
Hanover Stadtbahn
Encyclopedia

Stadtbahn
A ' is a tramway or light railway that includes segments built to rapid transit standards, usually as part of a process of conversion to a metro railway, mainly by the building of tunnels in the central city area....
light rail system in the city of Hanover
Hanover
Hanover or Hannover, on the river Leine, is the capital of the federal state of Lower Saxony , Germany and was once by personal union the family seat of the Hanoverian Kings of Great Britain, under their title as the dukes of Brunswick-Lüneburg...
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
that opened in September 1975, gradually replacing the city's tram
Tram
A tram is a passenger rail vehicle which runs on tracks along public urban streets and also sometimes on separate rights of way. It may also run between cities and/or towns , and/or partially grade separated even in the cities...
way network over the course of the following 25 years. As of 2005, it transports 115 million passengers per year. The system is run by Üstra
Üstra
üstra Hannoversche Verkehrsbetriebe AG is the operator of public transport in the city of Hanover, Germany.From 2003 to 2006, it had outsourced its operations, but officially resumed as a service provider on January 1, 2007.- History :...
, which was originally the abbreviation for Überlandwerke und Straßenbahnen Hannover AG.
Two types of light rail cars operate on the system, the TW 6000
TW 6000
The TW 6000 is a type of articulated light rail vehicle used on the Hanover Stadtbahn system, originally manufactured by Düwag, AEG, Kiepe and Siemens, the later batches being built by LHB ....
, built from 1974 to 1993, and the TW 2000
TW 2000
The TW 2000 is a Stadtbahn vehicle in operation on the Hanover Stadtbahn network in Hanover, Germany.- History :After winning the bid for the Expo 2000 in 1990, the city of Hanover faced the need to greatly improve its transportation system...
, built from 1997 to 1999. The system is extensively used, especially during trade shows on the Hanover fairground
Hanover fairground
The Hanover fairground is an exhibition area in the Mittelfeld district of Hanover, Germany. Featuring 496,000 m² of covered indoor space, 58,000 m² of open-air space, 27 halls and pavilions and a convention centre with 35 function rooms, it is the largest exhibition ground in the world.-...
like CeBIT
CeBIT
CeBIT is the world's largest and most international computer expo. CeBIT is held each year on the world's largest fairground in Hanover, Germany, and is a barometer of the state of the art in information technology...
or the Hannover Messe. It makes up for more than 60% of the GVH
Großraum-Verkehr Hannover
The Großraum-Verkehr Hannover is a transport association in Germany, operating in the Region Hannover metropolitan area in the state of Lower Saxony. It was founded on March 4, 1970 and is the second oldest transport association in Germany, only surpassed by the Hamburger Verkehrsverbund. The main...
transport association's total traffic and has 170 stops as well as 19 stations in tunnels, spanning over four cities, two counties and 115 kilometres of total line length. Hanover Stadtbahn is complemented by DB-owned S-Bahn Hannover
Hanover S-Bahn
The Hanover S-Bahn is an S-Bahn network operated by DB Regio in the area of Hanover in the German state capital of Lower Saxony...
, a suburban heavy rail network which links the outlying suburbs and towns, as well as Hanover Airport, to the city centre.
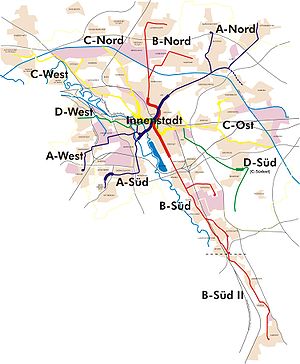
Network

Tram
A tram is a passenger rail vehicle which runs on tracks along public urban streets and also sometimes on separate rights of way. It may also run between cities and/or towns , and/or partially grade separated even in the cities...
ways, of which 82% have been upgraded so far to have their own right-of-way, and an U-Bahn-like system of tunnels in the city centre.
The network is owned by infra GmbH and covers nearly the whole city area. Parts of the network reach into the neighbouring towns of Garbsen, Isernhagen, Langenhagen, Laatzen and Ronnenberg as well as into the town of Sarstedt, which is in the borough of Hildesheim. The operator's concession is held by üstra Hannoversche Verkehrsbetriebe AG.
The system currently consists of three full Stadtbahn lines, respectively named (with their tunnels in brackets)
- A (Waterlooplatz – Lister Platz),
- B (Vahrenwald – Döhren)
- C (Königsworther Platz – Braunschweiger Platz).
A fourth tunnel, to be used for the D line (Goethestraße - Sallstraße), has been proposed but has not been realised so far due to the high costs of construction, currently estimated to be around €
Euro
The euro is the official currency of the eurozone: 17 of the 27 member states of the European Union. It is also the currency used by the Institutions of the European Union. The eurozone consists of Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg,...
1 billion. Nevertheless, the above-ground parts of the D line, most notably the D Süd, connecting the Hanover fairground
Hanover fairground
The Hanover fairground is an exhibition area in the Mittelfeld district of Hanover, Germany. Featuring 496,000 m² of covered indoor space, 58,000 m² of open-air space, 27 halls and pavilions and a convention centre with 35 function rooms, it is the largest exhibition ground in the world.-...
to the C tunnel, have been upgraded to proper Stadtbahn standards, some preparations for interchange with the current stations, like an empty station below the current Hauptbahnhof
Hannover Hauptbahnhof
is the Hauptbahnhof for the city of Hanover in Lower Saxony, Germany.-History:The first station on the current site, a temporary building serving the line to Lehrte, was erected in 1843...
station, have also been built in the past.
The whole Stadtbahn network uses various colours to differentiate between the lines. For example, a station that would service both A and B lines would have a blue and a red stripe on its station sign; stop on the D line would feature a lime stripe on the station sign, and so on. This scheme sometimes also recurs in the architecture of the stations, for example the station Kröpcke
Kröpcke
Kröpcke is the central place of the city of Hanover in Germany. The place is situated at the crossroads of Georgstraße, Karmarschstraße, Bahnhofstraße and Rathenaustraße. It is named after Wilhelm Kröpcke, one of the owners of the former Café Robby, which was erected on the then-nameless place in...
used to feature tilework that changes colours when stepping over between lines, i.e. yellow elements would be introduced in the red tiles when walking from the B to the C part of the station.
Individual routes operate within the main lines, diverting to various terminals at the city's edge. The route numbers are assigned to the lines as following (routes that only run during exhibitions on the Hanover fairground
Hanover fairground
The Hanover fairground is an exhibition area in the Mittelfeld district of Hanover, Germany. Featuring 496,000 m² of covered indoor space, 58,000 m² of open-air space, 27 halls and pavilions and a convention centre with 35 function rooms, it is the largest exhibition ground in the world.-...
are denoted in italics):
- A line - routes 3,7,9
- B line - routes 1,2,8,18
- C line - routes 4,5,6,11,16
- D line - routes 10 and 10E (10E is an express peak service, using parts of the A tunnel)
Whilst the number 6 and 16 services are using a large part of the D line, they are still denoted as C services by using the colour yellow on station signage.
The main hub of the network is Kröpcke
Kröpcke
Kröpcke is the central place of the city of Hanover in Germany. The place is situated at the crossroads of Georgstraße, Karmarschstraße, Bahnhofstraße and Rathenaustraße. It is named after Wilhelm Kröpcke, one of the owners of the former Café Robby, which was erected on the then-nameless place in...
, a large subterranean station in the city centre. Routes 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,16 and 18 call at this station, making it possible to reach every point on the A, B or C lines from every other point with one stepover only.
The D tunnel
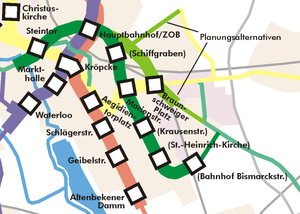
Whilst some preparations have been made, most notably an empty station under today's Hauptbahnhof station and a special arrangement of pillars at stations Steintor and Marienstraße to allow a tunnel to be built underneath, the plans could not be realised so far, due to the high costs. It would however be greatly beneficial to the D line, reducing stepover times to other lines. The current surface D line between Goetheplatz and Aegidientorplatz is regarded as a temporary solution for the time being, for example when the wye at Steintor was demolished after the tearing down of tram tracks that had been replaced by the C-Nord line, the points were not removed but just welded shut. During the renovation of the Hauptbahnhof
Hannover Hauptbahnhof
is the Hauptbahnhof for the city of Hanover in Lower Saxony, Germany.-History:The first station on the current site, a temporary building serving the line to Lehrte, was erected in 1843...
in 1999 and 2000, the tram tracks in front of the station were not replaced either.
Dead tunnels
Even though it is of a relatively young age, the Hanover Stadtbahn already has some buildings that are likely not to be used as intended. These are three tunnel stubs in the A and B tunnels.Under both the ramps Hammersteinstraße (A-Nord) and Vahrenwalder Platz (B-Nord) the tunnel continues until the ramp's end since the original U-Bahn plans had proposed an extension of the tunnels. Whilst this made some theoretical sense at the A-Nord due to the relatively narrow Podbielskistraße, an extension of the tunnel is completely unneeded on the rather wide Vahrenwalder Straße. The stubs currently house some technical service rooms.
A notably larger structure exists behind the middle tracks of the station Waterloo. It was originally supposed to extend a tunnel toward the A-West (line 9 toward Empelde) and to construct a turning loop. However, this would require tearing down the current A-West ramp at Gustav-Bratke-Allee which would disconnect the Glocksee depot from the network. Thus, this will likely never be carried out.
Stadtbahn lines opened
| Line | from | to | Opening date |
|---|---|---|---|
| The lines to Laatzen/Süd and Rethen were built according to Stadtbahn standards but used as tramway lines until September, 1982. | |||
| B-Süd | Laatzen/Nord | Laatzen/Süd* | Sep 20 1973 |
| A-Süd | Wallensteinstraße | Hauptbahnhof | Sep 26 1975 |
| A-Nord | Hauptbahnhof | Buchholz - Paracelsusweg - Fasanenkrug |
Apr 4 1976 |
| B-Süd | Laatzen/Süd | Rethen/Nord* | Jun 18 1976 |
| A-Süd | Wallensteinstraße | Mühlenberger Markt | Sep 25 1977 |
| C-Ost | Nackenberg | Med.Hochschule/Süd | Oct 1 1978 |
| A-West | Empelde | Schwarzer Bär | May 27, 1979 |
| B-Nord | Hauptbahnhof | Vahrenwald - Langenhagen - Alte Heide |
May 27, 1979 |
| B | Hauptbahnhof | Kröpcke B | May 27, 1979 |
| B-Süd | Kröpcke B | Schlägerstraße | May 31, 1981 |
| B-Süd | Betriebshof Döhren | Sep 2 1982 | |
| B-Süd | Schlägerstraße | Döhren - Messegelände - Rethen - Laatzen - Sarstedt |
Sep 26 1982 |
| C | Aegidientorplatz | Kröpcke C | Sep 26 1982 |
| C-West | Kröpcke C | Steintor | Mar 30 1983 |
| C-Ost | Med.Hochschule/Süd | Roderbruch | Sep 29 1984 |
| C-West | Steintor | Stöcken | Jun 2 1985 |
| C-Ost | Aegidientorplatz | Kleefeld - Roderbruch - Ostfeldstraße |
Sep 24 1989 |
| Freundallee | Sep 24 1989 | ||
| B-Nord | Lgh./Berliner Platz | Langenhagen | Sep 29 1991 |
| C-Nord | Steintor | (Nordstadt) - Haltenhoffstraße - Nordhafen |
Sep 26 1993 |
| C-Ost | Clausewitzstraße | Zoo | Sep 26 1993 |
| D-West | Brunnenstraße | Ahlem | May 29, 1994 |
| C-West | Hogrefestraße | Wissenschaftspark Marienwerder | Sep 24 1995 |
| C-West | Wissenschaftspark Marienwerder | Garbsen | Sep 29 1996 |
| C-West | Stadtfriedhof Stöcken | Betriebshof Fuhsestraße | Sep 26 1998 |
| D-Süd | Freundallee | Kinderkrankenhaus auf der Bult | Dec 5 1998 |
| A-Süd | Waterloo | Allerweg (Legionsbrücke) | May 29, 1999 |
| A-Süd | Mühlenberger Markt | Wettbergen | May 29, 1999 |
| D-Süd | Kinderkrankenhaus auf der Bult | Bünteweg/Tierärztliche Hochschule | May 30, 1999 |
| D-Süd | Bünteweg/Ti.Ho. | Kronsberg | Oct 13 1999 |
| D-Süd | Kronsberg | Messe/Ost | Feb 19 2000 |
| C-Ost | Ostfeldstraße | Anderten | 2002 |
| A-Nord | Paracelsusweg | Altwarmbüchen | June 2006 |
| A-Nord | Paracelsusweg | Schierholzstraße | Dec 12, 2010 |
See also
- üstraÜstraüstra Hannoversche Verkehrsbetriebe AG is the operator of public transport in the city of Hanover, Germany.From 2003 to 2006, it had outsourced its operations, but officially resumed as a service provider on January 1, 2007.- History :...
- intalliance AG
- TW 6000TW 6000The TW 6000 is a type of articulated light rail vehicle used on the Hanover Stadtbahn system, originally manufactured by Düwag, AEG, Kiepe and Siemens, the later batches being built by LHB ....
- TW 2000TW 2000The TW 2000 is a Stadtbahn vehicle in operation on the Hanover Stadtbahn network in Hanover, Germany.- History :After winning the bid for the Expo 2000 in 1990, the city of Hanover faced the need to greatly improve its transportation system...
- StadtbahnStadtbahnA ' is a tramway or light railway that includes segments built to rapid transit standards, usually as part of a process of conversion to a metro railway, mainly by the building of tunnels in the central city area....
- List of rapid transit systems

