
HRU (security)
Encyclopedia
The HRU security model is an operating system
level computer security model
which deals with the integrity
of access rights
in the system. It is an extension of the Graham-Denning model
, based around the idea of a finite set of procedures
being available to edit the access rights of a subject on an object
on an object  . It is named after its three authors, Michael A. Harrison, Walter L. Ruzzo and Jeffrey D. Ullman.
. It is named after its three authors, Michael A. Harrison, Walter L. Ruzzo and Jeffrey D. Ullman.
Along with presenting the model, Harrison, Ruzzo and Ullman also discussed the possibilities and limitations of proving the safety of systems using an algorithm
.
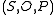 of current subjects
of current subjects 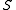 , current objects
, current objects 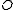 and an access matrix
and an access matrix 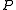 . Since the subjects are required to be part of the objects, the access matrix contains one row for each subject and one column for each subject and object. An entry for subject
. Since the subjects are required to be part of the objects, the access matrix contains one row for each subject and one column for each subject and object. An entry for subject  and object
and object  is a subset of the generic rights
is a subset of the generic rights 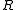 .
.
The commands are composed of primitive operations and can additionally have a list of pre-conditions that require certain rights to be present for a pair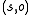 of subjects and objects.
of subjects and objects.
The primitive requests can modify the access matrix by adding or removing access rights for a pair of subjects and objects and by adding or removing subjects or objects. Creation of a subject or object requires the subject or object not to exist in the current configuration, while deletion of a subject or object requires it to have existed prior to deletion. In a complex command, a sequence of operations is executed only as a whole. A failing operation in a sequence makes the whole sequence fail, a form of database transaction
.
They showed that there is no such algorithm, thus the problem is undecidable
in the general case. They also showed a limitation of the model to commands with only one primitive operation to render the problem decidable.
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
level computer security model
Computer security model
A computer security model is a scheme for specifying and enforcing security policies.A security model may be founded upon a formal model of access rights, a model of computation, a model of distributed computing, or no particular theoretical grounding at all....
which deals with the integrity
Data integrity
Data Integrity in its broadest meaning refers to the trustworthiness of system resources over their entire life cycle. In more analytic terms, it is "the representational faithfulness of information to the true state of the object that the information represents, where representational faithfulness...
of access rights
Access control
Access control refers to exerting control over who can interact with a resource. Often but not always, this involves an authority, who does the controlling. The resource can be a given building, group of buildings, or computer-based information system...
in the system. It is an extension of the Graham-Denning model
Graham-Denning model
The Graham-Denning Model is a computer security model that shows how subjects and objects should be securely created and deleted.It also addresses how to assign specific access rights...
, based around the idea of a finite set of procedures
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
being available to edit the access rights of a subject
 on an object
on an object  . It is named after its three authors, Michael A. Harrison, Walter L. Ruzzo and Jeffrey D. Ullman.
. It is named after its three authors, Michael A. Harrison, Walter L. Ruzzo and Jeffrey D. Ullman.Along with presenting the model, Harrison, Ruzzo and Ullman also discussed the possibilities and limitations of proving the safety of systems using an algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
.
Description of the model
The HRU model defines a protection system consisting of a set of generic rights R and a set of commands C. An instantaneous description of the system is called a configuration and is defined as a tupleTuple
In mathematics and computer science, a tuple is an ordered list of elements. In set theory, an n-tuple is a sequence of n elements, where n is a positive integer. There is also one 0-tuple, an empty sequence. An n-tuple is defined inductively using the construction of an ordered pair...
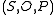 of current subjects
of current subjects 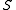 , current objects
, current objects 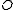 and an access matrix
and an access matrix 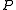 . Since the subjects are required to be part of the objects, the access matrix contains one row for each subject and one column for each subject and object. An entry for subject
. Since the subjects are required to be part of the objects, the access matrix contains one row for each subject and one column for each subject and object. An entry for subject  and object
and object  is a subset of the generic rights
is a subset of the generic rights 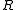 .
.The commands are composed of primitive operations and can additionally have a list of pre-conditions that require certain rights to be present for a pair
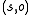 of subjects and objects.
of subjects and objects.The primitive requests can modify the access matrix by adding or removing access rights for a pair of subjects and objects and by adding or removing subjects or objects. Creation of a subject or object requires the subject or object not to exist in the current configuration, while deletion of a subject or object requires it to have existed prior to deletion. In a complex command, a sequence of operations is executed only as a whole. A failing operation in a sequence makes the whole sequence fail, a form of database transaction
Database transaction
A transaction comprises a unit of work performed within a database management system against a database, and treated in a coherent and reliable way independent of other transactions...
.
Discussion of safety
Harrison, Ruzzo and Ullman discussed whether there is an algorithm that takes an arbitrary initial configuration and answers the following question: is there an arbitrary sequence of commands that adds a generic right into a cell of the access matrix where it has not been in the initial configuration?They showed that there is no such algorithm, thus the problem is undecidable
Undecidable problem
In computability theory and computational complexity theory, an undecidable problem is a decision problem for which it is impossible to construct a single algorithm that always leads to a correct yes-or-no answer....
in the general case. They also showed a limitation of the model to commands with only one primitive operation to render the problem decidable.

