
Information gain ratio
Encyclopedia
Information Gain Calculation
Let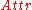 be the set of all attributes and
be the set of all attributes and 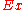 the set of all training examples,
the set of all training examples,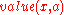 with
with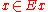 defines the value of a specific example
defines the value of a specific example  for attribute
for attribute 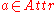 ,
, 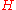 specifies the entropy.
specifies the entropy.The information gain for an attribute
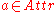 is defined as follows:
is defined as follows:
The information gain is equal to the total entropy for an attribute if for each of the attribute values a unique classification can be made for the result attribute. In this case the relative entropies subtracted from the total entropy are 0.
Intrinsic Value Calculation
The gain ratio for a test is defined as follows (where n is the number of examples left in the class after the test on the attribute):
Advantages
Information gain ratio biases the decision treeDecision tree learning
Decision tree learning, used in statistics, data mining and machine learning, uses a decision tree as a predictive model which maps observations about an item to conclusions about the item's target value. More descriptive names for such tree models are classification trees or regression trees...
against considering attributes with a large number of distinct values. So it solves the drawback of information gain -- namely, information gain applied to attributes that can take on a large number of distinct values might learn the training set
Training set
A training set is a set of data used in various areas of information science to discover potentially predictive relationships. Training sets are used in artificial intelligence, machine learning, genetic programming, intelligent systems, and statistics...
too well. For example, suppose that we are building a decision tree for some data describing a business's customers. Information gain is often used to decide which of the attributes are the most relevant, so they can be tested near the root of the tree. One of the input attributes might be the customer's credit card number. This attribute has a high information gain, because it uniquely identifies each customer, but we do not want to include it in the decision tree: deciding how to treat a customer based on their credit card number is unlikely to generalize to customers we haven't seen before.

