
Hindmarsh-Rose model
Encyclopedia
The Hindmarsh–Rose model of neuron
al activity is aimed to study the spiking-bursting behavior of the membrane potential
observed in experiments made with a single neuron. The relevant variable is the membrane potential, x(t), which is written in dimensionless units. There are two more variables, y(t) and z(t), which take into account the transport of ions across the membrane through the ion channel
s. The transport of sodium and potassium ions is made through fast ion channels and its rate is measured by y(t), which is called the spiking variable. The transport of other ions is made thorough slow channels, and is taken into account thorough z(t), which is called the bursting variable. Then, the Hindmarsh–Rose model has the mathematical form of a system of three nonlinear ordinary differential equation
s on the dimensionless dynamical variables x(t), y(t), and z(t). They read:
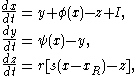
where
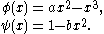
The model has six parameters: a, b, r, s, xR and I. It is very common to fix some of them and let the other to be control parameters. Usually the parameter I, which means the current that enters the neuron, is taken as a control parameter. Other control parameters used often in the literature are a, b or r, the first two modeling the working of the fast ion channels and the last one the slow ion channels, respectively. Very frequently, the parameters held fixed are s = 4 and xR = −8/5. When a or b are fixed the values given are a = 3 and b = 5. The parameter r is something of the order of 10−3, and I ranges between −10 and 10.
The third state equation: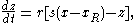
allows a great variety of dynamic behaviors of the membrane potential, described by variable x, including unpredictable behavior, which is referred to as chaotic dynamics
. This makes the Hindmarsh–Rose model very useful, because it is relatively simple and provides a good qualitative description of the many different patterns that are observed empirically.
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
al activity is aimed to study the spiking-bursting behavior of the membrane potential
Membrane potential
Membrane potential is the difference in electrical potential between the interior and exterior of a biological cell. All animal cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane composed of a lipid bilayer with a variety of types of proteins embedded in it...
observed in experiments made with a single neuron. The relevant variable is the membrane potential, x(t), which is written in dimensionless units. There are two more variables, y(t) and z(t), which take into account the transport of ions across the membrane through the ion channel
Ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient. They are present in the membranes that surround all biological cells...
s. The transport of sodium and potassium ions is made through fast ion channels and its rate is measured by y(t), which is called the spiking variable. The transport of other ions is made thorough slow channels, and is taken into account thorough z(t), which is called the bursting variable. Then, the Hindmarsh–Rose model has the mathematical form of a system of three nonlinear ordinary differential equation
Ordinary differential equation
In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is a relation that contains functions of only one independent variable, and one or more of their derivatives with respect to that variable....
s on the dimensionless dynamical variables x(t), y(t), and z(t). They read:
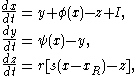
where
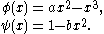
The model has six parameters: a, b, r, s, xR and I. It is very common to fix some of them and let the other to be control parameters. Usually the parameter I, which means the current that enters the neuron, is taken as a control parameter. Other control parameters used often in the literature are a, b or r, the first two modeling the working of the fast ion channels and the last one the slow ion channels, respectively. Very frequently, the parameters held fixed are s = 4 and xR = −8/5. When a or b are fixed the values given are a = 3 and b = 5. The parameter r is something of the order of 10−3, and I ranges between −10 and 10.
The third state equation:
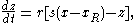
allows a great variety of dynamic behaviors of the membrane potential, described by variable x, including unpredictable behavior, which is referred to as chaotic dynamics
Chaos theory
Chaos theory is a field of study in mathematics, with applications in several disciplines including physics, economics, biology, and philosophy. Chaos theory studies the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, an effect which is popularly referred to as the...
. This makes the Hindmarsh–Rose model very useful, because it is relatively simple and provides a good qualitative description of the many different patterns that are observed empirically.
See also
- Biological neuron models
- Hodgkin–Huxley model
- Computational neuroscienceComputational neuroscienceComputational neuroscience is the study of brain function in terms of the information processing properties of the structures that make up the nervous system...
- Neural oscillation

