Geography of Grenada
Encyclopedia

Geography
Geography is the science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. A literal translation would be "to describe or write about the Earth". The first person to use the word "geography" was Eratosthenes...
of Grenada
Grenada
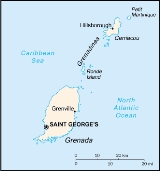
Grenada is an island country and Commonwealth Realm consisting of the island of Grenada and six smaller islands at the southern end of the Grenadines in the southeastern Caribbean Sea...
.
Grenada is a Caribbean
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean located in the tropics of the Western hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico and Central America to the west and southwest, to the north by the Greater Antilles, and to the east by the Lesser Antilles....
island
Island
An island or isle is any piece of sub-continental land that is surrounded by water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, cays or keys. An island in a river or lake may be called an eyot , or holm...
(one of the Grenadines
Grenadines
The Grenadines is a Caribbean island chain of over 600 islands in the Windward Islands.-Geographic boundaries:They are divided between the island nations of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and Grenada. They lie between the islands of Saint Vincent in the north and Grenada in the south. Neither...
) between the Caribbean Sea and Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
, north of Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago is an archipelagic state in the southern Caribbean, lying just off the coast of northeastern Venezuela and south of Grenada in the Lesser Antilles...
. It is located at 12°07′N 61°40′W. There are no large inland bodies of water on the island, which consists entirely of the state of Grenada. The coastline is 121 km long.
Grenada has 15 constituencies and speaks English. It is volcanic in origin and its topography/land scape is mountainous.
Natural resource
Natural resource
Natural resources occur naturally within environments that exist relatively undisturbed by mankind, in a natural form. A natural resource is often characterized by amounts of biodiversity and geodiversity existent in various ecosystems....
s include timber
Timber
Timber may refer to:* Timber, a term common in the United Kingdom and Australia for wood materials * Timber, Oregon, an unincorporated community in the U.S...
, tropical fruit
Fruit
In broad terms, a fruit is a structure of a plant that contains its seeds.The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state,...
and deepwater harbor
Harbor
A harbor or harbour , or haven, is a place where ships, boats, and barges can seek shelter from stormy weather, or else are stored for future use. Harbors can be natural or artificial...
s.
Grenada and its largely uninhabited outlying territories are the most southerly of the Windward Islands. The Grenadine Islands chain consists of some 600 islets; those south of the Martinique Channel
Martinique Channel
The Martinique Channel is a strait in the Caribbean Sea that separates Saint Vincent and the Grenadines from Grenada. It is located at ....
belong to Grenada, while those north of the channel are part of the nation of St. Vincent and the Grenadines. Located about 160 kilometers north of Venezuela, at approximately 12° north latitude and 61° west longitude, Grenada and its territories occupy a total area of 433 square kilometers. Grenada, known as the Spice Isle because of its production of nutmeg and mace, is the largest at 310 square kilometers, or about the size of Detroit. The island is oval shape and framed by a jagged southern coastline; its maximum width is thirty-four kilometers, and its maximum length is nineteen kilometers. St. George's
St. George's, Grenada
St. George's, population 89,018 , with an agglomeration of 4,500 people , is the capital of Grenada, . The city is surrounded by a hillside of an old volcano crater and is on a horseshoe-shaped harbor....
, the capital and the nation's most important harbor, is favorably situated near a lagoon on the southwestern coast. Of all the islands belonging to Grenada, only two are of consequence: Carriacou, with a population of a few thousand, and its neighbor Petit Martinique, roughly 40 kilometers northeast of Grenada and populated by some 700 inhabitants.
Part of the volcanic chain in the Lesser Antilles arc, Grenada and its possessions generally vary in elevation from under 300 meters to over 600 meters above sea level. Grenada is more rugged and densely foliated than its outlying possessions, but other geographical conditions are more similar. Grenada's landmass rises from a narrow, coastal plain in a generally north-south trending axis of ridges and narrow valleys. Mount St. Catherine is the highest peak at 840 meters.
Although many of the rocks and soils are of volcanic origin, the volcanic cones dotting Grenada are long dormant. The only known active volcano in the area is Kick 'em Jenny, just north between Grenada and Carriacou. Some of the drainage features on Grenada remain from its volcanic past. There are a few crater lakes, the largest of which is Grand Etang. The swift upper reaches of rivers, which occasionally overflow and cause flooding and landslides, generally cut deeply into the conic slopes. By contrast, many of the water courses in the lowlands tend to be sluggish and meandering.
Climate
The Grenadan climate is tropical, tempered by northeast trade winds. The land is volcanicVolcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
in origin with mountain
Mountain
Image:Himalaya_annotated.jpg|thumb|right|The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everestrect 58 14 160 49 Chomo Lonzorect 200 28 335 52 Makalurect 378 24 566 45 Mount Everestrect 188 581 920 656 Tibetan Plateaurect 250 406 340 427 Rong River...
s in the interior. The lowest point is at sea level
Sea level
Mean sea level is a measure of the average height of the ocean's surface ; used as a standard in reckoning land elevation...
, and the highest is 840 m (2,756 ft) on Mount Saint Catherine
Mount Saint Catherine, Grenada
Mount Saint Catherine is a stratovolcano and the highest mountain on the Caribbean island of Grenada. It is located in St. Mark's, Victoria. It is the youngest of five volcanoes which comprise the island. The volcano has a horseshoe-shaped crater open to the east, with several lava domes within...
.
The abundance of water is primarily caused by the tropical, wet climate. Yearly precipitation, largely generated by the warm and moisture-laden northeasterly trade winds, varies from more than 3500 millimetres (137.8 in) on the windward mountainsides to less than 1500 millimetres (59.1 in) in the lowlands. The greatest monthly totals are recorded throughout Grenada from June through November, the months when tropical storms and hurricanes are most likely to occur. Rainfall is less pronounced from December through May, when the equatorial low-pressure system moves south. Similarly, the highest humidities, usually close to 80 percent, are recorded during the rainy months, and values from 68 to 78 percent are registered during the drier period. Temperatures averaging 29 °C (84.2 °F) are constant throughout the year, however, with slightly higher readings in the lowlands. Nevertheless, diurnal ranges within a 24-hour period are appreciable: between 26 and 32 °C (78.8 and 89.6 °F) during the day and between 19 and 24 °C (66.2 and 75.2 °F) at night.
Statistics
Area:- Total: 340 km²
- Land: 340 km²
Maritime claims:
- Exclusive economic zone: 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
- Territorial sea: 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
Land use:
- Arable land: 15%
- Permanent crops: 18%
- Permanent pastures: 3%
- Forests and woodland: 9%
- Other: 55% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land:
- NA km²
Natural hazards:
- Lies on edge of hurricane belt; hurricane season lasts from June to November
Environment - current issues:
Environment - international agreements:
- Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the SeaLaw of the seaLaw of the sea may refer to:* United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea* Admiralty law* The Custom of the Sea...
, Ozone Layer Protection, Whaling
Geography - note:
- The administration of the islands of the Grenadines group is divided between Saint Vincent and the Grenadines (northern Grenadines) and Grenada (southern Grenadines)

