
Induction generator
Encyclopedia
An induction generator or asynchronous generator is a type of AC electrical generator
that uses the principles of induction motor
s to produce power. Induction generators operate by mechanically turning their rotor in generator mode, giving negative slip. In most cases, a regular AC asynchronous motor is used as a generator, without any internal modifications.
In normal motor operation, stator flux rotation is faster than the rotor rotation. This causes the stator flux to induce rotor currents, which create a rotor flux with magnetic polarity opposite to stator. In this way, the rotor is dragged along behind stator flux, at a value equal to the slip.
In generator operation, a prime mover
(turbine, engine) drives the rotor above the synchronous speed. The stator flux still induces currents in the rotor, but since the opposing rotor flux is now cutting the stator coils, an active current is produced in stator coils, and the motor now operates as a generator, sending power back to the electrical grid.
Induction generators are not, in general, self-exciting, meaning they require an electrical supply, at least initially, to produce the rotating magnetic flux
(although in practice an induction generator will often self start due to residual magnetism.) The electrical supply can be supplied from the electrical grid or, once it starts producing power, from the generator itself. The rotating magnetic flux from the stator
induces currents in the rotor, which also produces a magnetic field
. If the rotor turns slower than the rate of the rotating flux, the machine acts like an induction motor. If the rotor is turned faster, it acts like a generator, producing power at the synchronous frequency.
For a grid connected system, frequency and voltage at the machine will be dictated by the electric grid, since it is very small compared to the whole system.
For stand-alone systems, frequency and voltage are complex function of machine parameters, capacitance used for excitation, and load value and type.
installations due to their ability to produce useful power at varying rotor speeds. Induction generators are mechanically and electrically simpler than other generator types. They are also more rugged, requiring no brushes or commutators
.
Induction generators are particularly suitable and usually used for wind generating stations as in this case speed is always a variable factor, and the generator is easy on the gearbox.
Required capacitance per phase if capacitors are connected in delta:
For machine to run as an asynchronous generator, capacitor bank must supply minimum 4567 / 3 phases = 1523 VAR per phase. Voltage per capacitor is 440 V because capacitors are connected in delta.
Minimum capacitance per phase:
If load also absorbs reactive power, capacitor bank must be increased in size to compensate.
Prime mover speed should be used to generate frequency of 60 Hz:
Typically, slip should be similar to full-load value when machine is running as motor, but negative (generator operation):
Electrical generator
In electricity generation, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. A generator forces electric charge to flow through an external electrical circuit. It is analogous to a water pump, which causes water to flow...
that uses the principles of induction motor
Induction motor
An induction or asynchronous motor is a type of AC motor where power is supplied to the rotor by means of electromagnetic induction. These motors are widely used in industrial drives, particularly polyphase induction motors, because they are robust and have no brushes...
s to produce power. Induction generators operate by mechanically turning their rotor in generator mode, giving negative slip. In most cases, a regular AC asynchronous motor is used as a generator, without any internal modifications.
Principle of operation
Induction generators and motors produce electrical power when their rotor is turned faster than the synchronous frequency. For a typical four-pole motor (two pairs of poles on stator) operating on a 60 Hz electrical grid, synchronous speed is 1800 rotations per minute. The same four-pole motor operating on a 50 Hz grid will have a synchronous speed of 1500 RPM.In normal motor operation, stator flux rotation is faster than the rotor rotation. This causes the stator flux to induce rotor currents, which create a rotor flux with magnetic polarity opposite to stator. In this way, the rotor is dragged along behind stator flux, at a value equal to the slip.
In generator operation, a prime mover
Engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert energy into useful mechanical motion. Heat engines, including internal combustion engines and external combustion engines burn a fuel to create heat which is then used to create motion...
(turbine, engine) drives the rotor above the synchronous speed. The stator flux still induces currents in the rotor, but since the opposing rotor flux is now cutting the stator coils, an active current is produced in stator coils, and the motor now operates as a generator, sending power back to the electrical grid.
Excitation
Note that a source of excitation current for magnetizing flux (reactive power) for stator is still required, to induce rotor current.Induction generators are not, in general, self-exciting, meaning they require an electrical supply, at least initially, to produce the rotating magnetic flux
Magnetic flux
Magnetic flux , is a measure of the amount of magnetic B field passing through a given surface . The SI unit of magnetic flux is the weber...
(although in practice an induction generator will often self start due to residual magnetism.) The electrical supply can be supplied from the electrical grid or, once it starts producing power, from the generator itself. The rotating magnetic flux from the stator
Stator
The stator is the stationary part of a rotor system, found in an electric generator, electric motor and biological rotors.Depending on the configuration of a spinning electromotive device the stator may act as the field magnet, interacting with the armature to create motion, or it may act as the...
induces currents in the rotor, which also produces a magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
. If the rotor turns slower than the rate of the rotating flux, the machine acts like an induction motor. If the rotor is turned faster, it acts like a generator, producing power at the synchronous frequency.
Active power
Active power delivered to the line is proportional to slip above the synchronous speed. Full rated power of the generator is reached at very small slip values (motor dependent, typically 3%). At synchronous speed of 1800 rpm, generator will produce no power. When the driving speed is increased to 1860 rpm, full output power is produced. If the prime mover is unable to produce enough power to fully drive the generator, speed will remain somewhere between 1800 and 1860 rpm range.Required capacitance
A capacitor bank must supply reactive power to the motor when used in stand-alone mode. The reactive power supplied should be equal or greater than the reactive power that the machine normally draws when operating as a motor. Terminal voltage will increase with capacitance, but is limited by iron saturation.Grid and stand-alone connections
In induction generators the magnetizing flux is established by a capacitor bank connected to the machine in case of stand alone system and in case of grid connection it draws magnetizing current from the grid.For a grid connected system, frequency and voltage at the machine will be dictated by the electric grid, since it is very small compared to the whole system.
For stand-alone systems, frequency and voltage are complex function of machine parameters, capacitance used for excitation, and load value and type.
Use of induction generators
Induction generators are often used in wind turbines and some micro hydroMicro hydro
Micro hydro is a term used for hydroelectric power installations that typically produce up to 100 kW of electricity. These installations can provide power to an isolated home or small community, or are sometimes connected to electric power networks....
installations due to their ability to produce useful power at varying rotor speeds. Induction generators are mechanically and electrically simpler than other generator types. They are also more rugged, requiring no brushes or commutators
Commutator (electric)
A commutator is a rotary electrical switch in certain types of electric motors or electrical generators that periodically reverses the current direction between the rotor and the external circuit. In a motor, it applies power to the best location on the rotor, and in a generator, picks off power...
.
Induction generators are particularly suitable and usually used for wind generating stations as in this case speed is always a variable factor, and the generator is easy on the gearbox.
Example application
We must use 10 hp, 1760 r/min, 440 V, 3 phase induction motor as an asynchronous generator. Full-load current of the motor is 10 A and full-load power factor is 0.8.Required capacitance per phase if capacitors are connected in delta:
- Apparent power S = √3 E I = 1.73 * 440 * 10 = 7612 VA
- Active power P = S cos θ = 7612 * 0.8 = 6090 W
- Reactive power Q =
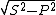 = 4567 VAR
= 4567 VAR
For machine to run as an asynchronous generator, capacitor bank must supply minimum 4567 / 3 phases = 1523 VAR per phase. Voltage per capacitor is 440 V because capacitors are connected in delta.
- Capacitive current Ic = Q/E = 1523/440 = 3.46 A
- Capacitive reactance per phase Xc = E/I = 127 Ω
Minimum capacitance per phase:
- C = 1 / (2*π*f*Xc) = 1 / (2 * 3.141 * 60 * 127) = 21 microfarads.
If load also absorbs reactive power, capacitor bank must be increased in size to compensate.
Prime mover speed should be used to generate frequency of 60 Hz:
Typically, slip should be similar to full-load value when machine is running as motor, but negative (generator operation):
- Slip = 1800 - 1760 = 40 rpm
- Required prime mover speed N = 1800 + Slip = 1840 rpm.

