
Helly metric
Encyclopedia
In game theory
, the Helly metric is used to assess the distance between two strategies
. It is named for Eduard Helly
.
Consider a game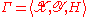 , between player I and II. Here,
, between player I and II. Here,  and
and  are the sets of pure strategies for players I and II respectively; and
are the sets of pure strategies for players I and II respectively; and 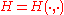 is the payoff function.
is the payoff function.
(in other words, if player I plays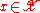 and player II plays
and player II plays 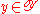 , then player I pays
, then player I pays 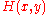 to player II).
to player II).
The Helly metric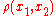 is defined as
is defined as
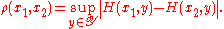
The metric so defined is symmetric, reflexive, and satisfies the triangle inequality
.
The Helly metric measures distances between strategies, not in terms of the differences between the strategies themselves, but in terms of the consequences of the strategies. Two strategies are distant if their payoffs are different. Note that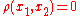 does not imply
does not imply  but it does imply that the consequences of
but it does imply that the consequences of 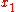 and
and 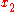 are identical; and indeed this induces an equivalence relation
are identical; and indeed this induces an equivalence relation
.
If one stipulates that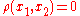 implies
implies  then the topology so induced is called the natural topology
then the topology so induced is called the natural topology
.
The metric on the space of player II's strategies is analogous:
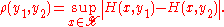
Note that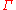 thus defines two Helly metrics: one for each player.
thus defines two Helly metrics: one for each player.
 -net). A set
-net). A set 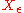 is an
is an  -net in the space
-net in the space  with metric
with metric 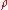 if for any
if for any 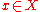 there exists
there exists 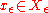 with
with 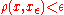 .
.
A metric space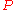 is conditionally compact if for any
is conditionally compact if for any 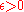 there exists a finite
there exists a finite  -net in
-net in 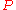 .
.
A game that is conditionally compact in the Helly metric has an -optimal strategy for any
-optimal strategy for any 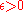 .
.
Game theory
Game theory is a mathematical method for analyzing calculated circumstances, such as in games, where a person’s success is based upon the choices of others...
, the Helly metric is used to assess the distance between two strategies
Strategy
Strategy, a word of military origin, refers to a plan of action designed to achieve a particular goal. In military usage strategy is distinct from tactics, which are concerned with the conduct of an engagement, while strategy is concerned with how different engagements are linked...
. It is named for Eduard Helly
Eduard Helly
Eduard Helly was a mathematician and the eponym of Helly's theorem, Helly families, Helly's selection theorem, Helly metric, and the Helly–Bray theorem. In 1912, Helly published a proof of Hahn–Banach theorem, 15 years before Hahn and Banach discovered it independently...
.
Consider a game
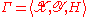 , between player I and II. Here,
, between player I and II. Here,  and
and  are the sets of pure strategies for players I and II respectively; and
are the sets of pure strategies for players I and II respectively; and 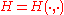 is the payoff function.
is the payoff function.(in other words, if player I plays
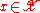 and player II plays
and player II plays 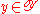 , then player I pays
, then player I pays 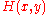 to player II).
to player II).The Helly metric
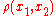 is defined as
is defined as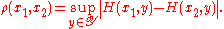
The metric so defined is symmetric, reflexive, and satisfies the triangle inequality
Triangle inequality
In mathematics, the triangle inequality states that for any triangle, the sum of the lengths of any two sides must be greater than or equal to the length of the remaining side ....
.
The Helly metric measures distances between strategies, not in terms of the differences between the strategies themselves, but in terms of the consequences of the strategies. Two strategies are distant if their payoffs are different. Note that
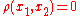 does not imply
does not imply  but it does imply that the consequences of
but it does imply that the consequences of  and
and  are identical; and indeed this induces an equivalence relation
are identical; and indeed this induces an equivalence relationEquivalence relation
In mathematics, an equivalence relation is a relation that, loosely speaking, partitions a set so that every element of the set is a member of one and only one cell of the partition. Two elements of the set are considered equivalent if and only if they are elements of the same cell...
.
If one stipulates that
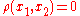 implies
implies  then the topology so induced is called the natural topology
then the topology so induced is called the natural topologyNatural topology
In any domain of mathematics, a space has a natural topology if there is a topology on the space which is "best adapted" to its study within the domain in question...
.
The metric on the space of player II's strategies is analogous:
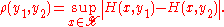
Note that
 thus defines two Helly metrics: one for each player.
thus defines two Helly metrics: one for each player.Conditional compactness
Notation (definition of an -net). A set
-net). A set 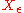 is an
is an  -net in the space
-net in the space  with metric
with metric 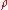 if for any
if for any 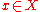 there exists
there exists 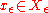 with
with 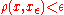 .
.A metric space
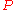 is conditionally compact if for any
is conditionally compact if for any  there exists a finite
there exists a finite  -net in
-net in 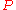 .
.A game that is conditionally compact in the Helly metric has an
 -optimal strategy for any
-optimal strategy for any  .
.
