
Infrared vision
Encyclopedia
Infrared vision can be defined as the capability of biological or artificial systems to detect infrared radiation. The terms thermal vision
and thermal imaging
, are also commonly used in this context since infrared emissions from a body are directly related to their temperature: hotter objects emit more energy in the infrared spectrum than colder ones.
The human body, as well as many moving or static objects of military or civil interest, is normally warmer than the surrounding environment. Since hotter objects emit more infrared energy than colder ones, it is relatively easy to identify them with an infrared detector
, day or night. Hence, the term night vision
is also used (sometimes misused) in the place of "infrared vision", since one of the original purposes in developing this kind of systems was to locate enemy targets at night. However, night vision
concerns the ability to see in the dark although not necessarily in the infrared spectrum. In fact, night vision equipment can be manufactured using one of two technologies : light intensifiers or infrared vision. The former technology uses a photocathode to convert light (in the visible or near infrared portions of the electromagnetic spectrum) to electrons, amplify the signal and transform it back to photons. Infrared vision on the other hand, uses an infrared detector working at mid or long wavelengths (invisible to the human eye) to capture the heat emitted by an object.
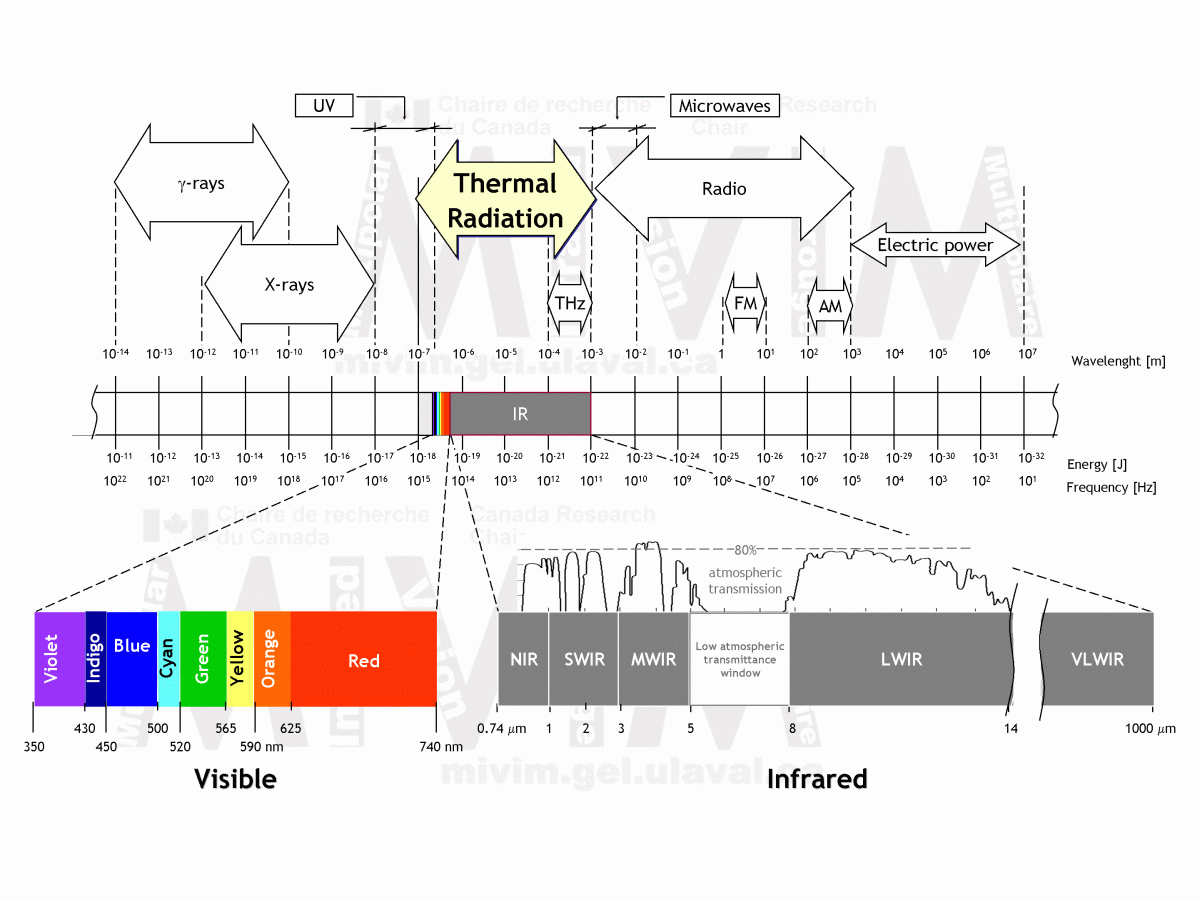 The entire electromagnetic spectrum
The entire electromagnetic spectrum
highlighting the infrared part located between the visible and the radio waves, is depicted in the figure. The IR spectrum can be subdivided into 5 regions, although this definition is somehow arbitrary and it differs from one author to another, ,. The subdivision presented here is based on a combination of the atmospheric transmittance windows, i.e. the wavelengths regions in which infrared radiation is better transmitted through the atmosphere, the detector materials used to build the infrared sensors and the main applications. In this way, the Near Infrared (NIR) band is mostly used in fiber optic telecommunication systems since silica (SiO2) provides a low attenuation losses medium for the infrared, whilst the Short Wave Infrared (SWIR) band allows to work on long-distance telecommunications (remote sensing) using a combinations of detector materials. The Medium Wavelength Infrared (MWIR) and the Long Wavelength Infrared (LWIR) bands find applications in Infrared Thermography for military or civil applications, e.g. target signature identification, surveillance, NonDestructive Evaluation, etc. The Very Long Wavelength Infrared (VLIR) band is used in spectroscopy and astronomy.
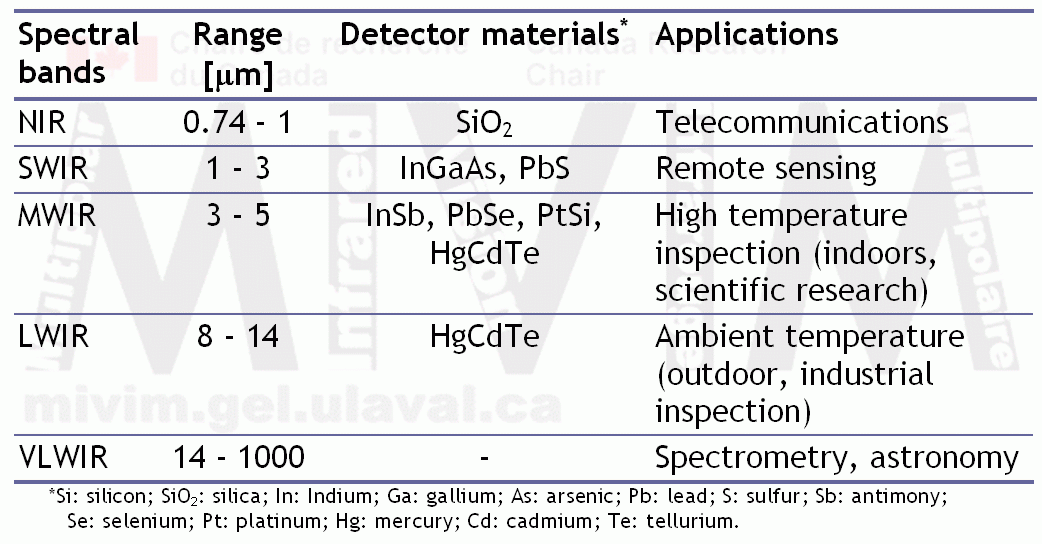 The MWIR band is preferred when inspecting high temperature objects and the LWIR band when working with near room temperature objects. Other important criteria for band selection are : the operating distance, indoor-outdoor operation, temperature and emissivity of the bodies of interest. For instance, long wavelengths (LWIR) are preferred for outdoor operation since they are less affected by radiation from the Sun. LWIR cameras are typically uncooled systems using a microbolometer Focal Plane Arrays commonly used in industrial IR applications, although cooled LWIR cameras using Mercury Cadmium Tellurium (MCT) detectors exists as well. On the contrary, the majority of the MWIR cameras require cooling, using either liquid nitrogen or a Stirling cycle cooler. Cooling to approximately -196°C (77 K), offer excellent thermal resolution, but it might restrict the span of applications to controlled environments.
The MWIR band is preferred when inspecting high temperature objects and the LWIR band when working with near room temperature objects. Other important criteria for band selection are : the operating distance, indoor-outdoor operation, temperature and emissivity of the bodies of interest. For instance, long wavelengths (LWIR) are preferred for outdoor operation since they are less affected by radiation from the Sun. LWIR cameras are typically uncooled systems using a microbolometer Focal Plane Arrays commonly used in industrial IR applications, although cooled LWIR cameras using Mercury Cadmium Tellurium (MCT) detectors exists as well. On the contrary, the majority of the MWIR cameras require cooling, using either liquid nitrogen or a Stirling cycle cooler. Cooling to approximately -196°C (77 K), offer excellent thermal resolution, but it might restrict the span of applications to controlled environments.
, navigation
, surveillance
and targeting
. For years, it developed slowly due to the high cost of the equipment and the low quality of available images. Since the development of the first commercial infrared cameras in the second half of 1960’s, however, the availability of new generations of infrared cameras coupled with growing computer power is providing exciting new civilian (and military) applications, to name only a few: Buildings and Infrastructure, Works of Art, Aerospace Components and Processes, Maintenance, Defect detection and characterization, Law Enforcement, Surveillance and Public Services, Medical and Veterinary Thermal Imaging. The electronic technique that uses Infrared Vision to “see” thermal energy, to monitor temperatures and thermal patterns is called Infrared Thermography and is described next.
Thermography
Infrared thermography, thermal imaging, and thermal video are examples of infrared imaging science. Thermal imaging cameras detect radiation in the infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum and produce images of that radiation, called thermograms...
and thermal imaging
Thermography
Infrared thermography, thermal imaging, and thermal video are examples of infrared imaging science. Thermal imaging cameras detect radiation in the infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum and produce images of that radiation, called thermograms...
, are also commonly used in this context since infrared emissions from a body are directly related to their temperature: hotter objects emit more energy in the infrared spectrum than colder ones.
The human body, as well as many moving or static objects of military or civil interest, is normally warmer than the surrounding environment. Since hotter objects emit more infrared energy than colder ones, it is relatively easy to identify them with an infrared detector
Infrared detector
An infrared detector is a photodetector that reacts to infrared radiation. The two main types of detectors are thermal and photonic.The thermal effects of the incident IR radiation can be followed through many temperature dependent phenomena....
, day or night. Hence, the term night vision
Night vision
Night vision is the ability to see in low light conditions. Whether by biological or technological means, night vision is made possible by a combination of two approaches: sufficient spectral range, and sufficient intensity range...
is also used (sometimes misused) in the place of "infrared vision", since one of the original purposes in developing this kind of systems was to locate enemy targets at night. However, night vision
Night vision
Night vision is the ability to see in low light conditions. Whether by biological or technological means, night vision is made possible by a combination of two approaches: sufficient spectral range, and sufficient intensity range...
concerns the ability to see in the dark although not necessarily in the infrared spectrum. In fact, night vision equipment can be manufactured using one of two technologies : light intensifiers or infrared vision. The former technology uses a photocathode to convert light (in the visible or near infrared portions of the electromagnetic spectrum) to electrons, amplify the signal and transform it back to photons. Infrared vision on the other hand, uses an infrared detector working at mid or long wavelengths (invisible to the human eye) to capture the heat emitted by an object.
The infrared spectrum

Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object....
highlighting the infrared part located between the visible and the radio waves, is depicted in the figure. The IR spectrum can be subdivided into 5 regions, although this definition is somehow arbitrary and it differs from one author to another, ,. The subdivision presented here is based on a combination of the atmospheric transmittance windows, i.e. the wavelengths regions in which infrared radiation is better transmitted through the atmosphere, the detector materials used to build the infrared sensors and the main applications. In this way, the Near Infrared (NIR) band is mostly used in fiber optic telecommunication systems since silica (SiO2) provides a low attenuation losses medium for the infrared, whilst the Short Wave Infrared (SWIR) band allows to work on long-distance telecommunications (remote sensing) using a combinations of detector materials. The Medium Wavelength Infrared (MWIR) and the Long Wavelength Infrared (LWIR) bands find applications in Infrared Thermography for military or civil applications, e.g. target signature identification, surveillance, NonDestructive Evaluation, etc. The Very Long Wavelength Infrared (VLIR) band is used in spectroscopy and astronomy.

Applications
Infrared vision is used extensively by the military for night visionNight vision
Night vision is the ability to see in low light conditions. Whether by biological or technological means, night vision is made possible by a combination of two approaches: sufficient spectral range, and sufficient intensity range...
, navigation
Navigation
Navigation is the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks...
, surveillance
Surveillance
Surveillance is the monitoring of the behavior, activities, or other changing information, usually of people. It is sometimes done in a surreptitious manner...
and targeting
Targeting (warfare)
Targeting is the process used to select objects or installations to be attacked, taken, or destroyed in warfare.Technologically advanced countries can generally select their targets in such a way as to minimize collateral damage and civilian casualties. This can fall by the wayside, however, during...
. For years, it developed slowly due to the high cost of the equipment and the low quality of available images. Since the development of the first commercial infrared cameras in the second half of 1960’s, however, the availability of new generations of infrared cameras coupled with growing computer power is providing exciting new civilian (and military) applications, to name only a few: Buildings and Infrastructure, Works of Art, Aerospace Components and Processes, Maintenance, Defect detection and characterization, Law Enforcement, Surveillance and Public Services, Medical and Veterinary Thermal Imaging. The electronic technique that uses Infrared Vision to “see” thermal energy, to monitor temperatures and thermal patterns is called Infrared Thermography and is described next.

