
Glochidium
Encyclopedia
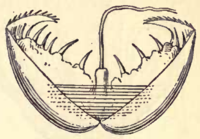
Larva
A larva is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle...
l stage of larger freshwater mussels, aquatic
Aquatic animal
An aquatic animal is an animal, either vertebrate or invertebrate, which lives in water for most or all of its life. It may breathe air or extract its oxygen from that dissolved in water through specialised organs called gills, or directly through its skin. Natural environments and the animals that...
bivalve mollusks in the families Unionidae
Unionidae
Unionidae is a family of freshwater mussels, the largest in the order Unionoida, the bivalve mollusks sometimes known as river mussels, naiads, or simply as unionids.The range of distribution for this family is world-wide...
and Margaritiferidae
Margaritiferidae
Margaritiferidae is a family of medium-sized freshwater mussels, aquatic bivalve mollusks in the order Unionoida. They are known as freshwater pearl mussels, because they are capable of producing pearls.-Genera within the family Margaritiferidae:...
, the river mussels and European freshwater pearl mussels.
This larva form has hooks, which enable it to attach itself to fish (for example to the gill
Gill
A gill is a respiratory organ found in many aquatic organisms that extracts dissolved oxygen from water, afterward excreting carbon dioxide. The gills of some species such as hermit crabs have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist...
s of a fish host species) for a period of time before it detaches and falls to the substrate and takes on the typical form of a juvenile mussel. Since a fish is active and free-swimming, this process helps distribute the mussel species to potential areas of habitat that it could not reach any other way.
This larval form used to be described as "parasitic worms" on the fish host, however, glochidia do not harm fish under normal circumstances. Overexposure or heavy infections of glochidia may eliminate the hosts ability to respire. This is because the tissue they parasitize will eventually convert to scar tissue and lose functionality.
Some mussels in the Unionidae, such as Ptychobranchus fasciolaris
Ptychobranchus fasciolaris
Ptychobranchus fasciolaris, common name the Kidneyshell, is a species of freshwater mussel, an aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Unionidae, the river mussels.- Distribution and conservation status :...
and P. greenii, release their glochidia in mucilaginous packets called conglutinates. The conglutinate has a sticky filament that allows it to adhere to the substrate so it is not washed away. There is also an even more specialized way of dispersal known as a super-conglutinate. The super-conglutinate resembles an aquatic fly larva or a fish egg, complete with a dark area that looks like an eyespot, and it is appetizing to fish. When a fish consumes it, it breaks up, releasing the glochidia. Mussels that produce conglutinates and super-conglutinates are often gill parasites, the glochidia attaching to the fish gills to continue their development into juveniles.

