Indirect inguinal hernia
Encyclopedia
An indirect inguinal hernia is an inguinal hernia
that results from the failure of embryonic closure of the deep inguinal ring
after the testicle
has passed through it. Like other inguinal hernias, it protrudes through the superficial inguinal ring. It is the most common cause of groin hernia
.
gives a coat to the testicle as it passes through this ring, forming a temporary connection called the processus vaginalis
. In normal development, the processus is obliterated once the testicle is completely descended. The permanent coat of peritoneum that remains around the testicle is called the tunica vaginalis
. The testicle remains connected to its blood vessels and the vas deferens, which make up the spermatic cord
and descend through the inguinal canal to the scrotum.
The deep inguinal ring, which is the beginning of the inguinal canal, remains as an opening in the fascia transversalis, which forms the muscular outer wall for the spermatic cord. When the opening is larger than necessary for passage of the spermatic cord, the stage is set for an indirect inguinal hernia. The protrusion of peritoneum through the internal inguinal ring can be considered an incomplete obliteration of the processus.
In an indirect inguinal hernia, the protrusion passes through the deep inguinal ring and is located lateral to the inferior epigastric artery. Hence, the conjoint tendon is not weakened.
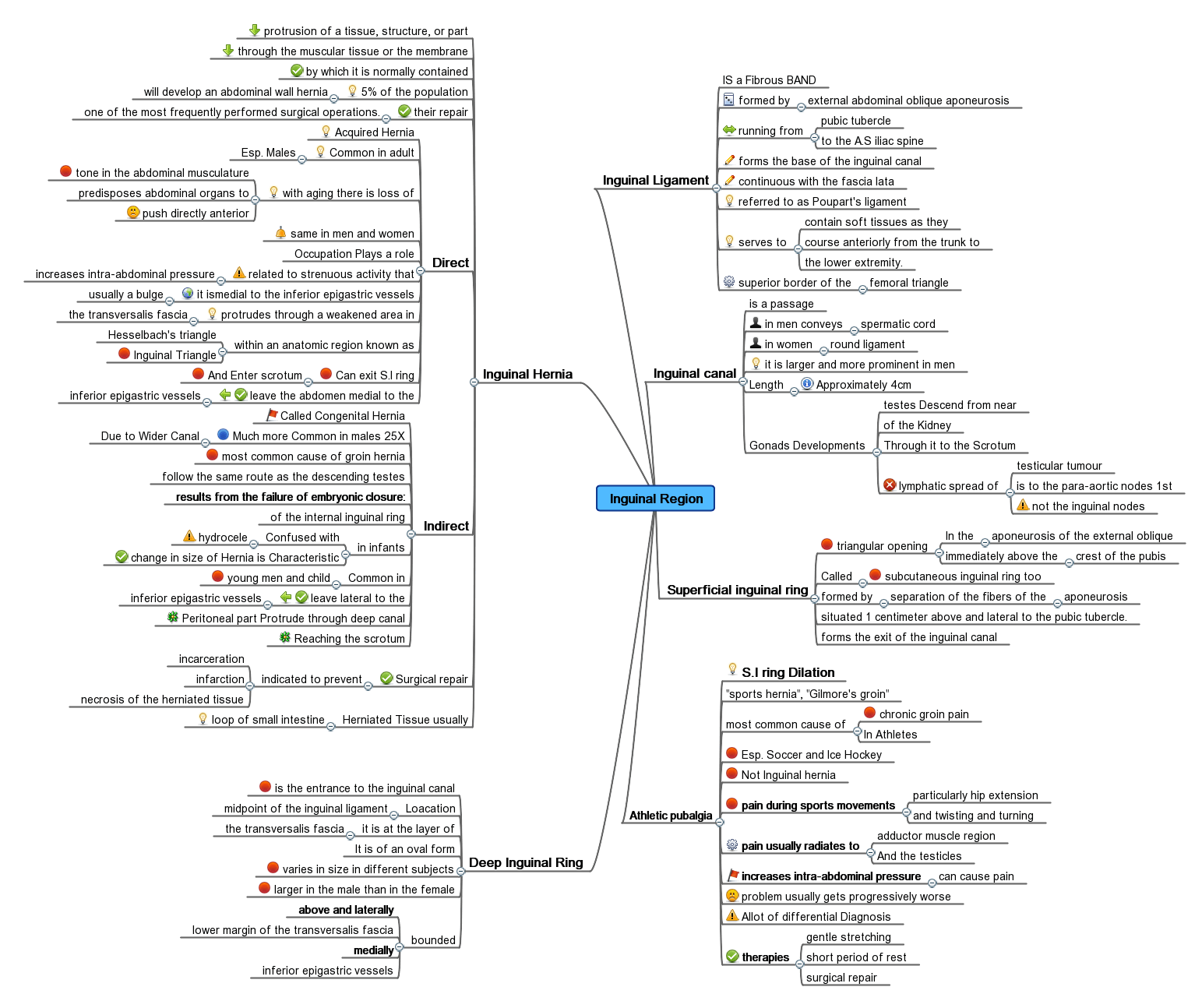 A hernia occurs when intra-abdominal contents, commonly including preperitoneal fatty tissues, the peritoneum itself, and eventually omentum and intestines, traverse the ring to enter the inguinal canal. As time passes, the hernia contents may enlarge, extend the length of the canal, and even exit the canal through the external inguinal ring, an opening in the external oblique fascia, into the scrotum.
A hernia occurs when intra-abdominal contents, commonly including preperitoneal fatty tissues, the peritoneum itself, and eventually omentum and intestines, traverse the ring to enter the inguinal canal. As time passes, the hernia contents may enlarge, extend the length of the canal, and even exit the canal through the external inguinal ring, an opening in the external oblique fascia, into the scrotum.
Failure of the processus vaginalis
to close properly is very common in infants and will usually leave only a small hole through which abdominal fluid can pass from the abdomen into the scrotum. This is termed a communicating hydrocele
and must be differentiated from a non-communicating hydrocele.
In a communicating hydrocele, the fluid collection will change in size from time to time as fluid may drain back and forth between abdominal cavity and scrotum and on examination there will be no way to "get over" the hydrocele when palpating. This is in contrast to a non-communicating hydrocele, which is a distinct entity that occurs when there is excess fluid formation within the scrotum for any number of reasons.
and vein
, indicating that it arose at the top of the inguinal canal.
Inguinal hernia
An inguinal hernia is a protrusion of abdominal-cavity contents through the inguinal canal. They are very common , and their repair is one of the most frequently performed surgical operations....
that results from the failure of embryonic closure of the deep inguinal ring
Deep inguinal ring
The deep inguinal ring is the entrance to the inguinal canal.-Location:...
after the testicle
Testicle
The testicle is the male gonad in animals. Like the ovaries to which they are homologous, testes are components of both the reproductive system and the endocrine system...
has passed through it. Like other inguinal hernias, it protrudes through the superficial inguinal ring. It is the most common cause of groin hernia
Groin hernia
A groin hernia is a hernia in the groin and can be one of the following:*Inguinal hernia: A hernia through the inguinal canal*Femoral hernia: A hernia through the femoral canal*Velpeau hernia: A rare hernia in the groin in front of the femoral blood vessels...
.
Presentation
In the male fetus, the peritoneumPeritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity or the coelom — it covers most of the intra-abdominal organs — in amniotes and some invertebrates...
gives a coat to the testicle as it passes through this ring, forming a temporary connection called the processus vaginalis
Processus vaginalis
The processus vaginalis is an embryonic developmental outpouching of the peritoneum.It is present from around the 12th week of gestation, and commences as a peritoneal outpouching.-Gender differences:...
. In normal development, the processus is obliterated once the testicle is completely descended. The permanent coat of peritoneum that remains around the testicle is called the tunica vaginalis
Tunica vaginalis
The tunica vaginalis is the serous covering of the testis.It is a pouch of serous membrane, derived from the processus vaginalis of the peritoneum, which in the fetus preceded the descent of the testis from the abdomen into the scrotum....
. The testicle remains connected to its blood vessels and the vas deferens, which make up the spermatic cord
Spermatic cord
The spermatic cord is the name given to the cord-like structure in males formed by the ductus deferens and surrounding tissue that run from the abdomen down to each testicle.-Contents of spermatic cord:...
and descend through the inguinal canal to the scrotum.
The deep inguinal ring, which is the beginning of the inguinal canal, remains as an opening in the fascia transversalis, which forms the muscular outer wall for the spermatic cord. When the opening is larger than necessary for passage of the spermatic cord, the stage is set for an indirect inguinal hernia. The protrusion of peritoneum through the internal inguinal ring can be considered an incomplete obliteration of the processus.
In an indirect inguinal hernia, the protrusion passes through the deep inguinal ring and is located lateral to the inferior epigastric artery. Hence, the conjoint tendon is not weakened.
Causes

Failure of the processus vaginalis
Processus vaginalis
The processus vaginalis is an embryonic developmental outpouching of the peritoneum.It is present from around the 12th week of gestation, and commences as a peritoneal outpouching.-Gender differences:...
to close properly is very common in infants and will usually leave only a small hole through which abdominal fluid can pass from the abdomen into the scrotum. This is termed a communicating hydrocele
Hydrocele
A hydrocoele denotes a pathological accumulation of serous fluid in a body cavity. It can also be noted as a minor malformation of newborns due to high levels of lead in the mother's blood during pregnancy....
and must be differentiated from a non-communicating hydrocele.
In a communicating hydrocele, the fluid collection will change in size from time to time as fluid may drain back and forth between abdominal cavity and scrotum and on examination there will be no way to "get over" the hydrocele when palpating. This is in contrast to a non-communicating hydrocele, which is a distinct entity that occurs when there is excess fluid formation within the scrotum for any number of reasons.
In females
In the female, groin hernias are only 4% as common as in males. Indirect inguinal hernia is still the most common groin hernia for females. If a woman has an indirect inguinal hernia, her internal inguinal ring is patent, which is abnormal for females. The protrusion of peritoneum is not called "processus vaginalis" in women, as this structure is related to the migration of the testicle to the scrotum. It is simply a hernia sac. The eventual destination of the hernia contents for a woman is the labium majoris on the same side, and hernias can enlarge one labium dramatically if they are allowed to progress.Treatment
During herniorraphy, the surgeon recognizes the "indirect" hernia by noting that the hernia sac begins lateral to the inferior epigastric arteryInferior epigastric artery
In human anatomy, inferior epigastric artery refers to the artery that arises from the external iliac artery and anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery...
and vein
Inferior epigastric vein
In human anatomy, inferior epigastric vein refers to the vein that drains into the external iliac vein and arises from the superior epigastric vein...
, indicating that it arose at the top of the inguinal canal.

