
Impression (dental)
Encyclopedia
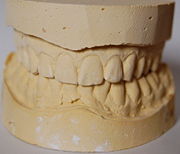
The required type of material for taking an impression and the area that it covers will depend on the clinical indication.
A correct taken dental impression will describ a part or all of a person's dentition
Dentition
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age...
and other areas of the oral cavity. The dental impression forms an imprint (i.e. a 'negative' mould) of those teeth and soft tissues, which can then be used to make a cast
Casting
In metalworking, casting involves pouring liquid metal into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowing it to cool and solidify. The solidified part is also known as a casting, which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process...
or 'positive' model
Model (physical)
A physical model is a smaller or larger physical copy of an object...
of the dentition
Dentition
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age...
. This may be used for the fabrication of dentures, crowns
Crown (dentistry)
A crown is a type of dental restoration which completely caps or encircles a tooth or dental implant. Crowns are often needed when a large cavity threatens the ongoing health of a tooth. They are typically bonded to the tooth using a dental cement. Crowns can be made from many materials, which...
or other prostheses and orthodontics.
An impression is carried out by placing a viscous liquid material into the mouth, usually in a customised dental impression tray. The material, usually an alginate, then sets to become an elastic solid, and, when removed from the mouth, provides a detailed and stable reproduction of teeth. Common materials used for dental impressions are sodium alginate, polyether and silicone
Silicone
Silicones are inert, synthetic compounds with a variety of forms and uses. Typically heat-resistant and rubber-like, they are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medical applications , cookware, and insulation....
s - both condensation
Condensation
Condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from gaseous phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition....
-cured
Curing (chemistry)
Curing is a term in polymer chemistry and process engineering that refers to the toughening or hardening of a polymer material by cross-linking of polymer chains, brought about by chemical additives, ultraviolet radiation, electron beam or heat...
silicones and addition-cured silicones, such as polyvinyl siloxane
Polyvinyl siloxane
Polyvinyl siloxane , introduced in the 1970s, is an addition reaction silicone elastomer, used in Dentistry as an impression material.To create the material, simply mix a blue putty with a white putty and the chemical reaction begins, in which case you have approximately 3-5 minutes before the...
. Historically plaster of Paris, zinc oxide eugenol
Zinc Oxide Eugenol
Zinc oxide eugenol is a material created by the combination of zinc oxide and eugenol contained in oil of cloves. An acid-base reaction takes place with the formation of zinc eugenolate chelate. The reaction is catalysed by water and is accelerated by the presence metal salts. ZOE can be used as...
and agar
Agar
Agar or agar-agar is a gelatinous substance derived from a polysaccharide that accumulates in the cell walls of agarophyte red algae. Throughout history into modern times, agar has been chiefly used as an ingredient in desserts throughout Asia and also as a solid substrate to contain culture medium...
have been used.

