
Geometric tomography
Encyclopedia
Geometric tomography is a mathematical field that focuses on problems of reconstructing homogeneous (often convex
) objects from tomographic data (this might be X-rays, projections, sections, brightness functions, or covariograms). More precisely, according to R.J. Gardner (who introduced the term), "Geometric tomography deals with the retrieval of information about a geometric object from data concerning its projections (shadows) on planes or cross-sections by planes."
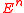 can be determined by parallel, coplanar
can be determined by parallel, coplanar
X-rays in a set of four directions whose slopes have a transcendental cross ratio.
Convex
'The word convex means curving out or bulging outward, as opposed to concave. Convex or convexity may refer to:Mathematics:* Convex set, a set of points containing all line segments between each pair of its points...
) objects from tomographic data (this might be X-rays, projections, sections, brightness functions, or covariograms). More precisely, according to R.J. Gardner (who introduced the term), "Geometric tomography deals with the retrieval of information about a geometric object from data concerning its projections (shadows) on planes or cross-sections by planes."
Theory
A key theorem in this area states that any convex body in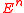 can be determined by parallel, coplanar
can be determined by parallel, coplanarX-rays in a set of four directions whose slopes have a transcendental cross ratio.

