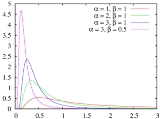
Inverse-gamma distribution
Overview
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
and statistics
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the inverse gamma distribution is a two-parameter family of continuous probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
s on the positive real line, which is the distribution of the reciprocal
Multiplicative inverse
In mathematics, a multiplicative inverse or reciprocal for a number x, denoted by 1/x or x−1, is a number which when multiplied by x yields the multiplicative identity, 1. The multiplicative inverse of a fraction a/b is b/a. For the multiplicative inverse of a real number, divide 1 by the...
of a variable distributed according to the gamma distribution. Perhaps the chief use of the inverse gamma distribution is in Bayesian statistics
Bayesian statistics
Bayesian statistics is that subset of the entire field of statistics in which the evidence about the true state of the world is expressed in terms of degrees of belief or, more specifically, Bayesian probabilities...
, where it serves as the conjugate prior
Conjugate prior
In Bayesian probability theory, if the posterior distributions p are in the same family as the prior probability distribution p, the prior and posterior are then called conjugate distributions, and the prior is called a conjugate prior for the likelihood...
of the variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
of a normal distribution.

