
Hubble volume
Encyclopedia
In cosmology
, the Hubble volume, or Hubble sphere, is the region of the Universe
surrounding an observer beyond which objects recede from the observer at a rate greater than the speed of light
, due to the expansion of the Universe.
The comoving
radius of the Hubble sphere is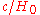 , where
, where  is the speed of light
is the speed of light
and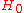 is the Hubble constant.
is the Hubble constant.
More generally, the term "Hubble volume" can be applied to any region of space with a volume of order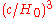 .
.
The term "Hubble volume" is also frequently (but mistakenly) used as a synonym
for the observable universe
; the latter is larger than the Hubble volume.
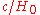 is known as the "Hubble length". It is equal to 13.9 billion light years in the standard cosmological model
is known as the "Hubble length". It is equal to 13.9 billion light years in the standard cosmological model
, similar to but somewhat larger than times the age of the universe
times the age of the universe
. This is because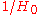 gives the age of the universe by a backward extrapolation which assumes that the recession speed of each galaxy has been constant since the Big Bang. In fact, recession speeds initially decelerate due to gravity, and are now accelerating due to dark energy
gives the age of the universe by a backward extrapolation which assumes that the recession speed of each galaxy has been constant since the Big Bang. In fact, recession speeds initially decelerate due to gravity, and are now accelerating due to dark energy
, so that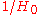 is only an approximation to the true age.
is only an approximation to the true age.
, objects at the Hubble limit have an average comoving speed of c relative to an observer on the Earth. This is significant, because, in a universe in which the Hubble parameter was constant, light emitted at the present time by objects outside the Hubble limit could never be seen by an observer on the Earth. However, the Hubble "constant" is not constant. In a decelerating Friedmann universe
, the Hubble sphere expands faster than the Universe and its boundary overtakes light emitted by receding galaxies. In an accelerating universe, the Hubble sphere expands more slowly than the Universe, and bodies move out of the Hubble sphere. So the Hubble limit need not define the cosmological event horizon
(that is, the boundary separating events visible at some time or other and those that are never visible), because (depending upon the cosmological model) light emitted at earlier times by objects outside the Hubble sphere still may eventually arrive inside the sphere and be seen by us. If, as is inferred from current observations, the expansion of the universe is in fact accelerating
, then at a later time, some objects within the Hubble limit no longer will be observed (by us) as they are today.
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology, as a branch of astronomy, is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its formation and evolution. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion...
, the Hubble volume, or Hubble sphere, is the region of the Universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
surrounding an observer beyond which objects recede from the observer at a rate greater than the speed of light
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
, due to the expansion of the Universe.
The comoving
Comoving distance
In standard cosmology, comoving distance and proper distance are two closely related distance measures used by cosmologists to define distances between objects...
radius of the Hubble sphere is
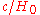 , where
, where  is the speed of light
is the speed of lightSpeed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
and
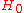 is the Hubble constant.
is the Hubble constant.More generally, the term "Hubble volume" can be applied to any region of space with a volume of order
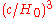 .
.The term "Hubble volume" is also frequently (but mistakenly) used as a synonym
Synonym
Synonyms are different words with almost identical or similar meanings. Words that are synonyms are said to be synonymous, and the state of being a synonym is called synonymy. The word comes from Ancient Greek syn and onoma . The words car and automobile are synonyms...
for the observable universe
Observable universe
In Big Bang cosmology, the observable universe consists of the galaxies and other matter that we can in principle observe from Earth in the present day, because light from those objects has had time to reach us since the beginning of the cosmological expansion...
; the latter is larger than the Hubble volume.
Expansion of the universe changed
The distance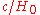 is known as the "Hubble length". It is equal to 13.9 billion light years in the standard cosmological model
is known as the "Hubble length". It is equal to 13.9 billion light years in the standard cosmological modelLambda-CDM model
ΛCDM or Lambda-CDM is an abbreviation for Lambda-Cold Dark Matter, which is also known as the cold dark matter model with dark energy...
, similar to but somewhat larger than
 times the age of the universe
times the age of the universeAge of the universe
The age of the universe is the time elapsed since the Big Bang posited by the most widely accepted scientific model of cosmology. The best current estimate of the age of the universe is 13.75 ± 0.13 billion years within the Lambda-CDM concordance model...
. This is because
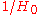 gives the age of the universe by a backward extrapolation which assumes that the recession speed of each galaxy has been constant since the Big Bang. In fact, recession speeds initially decelerate due to gravity, and are now accelerating due to dark energy
gives the age of the universe by a backward extrapolation which assumes that the recession speed of each galaxy has been constant since the Big Bang. In fact, recession speeds initially decelerate due to gravity, and are now accelerating due to dark energyDark energy
In physical cosmology, astronomy and celestial mechanics, dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and tends to accelerate the expansion of the universe. Dark energy is the most accepted theory to explain recent observations that the universe appears to be expanding...
, so that
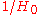 is only an approximation to the true age.
is only an approximation to the true age.Hubble limit
The boundary of the Hubble volume is known as the "Hubble limit". Per Hubble's lawHubble's law
Hubble's law is the name for the astronomical observation in physical cosmology that: all objects observed in deep space are found to have a doppler shift observable relative velocity to Earth, and to each other; and that this doppler-shift-measured velocity, of various galaxies receding from...
, objects at the Hubble limit have an average comoving speed of c relative to an observer on the Earth. This is significant, because, in a universe in which the Hubble parameter was constant, light emitted at the present time by objects outside the Hubble limit could never be seen by an observer on the Earth. However, the Hubble "constant" is not constant. In a decelerating Friedmann universe
Friedmann equations
The Friedmann equations are a set of equations in physical cosmology that govern the expansion of space in homogeneous and isotropic models of the universe within the context of general relativity...
, the Hubble sphere expands faster than the Universe and its boundary overtakes light emitted by receding galaxies. In an accelerating universe, the Hubble sphere expands more slowly than the Universe, and bodies move out of the Hubble sphere. So the Hubble limit need not define the cosmological event horizon
Event horizon
In general relativity, an event horizon is a boundary in spacetime beyond which events cannot affect an outside observer. In layman's terms it is defined as "the point of no return" i.e. the point at which the gravitational pull becomes so great as to make escape impossible. The most common case...
(that is, the boundary separating events visible at some time or other and those that are never visible), because (depending upon the cosmological model) light emitted at earlier times by objects outside the Hubble sphere still may eventually arrive inside the sphere and be seen by us. If, as is inferred from current observations, the expansion of the universe is in fact accelerating
Accelerating universe
The accelerating universe is the observation that the universe appears to be expanding at an increasing rate, which in formal terms means that the cosmic scale factor a has a positive second derivative, implying that the velocity at which a given galaxy is receding from us should be continually...
, then at a later time, some objects within the Hubble limit no longer will be observed (by us) as they are today.

