
Hazy Sighted Link State Routing Protocol
Encyclopedia
The Hazy-Sighted Link State Routing Protocol (HSLS) is a wireless mesh network
routing protocol
being developed by the CUWiN Foundation. This is an algorithm
allowing computer
s communicating via digital radio
in a mesh network to forward messages to computers that are out of reach of direct radio contact. Its network overhead is theoretically optimal, utilizing both proactive and reactive link-state
routing to limit network updates in space and time. Its inventors believe it is a more efficient protocol to route wired networks as well. HSLS was invented by researchers at BBN Technologies
.
are theoretically attractive because they find optimal routes, reducing waste of transmission capacity. The inventors of HSLS claim that routing protocols fall into three basically different schemes: proactive (such as OLSR), reactive (such as AODV), and algorithms that accept sub-optimal routings. If one graphs them, they become less efficient as they are more purely any single strategy, and the network grows larger. The best algorithms seem to be in a sweet spot in the middle.
The routing information is called a "link state update." The distance that a link-state is copied is the "time to live
" and is a count of the number of times it may be copied from one node to the next.
HSLS is said to optimally balance the features of proactive, reactive, and suboptimal routing approaches. These strategies are blended by limiting link state updates in time and space. By limiting the time to live the amount of transmission capacity is reduced. By limiting the times when a proactive routing update is transmitted, several updates can be collected and transmitted at once, also saving transmission capacity.
They then made some reasonable assumptions and used a mathematical optimization to find the times to transmit link state updates, and also the breadth of nodes that the link state updates should cover.
Basically, both should grow to the power of two as time increases. The theoretical optimal number is very near to two, with an error of only 0.7%. This is substantially smaller than the likely errors from the assumptions, so two is a perfectly reasonable number.
A local routing update is forced whenever a connection is lost. This is the reactive part of the algorithm. A local routing update behaves just the same as the expiration of a timer.
Otherwise, each time that the delay since the last update doubles, the node transmits routing information that doubles in the number of network-hops it considers. This continues up to some upper limit. An upper limit gives the network a global size and assures a fixed maximum response time for a network without any moving nodes.
The algorithm has a few special features to cope with cases that are common in radio networks, such as unidirectional links, and looped-transmission caused by out-of-date routing table
s. In particular, it reroutes all transmissions to nearby nodes whenever it loses a link to an adjacent node. It also retransmits its adjacency when this occurs. This is useful precisely because the most valuable, long-distance links are also the least reliable in a radio network;
The actual algorithm is quite simple.
The routing information and the data transfer are decentralized, and should therefore have good reliability and performance with no local hot spots.
The system requires capable nodes with large amounts of memory to maintain routing tables. Fortunately, these are becoming less expensive all the time.
The system gives a very quick, relatively accurate guess about whether a node is in the network, because complete, though out-of-date routing information is present in every node. However, this is not the same as knowing whether a node is in the network. This guess may be adequate for most tariff network use, like telephony, but it may not be adequate for safety-related military or avionics
.
HSLS has good scalability properties. The asymptotic scalability of its total overhead is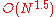 compared to standard link state which scales as
compared to standard link state which scales as 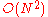 , where N is the number of nodes in the network.
, where N is the number of nodes in the network.
While the papers describing HSLS do not focus on security, techniques such as digital signature
s on routing updates can be used with HSLS (similar to OSPF with Digital Signatures), and BBN has implemented HSLS with digital signatures on neighbor discovery messages and link state updates. Such schemes are challenging in practice because in the ad hoc environment reachability of public key infrastructure
servers cannot be assured. Like almost all routing protocols, HSLS does not include mechanisms to protect data traffic. (See IPsec
and TLS
.)
Wireless mesh network
A wireless mesh network is a communications network made up of radio nodes organized in a mesh topology. Wireless mesh networks often consist of mesh clients, mesh routers and gateways.The mesh clients are often laptops, cell phones and other wireless devices while the mesh routers forward traffic...
routing protocol
Routing protocol
A routing protocol is a protocol that specifies how routers communicate with each other, disseminating information that enables them to select routes between any two nodes on a computer network, the choice of the route being done by routing algorithms. Each router has a priori knowledge only of...
being developed by the CUWiN Foundation. This is an algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
allowing computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
s communicating via digital radio
Digital radio
Digital radio has several meanings:1. Today the most common meaning is digital radio broadcasting technologies, such as the digital audio broadcasting system, also known as Eureka 147. In these systems, the analog audio signal is digitized into zeros and ones, compressed using formats such as...
in a mesh network to forward messages to computers that are out of reach of direct radio contact. Its network overhead is theoretically optimal, utilizing both proactive and reactive link-state
Link-state routing protocol
A link-state routing protocol is one of the two main classes of routing protocols used in packet switching networks for computer communications . Examples of link-state routing protocols include OSPF and IS-IS....
routing to limit network updates in space and time. Its inventors believe it is a more efficient protocol to route wired networks as well. HSLS was invented by researchers at BBN Technologies
BBN Technologies
BBN Technologies is a high-technology company which provides research and development services. BBN is based next to Fresh Pond in Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA...
.
Efficiency
HSLS was made to scale well to networks of over a thousand nodes, and on larger networks begins to exceed the efficiencies of the other routing algorithms. This is accomplished by using a carefully designed balance of update frequency, and update extent in order to propagate link state information optimally. Unlike traditional methods, HSLS does not flood the network with link-state information to attempt to cope with moving nodes that change connections with the rest of the network. Further, HSLS does not require each node to have the same view of the network.Why a link-state protocol?
Link-state algorithmsLink-state routing protocol
A link-state routing protocol is one of the two main classes of routing protocols used in packet switching networks for computer communications . Examples of link-state routing protocols include OSPF and IS-IS....
are theoretically attractive because they find optimal routes, reducing waste of transmission capacity. The inventors of HSLS claim that routing protocols fall into three basically different schemes: proactive (such as OLSR), reactive (such as AODV), and algorithms that accept sub-optimal routings. If one graphs them, they become less efficient as they are more purely any single strategy, and the network grows larger. The best algorithms seem to be in a sweet spot in the middle.
The routing information is called a "link state update." The distance that a link-state is copied is the "time to live
Time to live
Time to live is a mechanism that limits the lifespan of data in a computer or network. TTL may be implemented as a counter or timestamp attached to or embedded in the data. Once the prescribed event count or timespan has elapsed, data is discarded. In computer networking, TTL prevents a data...
" and is a count of the number of times it may be copied from one node to the next.
HSLS is said to optimally balance the features of proactive, reactive, and suboptimal routing approaches. These strategies are blended by limiting link state updates in time and space. By limiting the time to live the amount of transmission capacity is reduced. By limiting the times when a proactive routing update is transmitted, several updates can be collected and transmitted at once, also saving transmission capacity.
- By definition, a link-state algorithm uses the available information to produce the best route, so routing is as optimal as possible, given the available information.
- The suboptimal routing happens naturally because distant nodes get information less frequently.
- Minimizing proactive updates is the tricky part. The scheme is adapted from two limited link-state routing algorithms. One, "Near-Sighted Link-State Routing" is limited in space, in the number of node-hops that routing information may be transmitted. The other routing algorithm, "Discretized Link-State Routing" limits the times that the routing information may be transmitted. Since the optimal update attenuation in both space and time is about two, the result is a periodic proactive update, with fractal power-of-two node hop distances for the data (e.g. hop distances of 1, 2, 1, 4, 1, 2, 1, 8...).
- The reactive routing occurs because a failed attempt to use an adjacent link causes the next timer to expire, probably drawing in the information to find an alternate route. On each successive failure, a retry escalates the reaction to wider audiences of meshed nodes.
How it works
The designers started the tuning of these items by defining a measure of global network waste. This includes waste from transmitting route updates, and also waste from inefficient transmission paths. Their exact definition is "The total overhead is defined as the amount of bandwidth used in excess of the minimum amount of bandwidth required to forward packets over the shortest distance (in number of hops) by assuming that the nodes had instantaneous full-topology information."They then made some reasonable assumptions and used a mathematical optimization to find the times to transmit link state updates, and also the breadth of nodes that the link state updates should cover.
Basically, both should grow to the power of two as time increases. The theoretical optimal number is very near to two, with an error of only 0.7%. This is substantially smaller than the likely errors from the assumptions, so two is a perfectly reasonable number.
A local routing update is forced whenever a connection is lost. This is the reactive part of the algorithm. A local routing update behaves just the same as the expiration of a timer.
Otherwise, each time that the delay since the last update doubles, the node transmits routing information that doubles in the number of network-hops it considers. This continues up to some upper limit. An upper limit gives the network a global size and assures a fixed maximum response time for a network without any moving nodes.
The algorithm has a few special features to cope with cases that are common in radio networks, such as unidirectional links, and looped-transmission caused by out-of-date routing table
Routing table
In computer networking a routing table, or Routing Information Base , is a data table stored in a router or a networked computer that lists the routes to particular network destinations, and in some cases, metrics associated with those routes. The routing table contains information about the...
s. In particular, it reroutes all transmissions to nearby nodes whenever it loses a link to an adjacent node. It also retransmits its adjacency when this occurs. This is useful precisely because the most valuable, long-distance links are also the least reliable in a radio network;
Advantages
The network establishes pretty good routes in real time, and substantially reduces the number and size of messages sent to keep the network connected, compared to many other protocols. Many of the simpler mesh routing protocols just flood the whole network with routing information whenever a link changes.The actual algorithm is quite simple.
The routing information and the data transfer are decentralized, and should therefore have good reliability and performance with no local hot spots.
The system requires capable nodes with large amounts of memory to maintain routing tables. Fortunately, these are becoming less expensive all the time.
The system gives a very quick, relatively accurate guess about whether a node is in the network, because complete, though out-of-date routing information is present in every node. However, this is not the same as knowing whether a node is in the network. This guess may be adequate for most tariff network use, like telephony, but it may not be adequate for safety-related military or avionics
Avionics
Avionics are electronic systems used on aircraft, artificial satellites and spacecraft.Avionic systems include communications, navigation, the display and management of multiple systems and the hundreds of systems that are fitted to aircraft to meet individual roles...
.
HSLS has good scalability properties. The asymptotic scalability of its total overhead is
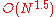 compared to standard link state which scales as
compared to standard link state which scales as 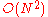 , where N is the number of nodes in the network.
, where N is the number of nodes in the network.Critiques
Because HSLS sends distant updates infrequently, nodes do not have recent information about whether a distant node is still present. This issue is present to some extent in all link state protocols, because the link state database may still contain an announcement from a failed node. However, protocols like OSPF will propagate a link state update from the failed nodes neighbors, and thus all nodes will learn quickly of the failed node's demise (or disconnection). With HSLS, one can't disambiguate between a node that is still present 10 hops away and a failed node until former neighbors send long-distance announcements. Thus, HSLS may fail in some circumstances requiring high assurance.While the papers describing HSLS do not focus on security, techniques such as digital signature
Digital signature
A digital signature or digital signature scheme is a mathematical scheme for demonstrating the authenticity of a digital message or document. A valid digital signature gives a recipient reason to believe that the message was created by a known sender, and that it was not altered in transit...
s on routing updates can be used with HSLS (similar to OSPF with Digital Signatures), and BBN has implemented HSLS with digital signatures on neighbor discovery messages and link state updates. Such schemes are challenging in practice because in the ad hoc environment reachability of public key infrastructure
Public key infrastructure
Public Key Infrastructure is a set of hardware, software, people, policies, and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store, and revoke digital certificates. In cryptography, a PKI is an arrangement that binds public keys with respective user identities by means of a certificate...
servers cannot be assured. Like almost all routing protocols, HSLS does not include mechanisms to protect data traffic. (See IPsec
IPsec
Internet Protocol Security is a protocol suite for securing Internet Protocol communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet of a communication session...
and TLS
Transport Layer Security
Transport Layer Security and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer , are cryptographic protocols that provide communication security over the Internet...
.)
See also
- Ad hoc routing protocol listAd hoc routing protocol listAn ad-hoc routing protocol is a convention, or standard, that controls how nodes decide which way to route packets between computing devices in a mobile ad hoc network ....
- AODV
- Champaign-Urbana Community Wireless NetworkChampaign-Urbana Community Wireless NetworkThe Champaign-Urbana Community Wireless Network is a special project of the Urbana-Champaign Independent Media Center . Started in 2000 by a group of developers wishing to take advantage of under-utilized Internet links purchased for public use , it began a partnership with UCIMC in 2004, gaining...
- DSRDynamic Source Routing'Dynamic Source Routing' is a routing protocol for wireless mesh networks. It is similar to AODV in that it forms a route on-demand when a transmitting computer requests one...
- ExOR (wireless network protocol)ExOR (wireless network protocol)Extremely Opportunistic Routing is a combination of routing protocol and media access control for a wireless ad-hoc network, invented by Sanjit Biswas and Robert Morris of the MIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, and described in a 2005 Paper....
- OLSR
External links
- OLSR fisheye - OLSR from olsr.org implemented the "fisheye" algorithm which is equivalent to HSLS
- NRLOLSR Prototype - extended OLSR to provide an optional HSLS capability

