
Internal resistance
Encyclopedia
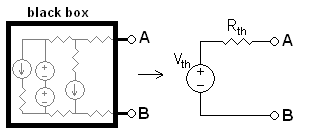
A practical electrical power source which is a linear electric circuit may, according to Thévenin's theorem
, be represented as an ideal voltage source in series with an impedance
. This resistance is termed the internal resistance of the source. When the power source delivers current
, the measured e.m.f.
(voltage output) is lower than the no-load voltage; the difference is the voltage (the product of current and resistance
) drop caused by the internal resistance. The concept of internal resistance applies to all kinds of electrical sources and is useful for analyzing many types of electrical circuits.
can be approximately modeled as a voltage source in series with a resistance. Internal resistance of a battery is dependent on the specific battery's size, chemical properties, age, temperature and the discharge current. Measurement of the internal resistance of a battery is a guide to its condition, but may not apply at other than the test conditions. Internal resistance depends upon temperature; for example, a fresh Energizer E91 AA
alkaline primary battery drops from about 0.9 ohms at -40 °C to about 0.1 ohms at 40 °C.
The internal resistance of a battery can be calculated from its open circuit voltage, voltage on-load, and the load current. An equivalent series resistance (ESR) meter
as used to measure the ESR of capacitors, essentially an AC milliohmmeter, can be used.
Internal resistance increases with the age of a battery, but for most battery types ranges from a fraction of an ohm to a few ohms.
In use the useful voltage produced by a disposable battery decreases until it drops so far that the battery must be discarded. This is largely due to an increase in internal resistance rather than a drop in the voltage of the equivalent source.
Thévenin's theorem
In circuit theory, Thévenin's theorem for linear electrical networks states that any combination of voltage sources, current sources, and resistors with two terminals is electrically equivalent to a single voltage source V and a single series resistor R. For single frequency AC systems the theorem...
, be represented as an ideal voltage source in series with an impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
. This resistance is termed the internal resistance of the source. When the power source delivers current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
, the measured e.m.f.
Electromotive force
In physics, electromotive force, emf , or electromotance refers to voltage generated by a battery or by the magnetic force according to Faraday's Law, which states that a time varying magnetic field will induce an electric current.It is important to note that the electromotive "force" is not a...
(voltage output) is lower than the no-load voltage; the difference is the voltage (the product of current and resistance
Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
) drop caused by the internal resistance. The concept of internal resistance applies to all kinds of electrical sources and is useful for analyzing many types of electrical circuits.

Batteries
BatteriesBattery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
can be approximately modeled as a voltage source in series with a resistance. Internal resistance of a battery is dependent on the specific battery's size, chemical properties, age, temperature and the discharge current. Measurement of the internal resistance of a battery is a guide to its condition, but may not apply at other than the test conditions. Internal resistance depends upon temperature; for example, a fresh Energizer E91 AA
AA battery
An AA battery is a standard size of battery. Batteries of this size are the most commonly used type of in portable electronic devices. An AA battery is composed of a single electrochemical cell...
alkaline primary battery drops from about 0.9 ohms at -40 °C to about 0.1 ohms at 40 °C.
The internal resistance of a battery can be calculated from its open circuit voltage, voltage on-load, and the load current. An equivalent series resistance (ESR) meter
ESR meter
An ESR meter is a two-terminal electronic measuring instrument designed and used primarily to measure the equivalent series resistance of real capacitors—the ESR of an ideal capacitor is zero—usually without the need to disconnect the capacitor from the circuit it is connected to...
as used to measure the ESR of capacitors, essentially an AC milliohmmeter, can be used.
Internal resistance increases with the age of a battery, but for most battery types ranges from a fraction of an ohm to a few ohms.
In use the useful voltage produced by a disposable battery decreases until it drops so far that the battery must be discarded. This is largely due to an increase in internal resistance rather than a drop in the voltage of the equivalent source.
External links
- Interconnection of two audio units - Output impedance and input impedance
- Effect of internal resistance of different types of rechargeable battery on performance, and change with state of charge and resting.

