
Identity 2.0
Encyclopedia
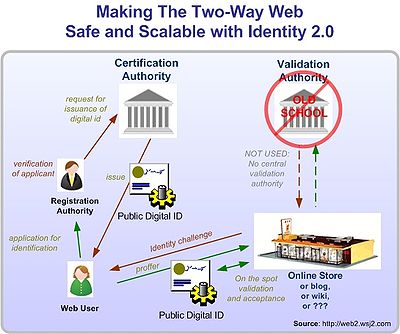
Digital identity
Digital identity is the aspect of digital technology that is concerned with the mediation of people's experience of their own identity and the identity of other people and things...
, is set of methods for identity
Online identity
An online identity, internet identity, or internet persona is a social identity that an Internet user establishes in online communities and websites...
verification on the internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
using emerging user-centric technologies such as Information Card
Information Card
Information Cards are personal digital identities that people can use online, and the key component of Identity metasystems. Visually, each Information Card has a card-shaped picture and a card name associated with it that enable people to organize their digital identities and to easily select...
s or OpenID
OpenID
OpenID is an open standard that describes how users can be authenticated in a decentralized manner, eliminating the need for services to provide their own ad hoc systems and allowing users to consolidate their digital identities...
. Identity 2.0 stems from the Web 2.0
Web 2.0
The term Web 2.0 is associated with web applications that facilitate participatory information sharing, interoperability, user-centered design, and collaboration on the World Wide Web...
theory of the World Wide Web transition. Its emphasis is a simple and open method of identitying transactions similar to those in the physical world, such as driver's license.
Industry analyst firm the Burton Group described it as follows: "In Identity 2.0, usage of identity more closely resembles today's offline identity systems, but with the advantages of a digital medium. As with a driver's license, the issuer provides the user with a certified document containing claims. The user can then choose to show this information when the situation requires".
The current internet model makes taking one's identification
Identification (information)
The function of identification is to map a known quantity to an unknown entity so as to make it known. The known quantity is called the identifier and the unknown entity is what needs identification. A basic requirement for identification is that the Id be unique. Ids may be scoped, that is, they...
difficult from site to site. This was described in the Burton Group report as, "today's identity systems—which represent a “1.0” architecture, feature strong support for domain management but exhibit scalability and flexibility limitations when faced with the broader identity requirements of Internet scenarios." In that light, user-centric proponents believe "federation protocols (from Liberty Alliance, the Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards [OASIS], and the Web Services working group) are bastions of a domain-centric model but do little to recast the architectural foundations of identity systems to support grander structures."
A major road block to creating Identity 2.0 is the strength of the existing infrastructure
Infrastructure
Infrastructure is basic physical and organizational structures needed for the operation of a society or enterprise, or the services and facilities necessary for an economy to function...
. Industry analysts Gartner
Gartner
Gartner, Inc. is an information technology research and advisory firm headquartered in Stamford, Connecticut, United States. It was known as GartnerGroup until 2001....
Research reflect this perspective in their August 2006 report, stating
"Identity 2.0 will be relevant to online companies — and particularly consumer-focused companies — but not before 2008. There are various Identity 2.0 initiatives — including Microsoft's CardSpace (formerly InfoCard), Sxip and HigginsHiggins trust frameworkHiggins is an open source project dedicated to giving individuals more control over their personal identity, profile and social network data.The project is organized into three main areas:...
. While all the initiatives leverage Internet and Web protocols, there are different approaches for storing identity attributes and in securing the interactions; these different approaches are not clearly interoperable and lack a unifying standards-based framework.
Success for Identity 2.0 approaches will also require service providers to modify their Web sites and services to request, accept and authenticate identity data from clients and identity providers. This presents a potential "chicken and egg" problem whereby consumers don’t perceive the need to create digital personas until services are available to use them."
A year later, Gartner published an updated perspective in their 2007 Hype Cycle Report on IAM Technologies, that positions user-centric, Identity 2.0 technologies such as OpenID, CardSpace and Higgins as "technology triggers" that are "on the rise", though two to five years away from mainstream adoption. They recommend that consumer facing organizations monitor the evolution of these "Personal Identity Frameworks".
In an Identity 2.0 approach, rather than using multiple username/passwords to register onto a website (like the current model), Identity 2.0 would allow users to use one ID that is transparent and flexible. Identity 2.0 is focused around the user, not centered around a directory. It requires identified transactions between users and agents (websites) using verifiable data, thus providing more traceable transactions.
Using one identity all of the time could lead to compromised privacy or security, especially in the following cases:
- when an open identity is phished or compromised,
- when users would not usually choose to use a strongly authenticated identity but are forced to do so by system properties or market pressure,
- when unrelated actions are linked with the purpose of predicting or controlling the behaviour of a user.
Verifiable but unlinkable data can be provided by users via anonymous digital credentials
Digital credential
Digital credentials are the digital equivalent of paper-based credentials. Just as a paper-based credential could be a passport, a Driver's license, a membership certificate or some kind of ticket to obtain some service, such as a cinema ticket or a public transport ticket, a digital credential is...
. The subtleties of building up trust in situations of less than perfect knowledge, which are intuitively understood in the physical world, are investigated by trust negotiation
Trust negotiation
Trust Negotiation is an approach to gradually establishing trust between strangers online through the iterative exchange of digital credentials. In contrast to a closed system, where the interacting entities have a preexisting relationship , trust negotiation is an open system, and complete...
.
See also
- AuthenticationAuthenticationAuthentication is the act of confirming the truth of an attribute of a datum or entity...
- Digital IdentityDigital identityDigital identity is the aspect of digital technology that is concerned with the mediation of people's experience of their own identity and the identity of other people and things...
- Higgins trust frameworkHiggins trust frameworkHiggins is an open source project dedicated to giving individuals more control over their personal identity, profile and social network data.The project is organized into three main areas:...
- Identity Metasystem
- Information CardInformation CardInformation Cards are personal digital identities that people can use online, and the key component of Identity metasystems. Visually, each Information Card has a card-shaped picture and a card name associated with it that enable people to organize their digital identities and to easily select...
- LIDLight-Weight IdentityLID is a management system for online digital identities developed in part by . It was first published in early 2005, and is the original URL-based identity system, later followed by OpenID. LID uses URLs as a verification of the user's identity, and makes use of several open-source protocols...
- SAMLSAMLSecurity Assertion Markup Language is an XML-based open standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between security domains, that is, between an identity provider and a service provider...
- XRI XDIXDIXDI is a generalized, extensible service for sharing, linking, and synchronizing structured data over the Internet and other data networks using XRI-addressable RDF graphs...
- YADISYadisYadis is a communications protocol for discovery of services such as OpenID, OAuth, and XDI connected to a Yadis ID. While intended to discover digital identity services, Yadis is not restricted to those. Other services can easily be included....
- Global Trust CenterGlobal Trust CenterGlobal Trust Center is an international not-for-profit organisation that aims to develop policies to protect the rights and integrity of individual users of digital communications while reaffirming accountability and legal values...
External links
- Phil Windley: Identity Management Architectures and Digital Identity

