
HMG-CoA
Encyclopedia
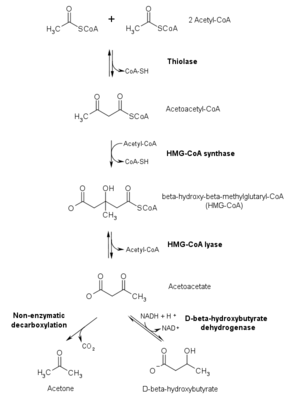
HMG-CoA is an intermediate in the Mevalonate pathway. It is formed from acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA by HMG-CoA synthase
.
HMG-CoA reductase
converts it into mevalonic acid
.
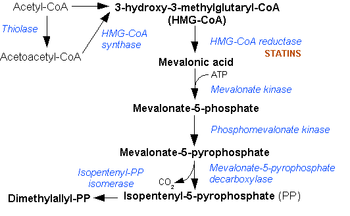 Also, HMG-CoA lyase breaks it into acetyl CoA and acetoacetate.
Also, HMG-CoA lyase breaks it into acetyl CoA and acetoacetate.
 It is also an intermediate in the metabolism of leucine
It is also an intermediate in the metabolism of leucine
. Its immediate precursor is 3-methylglutaconyl CoA.
HMG-CoA synthase
In molecular biology, HMG-CoA synthase is an enzyme which catalyzes the reaction in which Acetyl-CoA condenses with acetoacetyl-CoA to form 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA . It is the second reaction in the mevalonate-dependent isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway. HMG-CoA is an intermediate in both...
.
HMG-CoA reductase
HMG-CoA reductase
HMG-CoA reductase is the rate-controlling enzyme of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids...
converts it into mevalonic acid
Mevalonic acid
Mevalonic acid is a key organic compound in biochemistry. The anion of mevalonic acid, the predominant form in biological media, is known as mevalonate. This compound is of major pharmaceutical importance...
.


Leucine
Leucine is a branched-chain α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2. Leucine is classified as a hydrophobic amino acid due to its aliphatic isobutyl side chain. It is encoded by six codons and is a major component of the subunits in ferritin, astacin and other 'buffer' proteins...
. Its immediate precursor is 3-methylglutaconyl CoA.

