
Hapke parameters
Encyclopedia
The Hapke parameters are a set of parameters for a quasi-experimental model that are commonly used to describe the
directional reflectance properties
of the airless regolith
surfaces of bodies in the solar system
. They were developed by astronomer Bruce Hapke at the University of Pittsburgh
.
The quantities are :
The Hapke parameters can be used to derive other albedo and scattering properties such as the geometric albedo
, the phase integral, and the Bond albedo
.
directional reflectance properties
Bidirectional reflectance distribution function
The bidirectional reflectance distribution function is a four-dimensional function that defines how light is reflected at an opaque surface...
of the airless regolith
Regolith
Regolith is a layer of loose, heterogeneous material covering solid rock. It includes dust, soil, broken rock, and other related materials and is present on Earth, the Moon, some asteroids, and other terrestrial planets and moons.-Etymology:...
surfaces of bodies in the solar system
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
. They were developed by astronomer Bruce Hapke at the University of Pittsburgh
University of Pittsburgh
The University of Pittsburgh, commonly referred to as Pitt, is a state-related research university located in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. Founded as Pittsburgh Academy in 1787 on what was then the American frontier, Pitt is one of the oldest continuously chartered institutions of...
.
The quantities are :
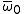 — Single scattering albedoAlbedoAlbedo , or reflection coefficient, is the diffuse reflectivity or reflecting power of a surface. It is defined as the ratio of reflected radiation from the surface to incident radiation upon it...
— Single scattering albedoAlbedoAlbedo , or reflection coefficient, is the diffuse reflectivity or reflecting power of a surface. It is defined as the ratio of reflected radiation from the surface to incident radiation upon it...
. This is the ratio of scattering efficiency to total light extinction (which includes also absorption), for small-particle scattering of light. That is,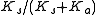 , where
, where 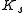 is the scattering coefficient, and
is the scattering coefficient, and 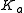 is the absorption coefficient
is the absorption coefficient — The width of the opposition surge.
— The width of the opposition surge.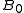 or
or 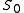 — The strength of the opposition surge.
— The strength of the opposition surge.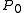 or g — The particle phase function parameter, also called the asymmetry factor.
or g — The particle phase function parameter, also called the asymmetry factor.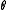 — The effective surface tilt, also called the macroscopic roughness angle.
— The effective surface tilt, also called the macroscopic roughness angle.
The Hapke parameters can be used to derive other albedo and scattering properties such as the geometric albedo
Geometric albedo
The geometric albedo of an astronomical body is the ratio of its actual brightness at zero phase angle to that of an idealized flat, fully reflecting, diffusively scattering disk with the same cross-section....
, the phase integral, and the Bond albedo
Bond albedo
The Bond albedo, named after the American astronomer George Phillips Bond , who originally proposed it, is the fraction of power in the total electromagnetic radiation incident on an astronomical body that is scattered back out into space...
.

