
Gravity Gradiometry
Encyclopedia
Gravity gradiometry is the study and measurement of variations in the
acceleration
due to gravity. The gravity gradient is the spatial rate of change of gravitational acceleration.
Gravity gradiometry is used by oil, gas and mining companies to measure the density of the subsurface, effectively the rate of change of rock properties. From this information it is possible to build a picture of subsurface anomalies which can then be used to more accurately target oil, gas and mineral deposits. It is also used to image water column density, when locating submerged objects, or determining water depth (bathymetry
).
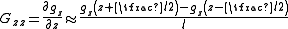
The two gravity measurements are provided by accelerometers which are matched and aligned to a high level of accuracy.
, which is equivalent to 10-9 s-2 (or 10-4 mGal/m). A person walking past at a distance of 2 metres would provide a gravity gradient signal approximately one Eotvos. Mountains can give signals of several hundred Eotvos.
Conversely, gravity measurements have more signal power at low frequency therefore making them more sensitive to regional signals and deeper sources.
structures, Kimberlite
pipes, etc. Other applications include tunnel and bunker detection
and the recent GOCE
mission that aim to improve the knowledge of ocean circulation.
gravity gradiometer is based on a classified system originally developed by the US Defence Department
and deployed on US Navy Ohio Class
Trident submarines designed to aid covert navigation. The existence of the gravity gradiometer was famously exposed in the film “The Hunt for Red October”. The system was declassified and in 1994 and adapted for mineral exploration.
There are two types of Lockheed Martin gravity gradiometers currently in operation: the 3D FTG, (Full Tensor Gravity Gradiometer, deployed in either a fixed wing aircraft or a ship) and the FALCON gradiometer (a partial tensor system with 8 accelerometers and deployed in a fixed wing aircraft or a helicopter). The 3D FTG system contains three Gravity Gradiometry Instruments (GGI’s), each consisting of two opposing pairs of accelerometers arranged on a spinning disc with measurement direction in the spin direction.
This is the gravity gradiometer deployed on the European Space Agency’s GOCE
mission. It is a three-axis diagonal gradiometer based on three pairs of electrostatic servo-controlled accelerometers.
Superconductive Gravity Gradiometer
An evolution of technology originally developed for the afore mentioned European Space Agency mission, the EGG, (Exploration Gravity Gradiometer), developed by ARKeX, uses two key principles of Super Conductivity to deliver its performance: the “Meissner effect
”, which provides levitation of the EGG proof masses and “flux quantization
”, which gives the EGG its inherent stability. The EGG has been specifically designed for high dynamic survey environments.
Ribbon Sensor Gradiometer
The Gravitec gravity gradiometer sensor consists of a single sensing element (a ribbon) that responds to gravity gradient forces. It is designed for borehole applications.
UWA Gravity Gradiometer
The UWA Gravity Gradiometer uses an orthogonal quadrupole responder (OQR) design based on pairs of micro-flexure supported balance beams.
GOCE mission payload
The EGG - Superconducting Gravity Gradiometer Tool for Exploration
Description of and Results from a Novel Borehole Gravity Gradiometer
acceleration
Acceleration
In physics, acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time. In one dimension, acceleration is the rate at which something speeds up or slows down. However, since velocity is a vector, acceleration describes the rate of change of both the magnitude and the direction of velocity. ...
due to gravity. The gravity gradient is the spatial rate of change of gravitational acceleration.
Gravity gradiometry is used by oil, gas and mining companies to measure the density of the subsurface, effectively the rate of change of rock properties. From this information it is possible to build a picture of subsurface anomalies which can then be used to more accurately target oil, gas and mineral deposits. It is also used to image water column density, when locating submerged objects, or determining water depth (bathymetry
Bathymetry
Bathymetry is the study of underwater depth of lake or ocean floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry. The name comes from Greek βαθύς , "deep", and μέτρον , "measure"...
).
Measuring the gravity gradient
Gravity gradiometers measure the spatial derivatives of the gravity vector. The most frequently used and intuitive component is the vertical gravity gradient, Gzz, which represents the rate of change of vertical gravity (gz) with height (z). It can be deduced by differencing the value of gravity at two points separated by a small vertical distance, l, and dividing by this distance.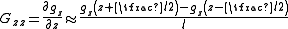
The two gravity measurements are provided by accelerometers which are matched and aligned to a high level of accuracy.
Units
The unit of gravity gradient is the EotvosEotvos (unit)
The eotvos is a unit of acceleration divided by distance that was used in conjunction with the older centimeter-gram-second system of units. The eotvos is defined as 1/1,000,000,000 galileo per centimetre...
, which is equivalent to 10-9 s-2 (or 10-4 mGal/m). A person walking past at a distance of 2 metres would provide a gravity gradient signal approximately one Eotvos. Mountains can give signals of several hundred Eotvos.
Gravity gradient tensor
Full tensor gradiometers measure the rate of change of the gravity vector in all three perpendicular directions giving rise to a gravity gradient tensor (Fig 1).Comparison to gravity
Being the derivatives of gravity, the spectral power of gravity gradient signals is pushed to higher frequencies. This generally makes the gravity gradient anomaly more localised to the source than the gravity anomaly. The table (below) and graph (Fig 2) compare the gz and Gzz responses from a point source,| Gravity (gz) | Gravity gradient (Gzz) | |
|---|---|---|
| Signal | 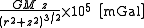 |
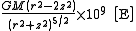 |
| Peak signal (r = 0) | 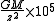 |
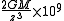 |
| Full width at half maximum | 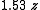 |
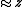 |
| Wavelength (λ) | 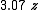 |
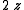 |
Conversely, gravity measurements have more signal power at low frequency therefore making them more sensitive to regional signals and deeper sources.
Dynamic survey environments (airborne and marine)
The derivative measurement sacrifices the overall energy in the signal, but significantly reduces the noise due to motional disturbance. On a moving platform, the acceleration disturbance measured by the two accelerometers is the same so that when forming the difference, it cancels in the gravity gradient measurement. This is the principle reason for deploying gradiometers in airborne/marine surveys where the acceleration levels are orders of magnitude greater than the signals of interest. The signal to noise ratio benefits most at high frequency (above 0.01 Hz), where the airborne acceleration noise is largest.Applications
Gravity gradiometry has predominately been used to image subsurface geology to aid hydrocarbon and mineral exploration. Over 2.5 million line km has now been surveyed using the technique. The surveys highlight gravity anomalies that can be related to geological features such as Salt diapirs, Fault systems, ReefReef
In nautical terminology, a reef is a rock, sandbar, or other feature lying beneath the surface of the water ....
structures, Kimberlite
Kimberlite
Kimberlite is a type of potassic volcanic rock best known for sometimes containing diamonds. It is named after the town of Kimberley in South Africa, where the discovery of an diamond in 1871 spawned a diamond rush, eventually creating the Big Hole....
pipes, etc. Other applications include tunnel and bunker detection
and the recent GOCE
Gravity Field and Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer
The Gravity Field and Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer is an ESA satellite that was launched on March 17, 2009. It is a satellite carrying a highly sensitive gravity gradiometer which detects fine density differences in the crust and oceans of the Earth.GOCE data will have many uses,...
mission that aim to improve the knowledge of ocean circulation.
Lockheed Martin Gravity Gradiometers
The Lockheed MartinLockheed Martin
Lockheed Martin is an American global aerospace, defense, security, and advanced technology company with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It is headquartered in Bethesda, Maryland, in the Washington Metropolitan Area....
gravity gradiometer is based on a classified system originally developed by the US Defence Department
and deployed on US Navy Ohio Class
Ohio class submarine
The Ohio class is a class of nuclear-powered submarines used by the United States Navy. The United States has 18 Ohio-class submarines:...
Trident submarines designed to aid covert navigation. The existence of the gravity gradiometer was famously exposed in the film “The Hunt for Red October”. The system was declassified and in 1994 and adapted for mineral exploration.
There are two types of Lockheed Martin gravity gradiometers currently in operation: the 3D FTG, (Full Tensor Gravity Gradiometer, deployed in either a fixed wing aircraft or a ship) and the FALCON gradiometer (a partial tensor system with 8 accelerometers and deployed in a fixed wing aircraft or a helicopter). The 3D FTG system contains three Gravity Gradiometry Instruments (GGI’s), each consisting of two opposing pairs of accelerometers arranged on a spinning disc with measurement direction in the spin direction.
Other Gradiometers
Electrostatic Gravity GradiometerThis is the gravity gradiometer deployed on the European Space Agency’s GOCE
Gravity Field and Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer
The Gravity Field and Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer is an ESA satellite that was launched on March 17, 2009. It is a satellite carrying a highly sensitive gravity gradiometer which detects fine density differences in the crust and oceans of the Earth.GOCE data will have many uses,...
mission. It is a three-axis diagonal gradiometer based on three pairs of electrostatic servo-controlled accelerometers.
Superconductive Gravity Gradiometer
An evolution of technology originally developed for the afore mentioned European Space Agency mission, the EGG, (Exploration Gravity Gradiometer), developed by ARKeX, uses two key principles of Super Conductivity to deliver its performance: the “Meissner effect
Meissner effect
The Meissner effect is the expulsion of a magnetic field from a superconductor during its transition to the superconducting state. The German physicists Walther Meissner and Robert Ochsenfeld discovered the phenomenon in 1933 by measuring the magnetic field distribution outside superconducting tin...
”, which provides levitation of the EGG proof masses and “flux quantization
Flux quantization
Flux quantization is a quantum phenomenon in which the magnetic fieldis quantized in the unit of h / 2e,also known variously as flux quanta, fluxoids, vortices or fluxons.Flux quantization occurs in Type II superconductors subjected to a magnetic field...
”, which gives the EGG its inherent stability. The EGG has been specifically designed for high dynamic survey environments.
Ribbon Sensor Gradiometer
The Gravitec gravity gradiometer sensor consists of a single sensing element (a ribbon) that responds to gravity gradient forces. It is designed for borehole applications.
UWA Gravity Gradiometer
The UWA Gravity Gradiometer uses an orthogonal quadrupole responder (OQR) design based on pairs of micro-flexure supported balance beams.
External links
Advances and Challenges in the Development and Deployment of Gravity Gradiometer SystemsGOCE mission payload
The EGG - Superconducting Gravity Gradiometer Tool for Exploration
Description of and Results from a Novel Borehole Gravity Gradiometer
See also
- Gravity-gradient stabilizationGravity-gradient stabilizationGravity-gradient stabilization is a method of stabilizing artificial satellites or space tethers in a fixed orientation using only the orbited body's mass distribution and the Earth's gravitational field. The main advantage over using active stabilization with propellants, gyroscopes or reaction...
- Robert L. Forward#Forward Mass Detector

