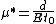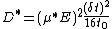Haynes - Shockley experiment
Encyclopedia
The Haynes–Shockley experiment was a classic experiment that demonstrated that diffusion of minority carriers in a semiconductor
could result in a current. The experiment was reported in a paper by Shockley
, Pearson, and Haynes in 1949.
The experiment can be used to measure carrier mobility
, carrier lifetime
, and diffusion coefficient.
In the experiment, a piece of semiconductor gets a pulse of hole
s, for example, as induced by voltage or a short laser
pulse.
To see the effect, we consider a n-type semiconductor
with the length d. We are interested in determining the mobility
of the carriers, diffusion constant and relaxation time
. In the following, we reduce the problem to one dimension.
The equations for electron and hole currents are:
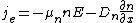
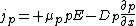
where the first part is the drift current
and the second is the diffusion current
.
We consider the continuity equation
:
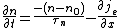
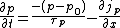
The electrons and the holes recombine with the time .
.
We define and
and 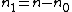 so the upper equations can be rewritten as:
so the upper equations can be rewritten as:
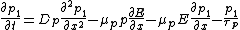
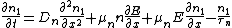
In a simple approximation, we can consider the electric field to be constant between the left and right electrodes and neglect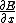 . However, as electrons and holes diffuse at a different speed, the material has a local electric charge, inducing an inhomogeneous electric field which can be calculated with Gauss's law
. However, as electrons and holes diffuse at a different speed, the material has a local electric charge, inducing an inhomogeneous electric field which can be calculated with Gauss's law
:
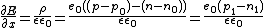
We make the following change of variables: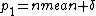 ,
, 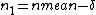 , and suppose
, and suppose 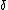 to be much smaller than
to be much smaller than 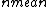 . The two initial equations write:
. The two initial equations write:
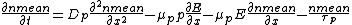
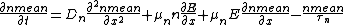
Thanks to Einstein relation
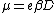 , these two equations can be combined:
, these two equations can be combined:
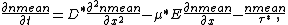
where for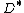 ,
, 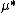 and
and 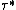 holds:
holds: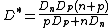 ,
, 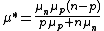 and
and 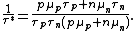
Considering n>>p or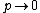 (that is a fair approximation for a semiconductor with only few holes injected), we see that
(that is a fair approximation for a semiconductor with only few holes injected), we see that 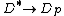 ,
, 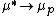 and
and 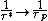 . The semiconductor behaves as if there were only holes traveling in it.
. The semiconductor behaves as if there were only holes traveling in it.
The final equation for the carriers is:
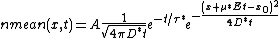
This can be interpreted as a delta function that is created immediately after the pulse. Holes then start to travel towards the electrode where we detect them. The signal then is Gaussian curve shaped.
Parameters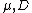 and
and  can be obtained from the shape of the signal.
can be obtained from the shape of the signal.
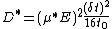
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
could result in a current. The experiment was reported in a paper by Shockley
William Shockley
William Bradford Shockley Jr. was an American physicist and inventor. Along with John Bardeen and Walter Houser Brattain, Shockley co-invented the transistor, for which all three were awarded the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics.Shockley's attempts to commercialize a new transistor design in the 1950s...
, Pearson, and Haynes in 1949.
The experiment can be used to measure carrier mobility
Electron mobility
In solid-state physics, the electron mobility characterizes how quickly an electron can move through a metal or semiconductor, when pulled by an electric field. In semiconductors, there is an analogous quantity for holes, called hole mobility...
, carrier lifetime
Carrier Lifetime
A definition in semiconductor physics, carrier lifetime is defined as the average time it takes for a minority carrier to recombine. The process through which this is done is typically known as minority carrier recombination....
, and diffusion coefficient.
In the experiment, a piece of semiconductor gets a pulse of hole
Electron hole
An electron hole is the conceptual and mathematical opposite of an electron, useful in the study of physics, chemistry, and electrical engineering. The concept describes the lack of an electron at a position where one could exist in an atom or atomic lattice...
s, for example, as induced by voltage or a short laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
pulse.
To see the effect, we consider a n-type semiconductor
N-type semiconductor
N-type semiconductors are a type of extrinsic semiconductor where the dopant atoms are capable of providing extra conduction electrons to the host material . This creates an excess of negative electron charge carriers....
with the length d. We are interested in determining the mobility
Electron mobility
In solid-state physics, the electron mobility characterizes how quickly an electron can move through a metal or semiconductor, when pulled by an electric field. In semiconductors, there is an analogous quantity for holes, called hole mobility...
of the carriers, diffusion constant and relaxation time
Relaxation time
In the physical sciences, relaxation usually means the return of a perturbed system into equilibrium.Each relaxation process can be characterized by a relaxation time τ...
. In the following, we reduce the problem to one dimension.
The equations for electron and hole currents are:
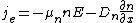
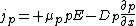
where the first part is the drift current
Drift current
In condensed matter physics and electrochemistry, drift current is the electric current, or movement of charge carriers, which is due to the applied electric field, often stated as the electromotive force over a given distance.When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor material,the...
and the second is the diffusion current
Diffusion current
-Introduction:Diffusion current is a current in a semiconductor caused by the diffusion of charge carriers . Diffusion current can be in the same or opposite direction of a drift current, that is formed due to the electric field in the semiconductor...
.
We consider the continuity equation
Continuity equation
A continuity equation in physics is a differential equation that describes the transport of a conserved quantity. Since mass, energy, momentum, electric charge and other natural quantities are conserved under their respective appropriate conditions, a variety of physical phenomena may be described...
:
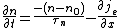
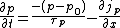
The electrons and the holes recombine with the time
 .
.We define
 and
and 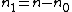 so the upper equations can be rewritten as:
so the upper equations can be rewritten as: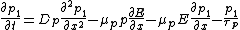
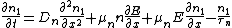
In a simple approximation, we can consider the electric field to be constant between the left and right electrodes and neglect
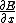 . However, as electrons and holes diffuse at a different speed, the material has a local electric charge, inducing an inhomogeneous electric field which can be calculated with Gauss's law
. However, as electrons and holes diffuse at a different speed, the material has a local electric charge, inducing an inhomogeneous electric field which can be calculated with Gauss's lawGauss's law
In physics, Gauss's law, also known as Gauss's flux theorem, is a law relating the distribution of electric charge to the resulting electric field. Gauss's law states that:...
:
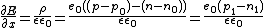
We make the following change of variables:
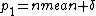 ,
, 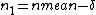 , and suppose
, and suppose 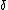 to be much smaller than
to be much smaller than 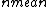 . The two initial equations write:
. The two initial equations write: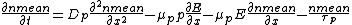
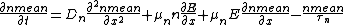
Thanks to Einstein relation
Einstein relation
Einstein relation can refer to*Einstein relation , a kinetic relation found independently by Albert Einstein and Marian Smoluchowski *Mass–energy equivalence, sometimes called Einstein's mass-energy relation...
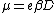 , these two equations can be combined:
, these two equations can be combined: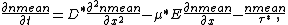
where for
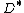 ,
, 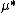 and
and 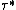 holds:
holds: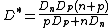 ,
, 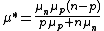 and
and 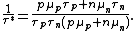
Considering n>>p or
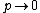 (that is a fair approximation for a semiconductor with only few holes injected), we see that
(that is a fair approximation for a semiconductor with only few holes injected), we see that 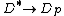 ,
, 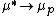 and
and 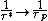 . The semiconductor behaves as if there were only holes traveling in it.
. The semiconductor behaves as if there were only holes traveling in it.The final equation for the carriers is:
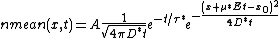
This can be interpreted as a delta function that is created immediately after the pulse. Holes then start to travel towards the electrode where we detect them. The signal then is Gaussian curve shaped.
Parameters
 and
and  can be obtained from the shape of the signal.
can be obtained from the shape of the signal.