mathematical statistics distinguished him not only from older medical statisticians like Major Greenwood but contemporaries like...
and Philip Hall
Philip Hall
Philip Hall FRS , was an English mathematician.His major work was on group theory, notably on finite groups and solvable groups.-Biography:...
, is probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
for a random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
defined as sum of a number of independent random variables, each having a uniform distribution
Uniform distribution (continuous)
In probability theory and statistics, the continuous uniform distribution or rectangular distribution is a family of probability distributions such that for each member of the family, all intervals of the same length on the distribution's support are equally probable. The support is defined by...
. For this reason it is also known as the uniform sum distribution.
The generation of pseudo-random number
Pseudo-random number sampling
Pseudo-random number sampling or non-uniform pseudo-random variate generation is the numerical practice of generating pseudo-random numbers that are distributed according to a given probability distribution....
s having an approximately normal distribution is sometimes accomplished by computing the sum of a number of pseudo-random numbers having a uniform distribution; usually for the sake of simplicity of programming. Rescaling the Irwin–Hall distribution provides the exact distribution of the random varites being generated.
This distribution is sometimes confused with the Bates distribution
Bates distribution
In probability and statistics, the Bates distribution, is a probability distribution of the mean of a number of statistically independent uniformly distributed random variables on the unit interval...
, which is the mean (not sum) of n independent random variables uniformly distributed from 0 to 1.
Definition
The Irwin–Hall distribution is the continuous probability distributionProbability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
for the sum of n independent and identically distributed U(0, 1)
Uniform distribution (continuous)
In probability theory and statistics, the continuous uniform distribution or rectangular distribution is a family of probability distributions such that for each member of the family, all intervals of the same length on the distribution's support are equally probable. The support is defined by...
random variables:
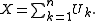
The probability density function
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
(pdf) is given by
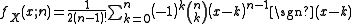
where sgn(x − k) denotes the sign function
Sign function
In mathematics, the sign function is an odd mathematical function that extracts the sign of a real number. To avoid confusion with the sine function, this function is often called the signum function ....
:
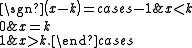
Thus the pdf is a spline
Spline (mathematics)
In mathematics, a spline is a sufficiently smooth piecewise-polynomial function. In interpolating problems, spline interpolation is often preferred to polynomial interpolation because it yields similar results, even when using low-degree polynomials, while avoiding Runge's phenomenon for higher...
(piecewise polynomial function) of degree n − 1 over the knots 0, 1, ..., n. In fact, for x between the knots located at k and k + 1, the pdf is equal to
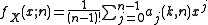
where the coefficients aj(k,n) may be found from a recurrence relation
Recurrence relation
In mathematics, a recurrence relation is an equation that recursively defines a sequence, once one or more initial terms are given: each further term of the sequence is defined as a function of the preceding terms....
over k
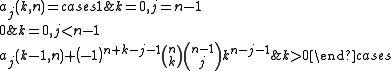
The coefficients are also A188816 in OEIS
On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences
The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences , also cited simply as Sloane's, is an online database of integer sequences, created and maintained by N. J. A. Sloane, a researcher at AT&T Labs...
. The coefficients for the cumulative distribution is A188668.
The mean
Mean
In statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
and variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
are n/2 and n/12, respectively.
Special cases
- For n = 1, X follows a uniform distributionUniform distribution (continuous)In probability theory and statistics, the continuous uniform distribution or rectangular distribution is a family of probability distributions such that for each member of the family, all intervals of the same length on the distribution's support are equally probable. The support is defined by...
: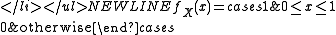
- For n = 2, X follows a triangular distribution:
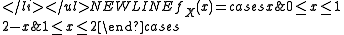
- For n = 3,
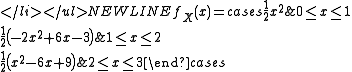
- For n = 4,

- For n = 5,
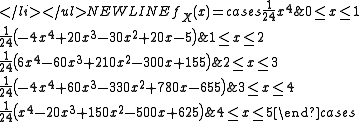
- For n = 5,
- For n = 4,
- For n = 3,
- For n = 2, X follows a triangular distribution:

