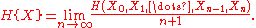Information source (mathematics)
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, an information source is a sequence of random variable
s ranging over a finite alphabet Γ, having a stationary distribution
.
The uncertainty, or entropy rate
, of an information source is defined as
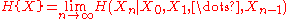
where
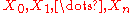
is the sequence of random variables defining the information source, and
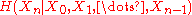
is the conditional information entropy
of the sequence of random variables. Equivalently, one has
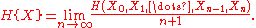
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, an information source is a sequence of random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
s ranging over a finite alphabet Γ, having a stationary distribution
Stationary distribution
Stationary distribution may refer to:* The limiting distribution in a Markov chain* The marginal distribution of a stationary process or stationary time series* The set of joint probability distributions of a stationary process or stationary time series...
.
The uncertainty, or entropy rate
Entropy rate
In the mathematical theory of probability, the entropy rate or source information rate of a stochastic process is, informally, the time density of the average information in a stochastic process...
, of an information source is defined as
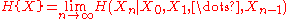
where
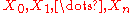
is the sequence of random variables defining the information source, and
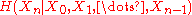
is the conditional information entropy
Information entropy
In information theory, entropy is a measure of the uncertainty associated with a random variable. In this context, the term usually refers to the Shannon entropy, which quantifies the expected value of the information contained in a message, usually in units such as bits...
of the sequence of random variables. Equivalently, one has