
Inverse Faraday effect
Encyclopedia
The inverse Faraday effect is the effect opposite to the Faraday effect
. A static magnetization
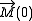 is induced by an external oscillating electrical field with the frequency
is induced by an external oscillating electrical field with the frequency 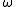 , which can be achieved with a high intensity laser
, which can be achieved with a high intensity laser
pulse for example. The induced magnetization is proportional to the vector product of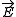 and
and  :
:
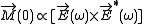
From this equation we see that the circularly polarized light with the frequency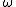 should induce a magnetization along the wave vector
should induce a magnetization along the wave vector
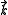 . Because
. Because 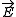 is in the vector product, left- and right-handed polarization waves should induce magnetization of opposite signs.
is in the vector product, left- and right-handed polarization waves should induce magnetization of opposite signs.
The induced magnetization is comparable to the saturated magnetization of the media.
Faraday effect
In physics, the Faraday effect or Faraday rotation is a Magneto-optical phenomenon, that is, an interaction between light and a magnetic field in a medium...
. A static magnetization
Magnetization
In classical electromagnetism, magnetization or magnetic polarization is the vector field that expresses the density of permanent or induced magnetic dipole moments in a magnetic material...
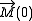 is induced by an external oscillating electrical field with the frequency
is induced by an external oscillating electrical field with the frequency 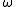 , which can be achieved with a high intensity laser
, which can be achieved with a high intensity laserLaser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
pulse for example. The induced magnetization is proportional to the vector product of
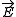 and
and  :
: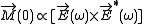
From this equation we see that the circularly polarized light with the frequency
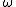 should induce a magnetization along the wave vector
should induce a magnetization along the wave vectorWave vector
In physics, a wave vector is a vector which helps describe a wave. Like any vector, it has a magnitude and direction, both of which are important: Its magnitude is either the wavenumber or angular wavenumber of the wave , and its direction is ordinarily the direction of wave propagation In...
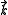 . Because
. Because 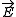 is in the vector product, left- and right-handed polarization waves should induce magnetization of opposite signs.
is in the vector product, left- and right-handed polarization waves should induce magnetization of opposite signs.The induced magnetization is comparable to the saturated magnetization of the media.

